Overview
Navigating Maryland income tax payments can feel overwhelming, but you are not alone in this journey. This article serves as a comprehensive guide, designed to help you master the intricacies of the state's progressive tax structure. We understand that understanding filing requirements, payment methods, and common issues can be daunting. That's why we provide detailed information to empower you.
You'll find specific income thresholds for filing, various payment options available, and troubleshooting advice. Each section is crafted to ensure you feel informed and supported as you navigate your tax obligations. Remember, it's common to have questions, and we're here to help.
Take a moment to reflect on your own experiences with taxes. What challenges have you faced? By addressing these concerns, we aim to build your confidence in managing your tax responsibilities. You deserve to feel empowered and knowledgeable about your financial obligations.
In summary, this guide is not just about taxes; it's about supporting you through a process that can often feel isolating. We encourage you to explore the information provided and take proactive steps towards understanding your Maryland income tax payments. You have the tools to succeed, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
Navigating the intricacies of Maryland's income tax system can feel overwhelming. We understand that the progressive tax rates and varying local taxes can significantly impact your financial obligations. This comprehensive guide is here to help you every step of the way. We’ll demystify the process, offering you a clear approach to understanding your tax responsibilities, filing requirements, and payment options.
It's common to feel uncertain with so many factors at play, including income levels and residency status. How can you ensure that you meet your obligations without falling into common pitfalls? You are not alone in this journey, and we’re here to support you in making sense of it all.
Understand Maryland's Income Tax Structure
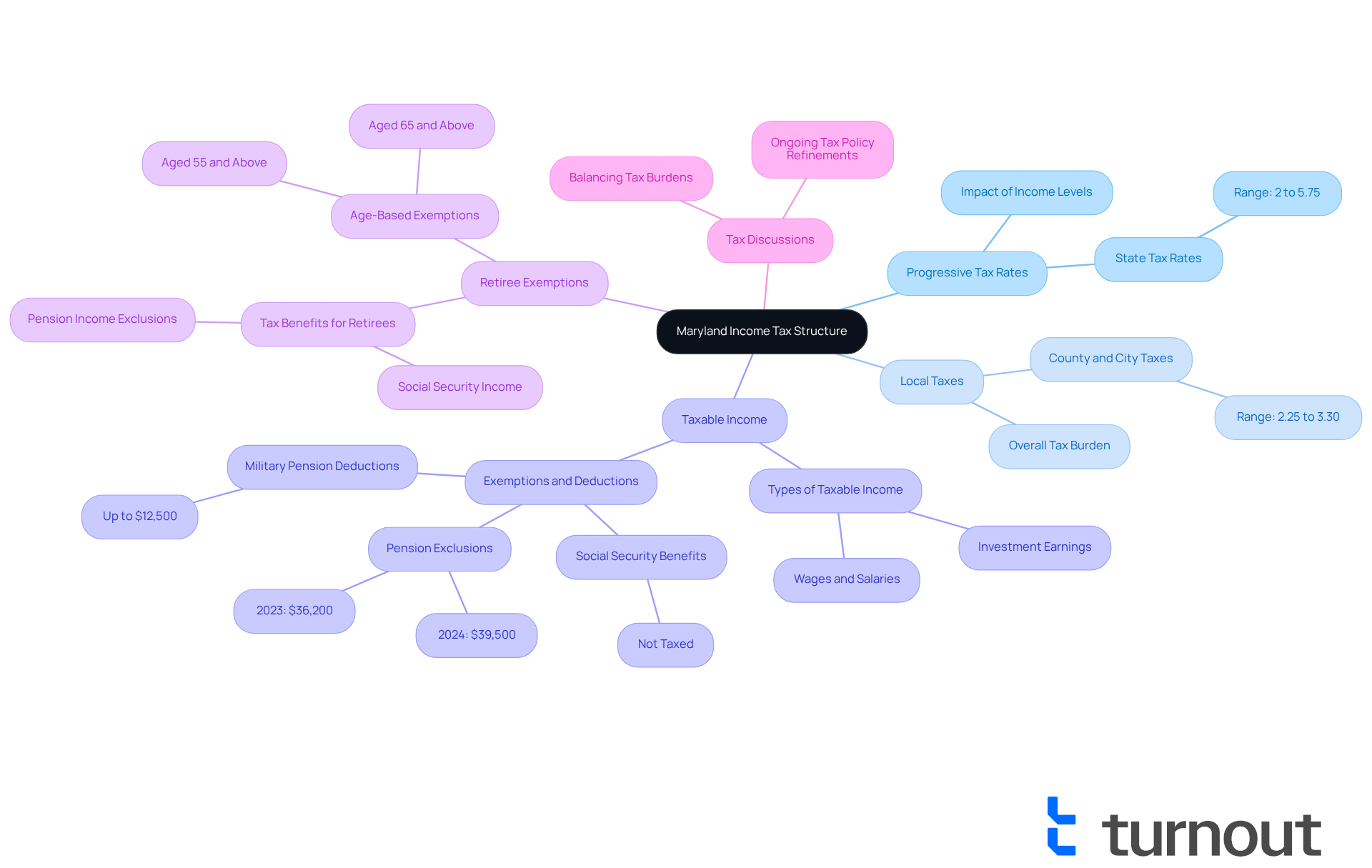
Maryland's revenue tax system operates on a progressive scale, meaning that tax rates increase with higher earnings. The state sets a base tax rate that ranges from 2% to 5.75%, depending on your earnings bracket. Additionally, local authorities, including each county and Baltimore City, have the ability to impose their own taxes on earnings, typically between 2.25% and 3.30%. This local tax can significantly affect your overall tax burden.
We understand that navigating taxes can be overwhelming. Most types of revenue, including wages, salaries, and certain investment earnings, are subject to taxation. However, there are specific exemptions and regulations that can ease your tax obligations. For instance, retirees benefit from the fact that Social Security benefits are not taxed in Maryland, allowing them to fully deduct this income when filing their state tax returns. Furthermore, retirees aged 65 and above can exclude up to $36,200 in pension earnings for 2023 and $39,500 for 2024. Military retirees also have the opportunity to deduct up to $12,500 of their military pension from taxable earnings.
Understanding these components is crucial for determining your tax obligations and planning your Maryland income tax payment. As Maryland continues to refine its tax policies, recent discussions highlight the importance of balancing tax burdens across different income levels. This ensures that the system remains fair and efficient for everyone. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you navigate these complexities.
Determine Your Filing Requirements
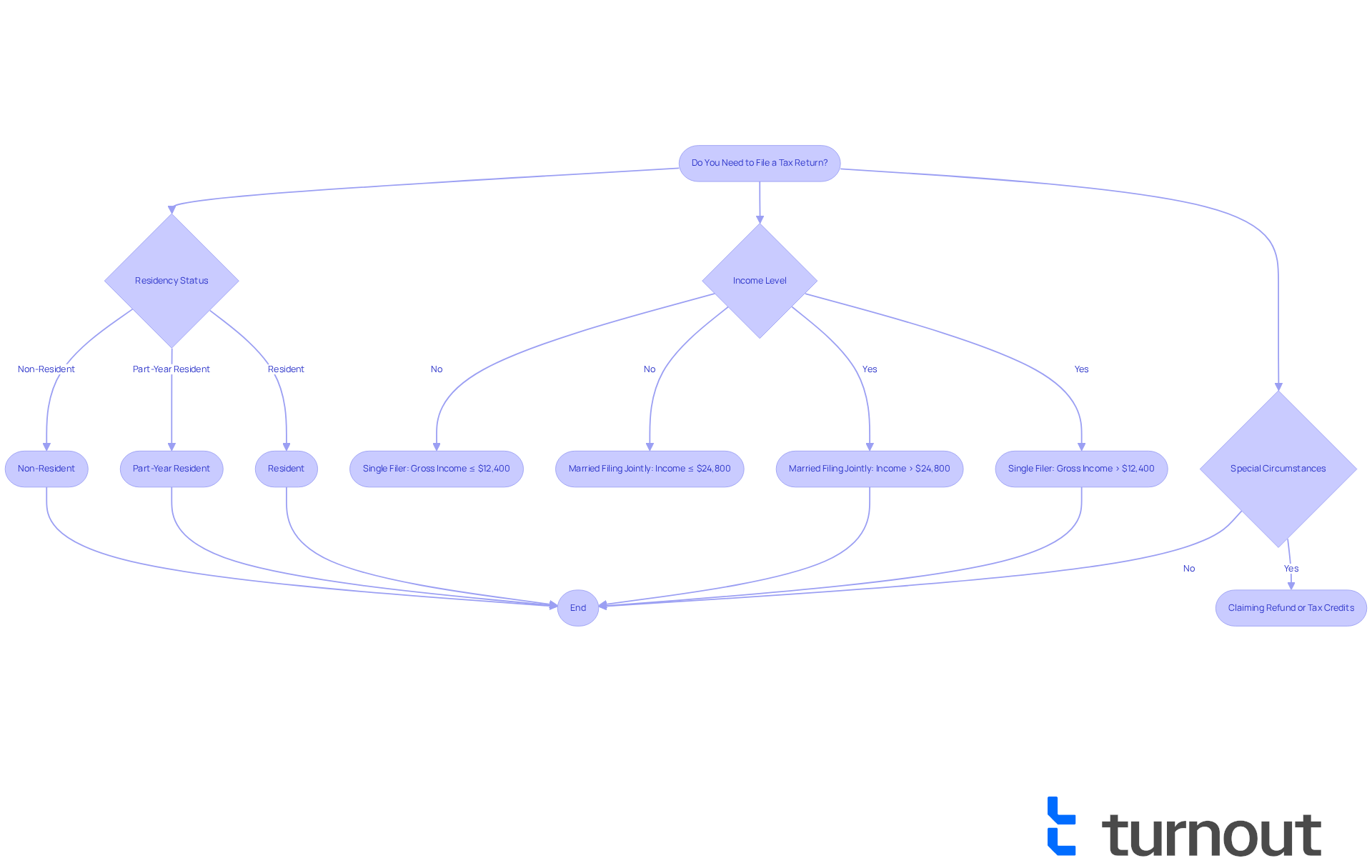
Are you feeling uncertain about your Maryland income tax payment and whether you need to file a tax return? You're not alone, and we're here to help you navigate this process with ease. Here are some important factors to consider:
- Income Level: For the 2025 tax year, if you are a single filer and your gross income exceeds $12,400, or if you are married filing jointly with earnings over $24,800, you will need to submit a filing.
- Residency Status: Understanding your residency status is vital, as different filing requirements apply to Maryland residents, part-year residents, and non-residents.
- Special Circumstances: Even if your earnings fall below the threshold, you might still need to file if you're claiming a refund or are eligible for tax credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit or the Child Tax Credit.
For example, if you are a single person earning $13,000 in 2025, you would need to file. Similarly, a married couple with total earnings of $24,000 is also required to file. However, if a single filer earns $11,000, they may not need to file unless they qualify for specific credits.
We understand that tax season can be overwhelming, but staying informed is key. For the most current filing requirements and thresholds regarding Maryland income tax payment, please review the State Comptroller's website to ensure you are compliant. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and seeking assistance is a positive step forward.
Follow the Steps to Make Your Tax Payment
Making your Maryland income tax payment can feel daunting, but we're here to guide you through the straightforward steps:
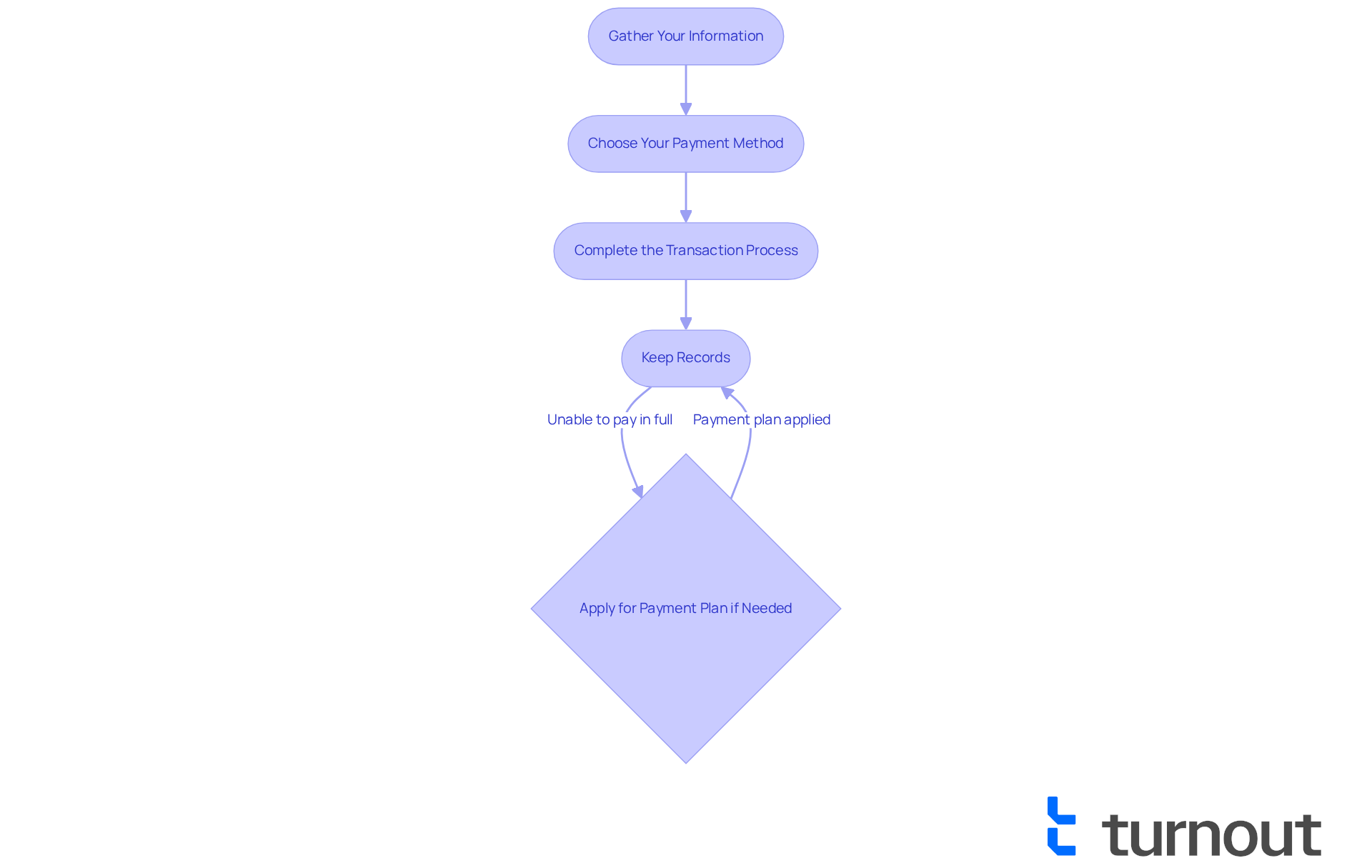
- Gather Your Information: Start by collecting your tax documents, including your Social Security number, income statements, and any deductions or credits you plan to claim. We understand that organizing these details can be overwhelming, but having everything ready will make the process smoother.
- Choose Your Payment Method: Maryland offers several options for making payments, so you can select what works best for you:
- Online: You can use the Maryland Comptroller's website to pay via credit card or electronic check. Just a heads up, there’s a service fee of 2.45% for credit card payments, collected by NICUSA, Inc.
- By Mail: If you prefer, send a check or money order with your tax return to the appropriate address:
- For refunds or no taxes owed: Comptroller of Maryland, Revenue Administration Division, 110 Carroll Street, Annapolis, MD 21411-0001.
- For amounts due: Processing Fees, PO Box 8888, Annapolis, MD 21401-8888.
- In-Person: You can visit a local Comptroller's office to make a transaction directly, which can be reassuring if you have questions.
- Direct Online Transaction: Maryland taxpayers can create an account with the MD Individual Taxpayer Online Service Center to submit funds directly from their bank accounts, and this option is free.
- Complete the Transaction Process: If you’re paying online, simply follow the prompts to enter your information and confirm your transaction. If you’re sending it by mail, please ensure your remittance is postmarked by the due date to avoid any penalties.
- Keep Records: It's important to save copies of your confirmation of transaction and any correspondence for your records. This documentation is essential in case of future inquiries or audits.
If you find yourself unable to pay your tax bill in full, don’t worry—you can apply for a payment plan with the state tax agency. Maryland also provides helpful resources, such as tax calculators and FAQs, to assist you in navigating the process of Maryland income tax payment with confidence. For secure online filing, consider using the iFile system, and you can access instructional videos for guidance on completing your taxes online. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we are here to help.
Troubleshoot Common Tax Payment Issues
Even with careful planning, we understand that issues can arise during the tax settlement process. It's common to feel overwhelmed, but knowing how to address these challenges can make a difference. Here are some common problems and supportive solutions:
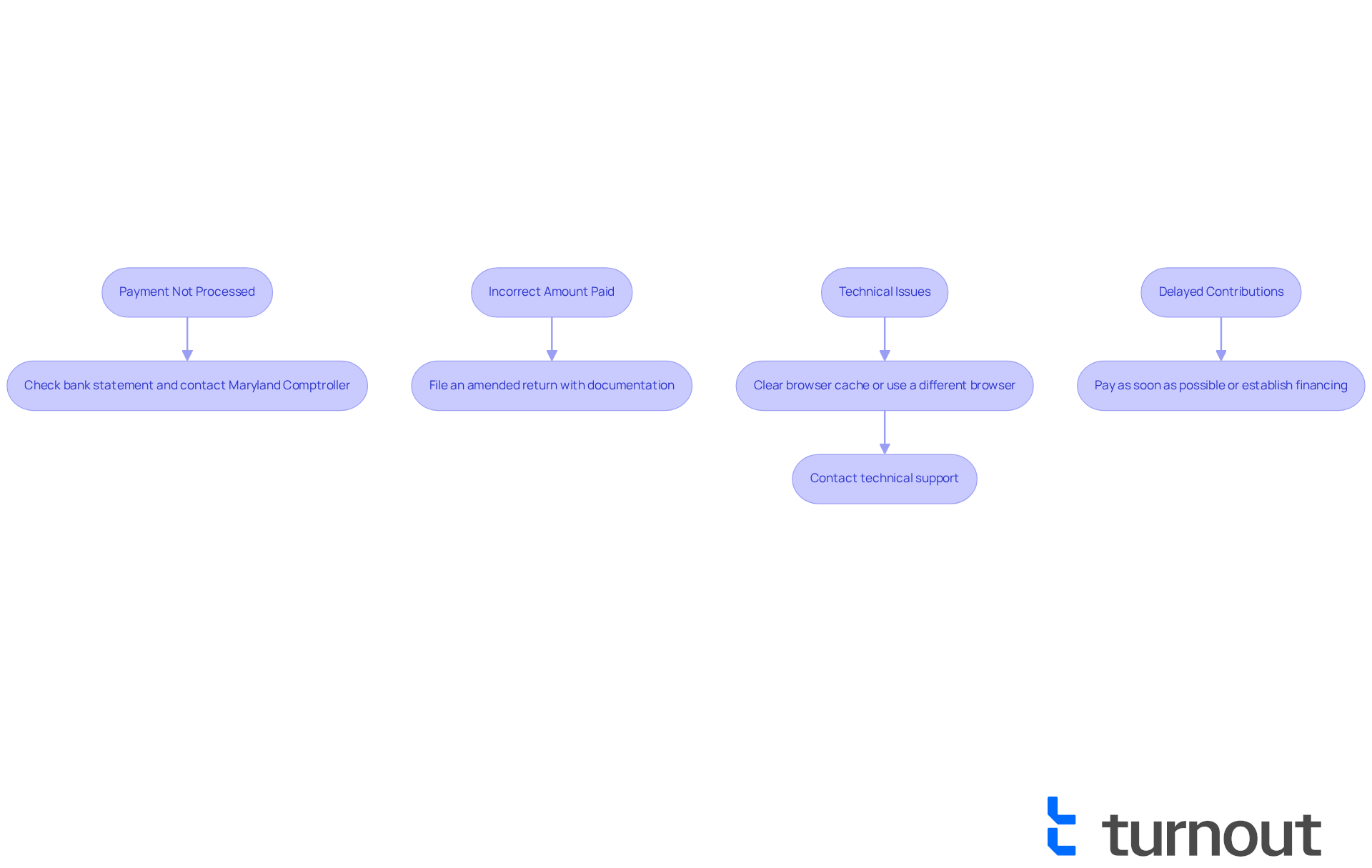
- Payment Not Processed: If you believe you made a payment but it hasn't been processed, check your bank statement for any transactions. If no record exists, please reach out to the Maryland Comptroller's office for assistance with your Maryland income tax payment. We're here to help.
- Incorrect Amount Paid: If you realize you've paid the wrong amount, don’t worry. You can file an amended return to correct the error. Just ensure you include any necessary documentation.
- Technical Issues: If you encounter problems while using the online transaction system, try clearing your browser cache or using a different browser. If issues persist, contacting technical support for help can be a great step forward.
- Delayed Contributions: If you miss the due date, be proactive. Paying as soon as possible can help minimize penalties and interest. If you’re unable to cover the entire sum, consider establishing a financing arrangement.
By being aware of these common issues and knowing how to address them, you can navigate the Maryland income tax payment process with greater confidence. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we are here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Navigating Maryland's income tax payment process can feel overwhelming at first, but understanding its structure and requirements is key to a smoother experience. We recognize that tax obligations can be daunting, and this guide aims to provide clarity. By familiarizing yourself with Maryland's progressive tax system, recognizing your filing requirements, and following the step-by-step payment process, you can approach your responsibilities with confidence.
It's important to know your income level, residency status, and any potential deductions available, especially if you are a retiree or military personnel. We also highlight the various payment methods offered by Maryland, including convenient online options, mail-in payments, and in-person transactions, all designed to fit your preferences. If you encounter common issues like payment processing errors or incorrect amounts, remember that you are not alone; we’re here to help you navigate those challenges.
Ultimately, staying informed and proactive is essential for Maryland income tax payments. By utilizing the available resources and understanding the process, you can ensure compliance while minimizing stress. Embracing this knowledge empowers you to tackle your tax responsibilities effectively, paving the way for a smoother financial journey ahead. Remember, we believe in your ability to manage this process, and we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the structure of Maryland's income tax system?
Maryland's income tax system operates on a progressive scale, meaning tax rates increase with higher earnings. The base tax rate ranges from 2% to 5.75%, depending on the earnings bracket.
Do local authorities impose additional taxes in Maryland?
Yes, local authorities, including each county and Baltimore City, can impose their own taxes on earnings, typically ranging between 2.25% and 3.30%.
What types of income are subject to Maryland income tax?
Most types of revenue, including wages, salaries, and certain investment earnings, are subject to taxation in Maryland.
Are there any exemptions for retirees regarding Maryland income tax?
Yes, Social Security benefits are not taxed in Maryland, allowing retirees to fully deduct this income when filing their state tax returns. Additionally, retirees aged 65 and above can exclude up to $36,200 in pension earnings for 2023 and $39,500 for 2024.
Can military retirees deduct any portion of their pension from taxable earnings in Maryland?
Yes, military retirees can deduct up to $12,500 of their military pension from taxable earnings.
Why is it important to understand Maryland's income tax components?
Understanding these components is crucial for determining tax obligations and planning Maryland income tax payments effectively.
What recent discussions have taken place regarding Maryland's tax policies?
Recent discussions highlight the importance of balancing tax burdens across different income levels to ensure that the system remains fair and efficient for everyone.




