Introduction
Navigating the complexities of IRS penalties can feel overwhelming, especially as the stakes seem to rise each year. We understand that many taxpayers are anxious about their financial obligations. With the IRS recently announcing possible avenues for waiving penalties and interest for tax year 2025, you might be wondering how these changes could benefit you.
This article explores the various options available for relief, detailing the criteria and processes involved. We’ll weigh the pros and cons of each approach, providing you with the information you need to make informed decisions. As you seek clarity amidst your financial challenges, remember: you are not alone in this journey. The question remains: will the IRS truly offer the reprieve that many desperately need? Let's find out together.
Understanding IRS Penalties and Interest
IRS sanctions can be daunting, often stemming from not filing or paying taxes on time. We understand how these penalties can significantly impact your financial situation. Here’s what you need to know:
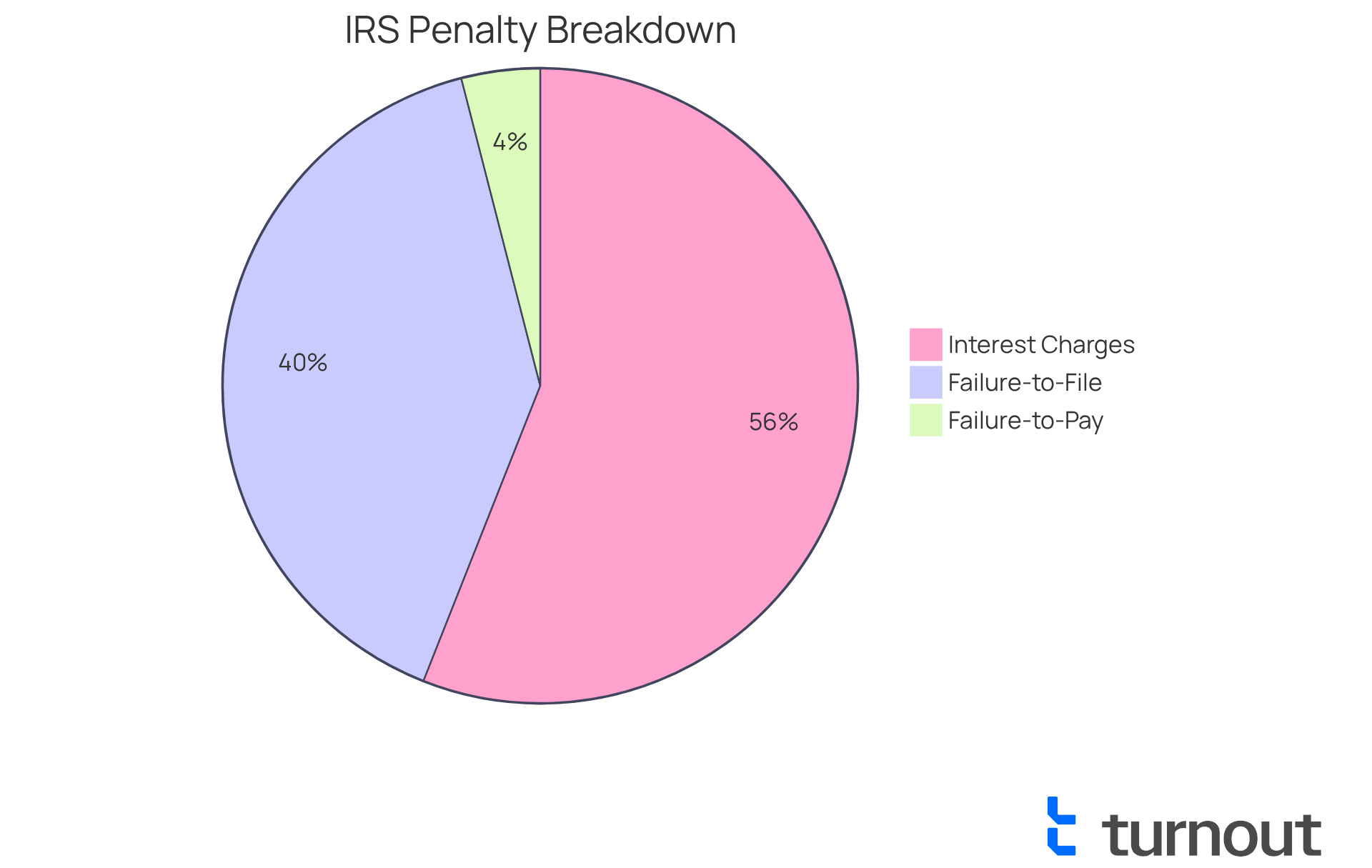
- Failure-to-File Penalty: If you miss the deadline, you could face a penalty of 5% of the unpaid tax for each month your return is late, up to a maximum of 25%.
- Failure-to-Pay Charge: This charge typically amounts to 0.5% of the unpaid tax for each month it remains unpaid, also capping at 25%.
- Interest Charges: Interest on unpaid taxes accumulates daily, compounding at a rate set quarterly by the IRS. For 2025, that rate is 7%.
Additionally, if individual taxpayers submit their returns more than 60 days late, the minimum fine has increased to $525 in 2025, up from $510 in 2024. This change reflects a stricter enforcement of filing deadlines. In fiscal year 2024, the IRS assessed a staggering $17.8 billion in additional taxes for returns not filed on time, highlighting the serious consequences of late filings.
It's common to feel overwhelmed by these penalties, but prompt action can help lessen these consequences and prevent mounting financial obligations. Moreover, the IRS has announced options for reducing penalties for tax year 2025, leading many to wonder, will the IRS waive penalties and interest, which may provide some relief for those facing fines. Remember, as the IRS states, "Interest will accumulate on any unpaid tax, charges, and interest until the balance is settled completely."
You are not alone in this journey. We're here to help you navigate these challenges and find the best path forward.
Exploring Available Relief Options for IRS Penalties
Taxpayers often find themselves overwhelmed by IRS penalties and are left asking, will the IRS waive penalties and interest? Fortunately, there are several avenues available for relief, each with its own eligibility criteria and application processes that can help ease your burden:
-
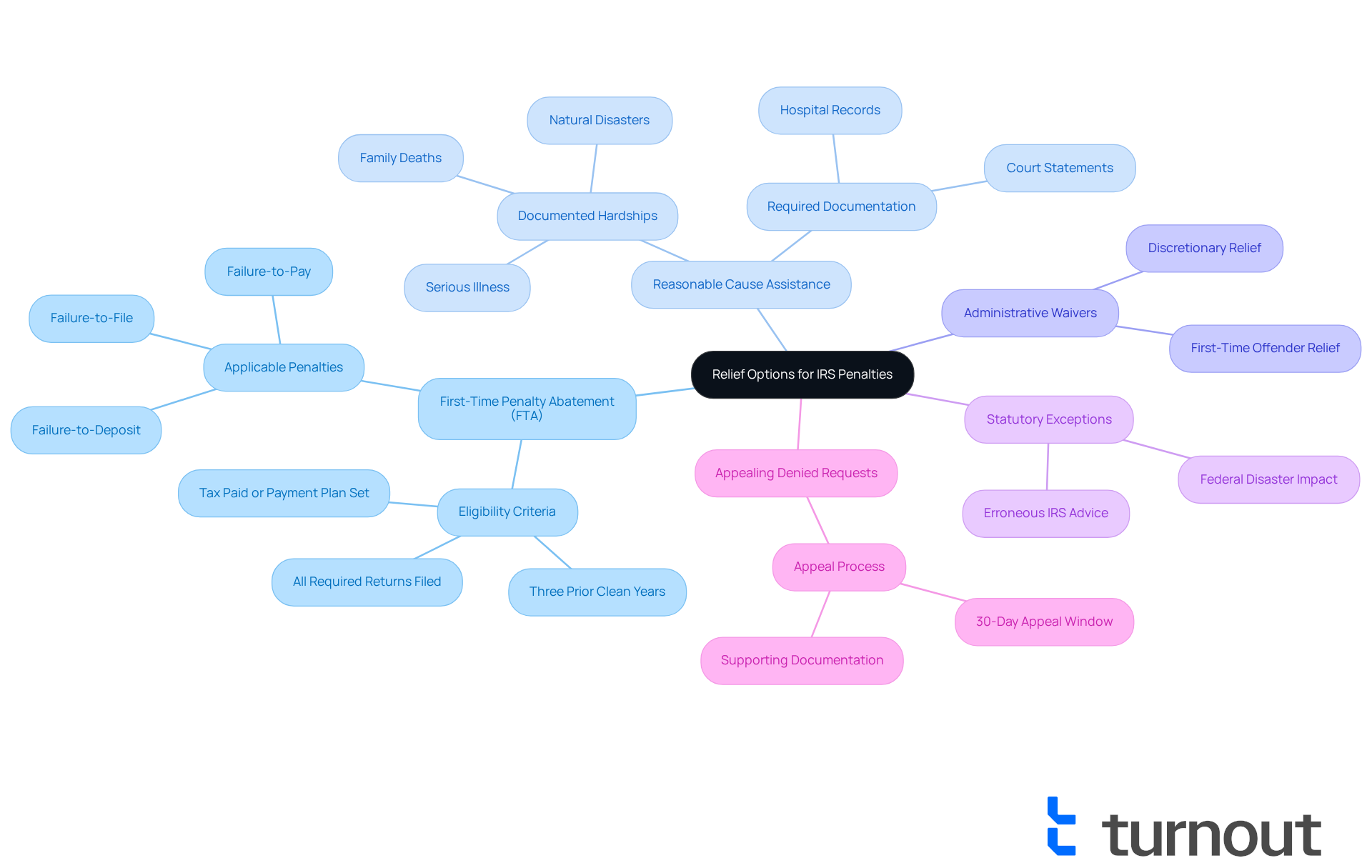
First-Time Penalty Abatement (FTA): If you’ve maintained a clean compliance history for the past three years, you might qualify for a one-time waiver of penalties. As of 2025, around 37% of individuals are eligible for FTA applications, especially those who have filed all required returns and addressed any outstanding tax liabilities. Remember, a clean history is crucial. As tax professionals often say, "You qualify when you filed every required return, fixed oversight issues, and paid or set a plan on the balance."
-
Reasonable Cause Assistance: Life can throw unexpected challenges your way, and if your non-compliance was due to circumstances beyond your control-like natural disasters or serious illness-you may seek support. The IRS has granted reasonable cause assistance in various cases, especially when you provide adequate documentation of your hardships. Claims backed by hospital records or court statements have successfully led to fee waivers. Documented hardships can include family deaths or significant medical issues.
-
Administrative Waivers: If you’re a first-time offender, the IRS may exercise discretion to grant relief for specific fines. This option can be particularly beneficial, allowing for a more flexible evaluation process.
-
Statutory Exceptions: In certain situations, fines may be forgiven if you were affected by a federal disaster or relied on erroneous IRS advice. It’s important to document these circumstances thoroughly to support your claims.
-
Appealing Denied Requests: If your request for FTA is denied, don’t lose hope. You have the option to appeal the decision within 30 days of rejection. This step is crucial for those who believe they meet the eligibility criteria.
Understanding these options is vital for anyone navigating the complexities of whether the IRS will waive penalties and interest. Consulting with tax professionals can provide personalized guidance tailored to your situation. As specialists often suggest, "Taxpayers should consult with their tax advisers to ascertain whether assistance is available and the best course of action for their specific circumstances." Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to help you find relief.
Qualifying for IRS Penalty Relief: Criteria and Processes
Navigating IRS penalty relief can feel overwhelming, especially when wondering if the IRS will waive penalties and interest, but you’re not alone in this journey. To qualify for relief, there are specific criteria you need to meet:
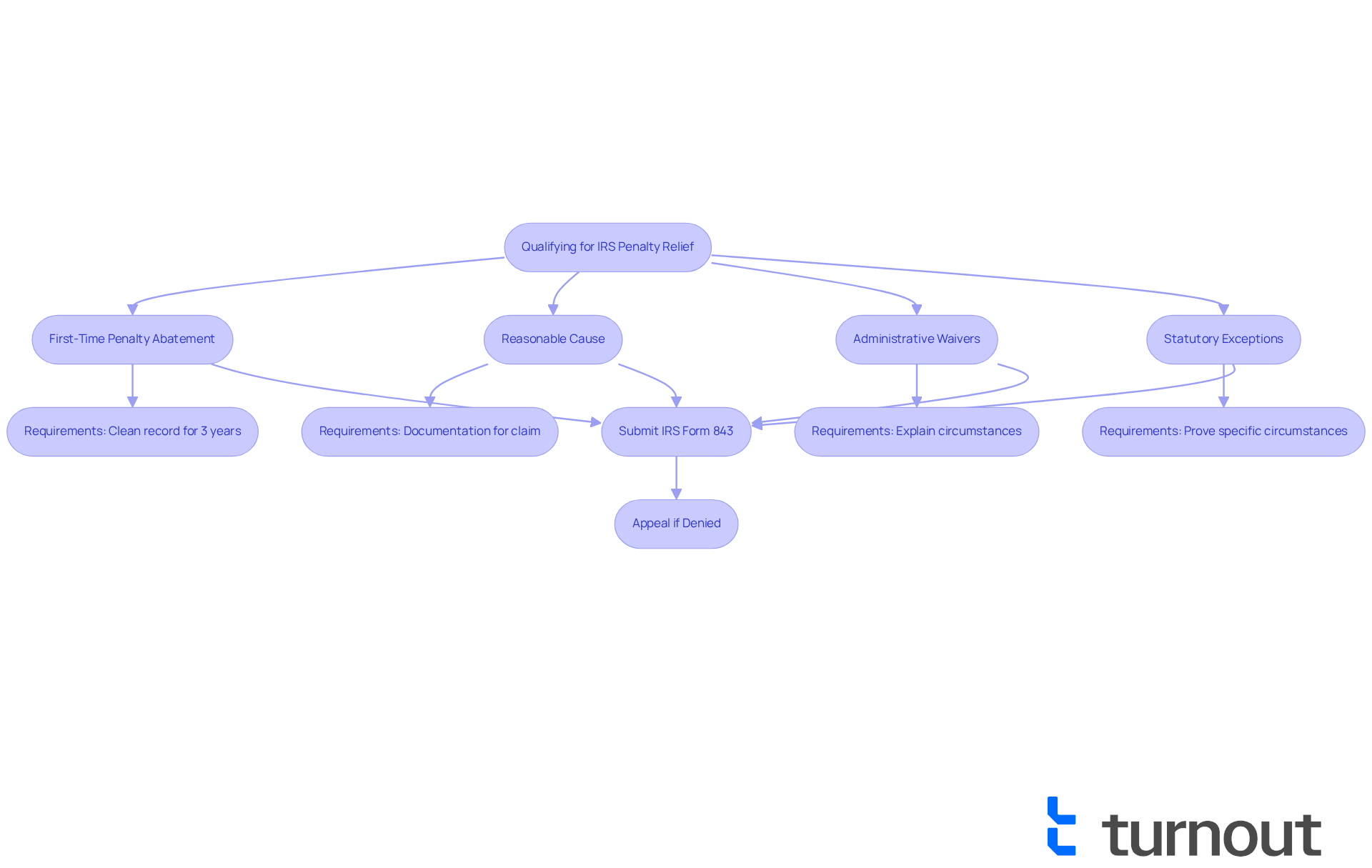
- First-Time Penalty Abatement: You must have filed all required returns and paid any taxes due for the past three years without penalties. If you haven’t submitted all necessary returns, it’s tough to qualify for first-time abatement. A clean violation history is essential for eligibility.
- Reasonable Cause: It’s important to provide documentation that supports your claim. This could include medical records or evidence of natural disasters, showing that you acted with ordinary care and prudence.
- Administrative Waivers: Be ready to explain your circumstances and provide any relevant documentation to support your request.
- Statutory Exceptions: You’ll need to prove the specific circumstances that qualify for statutory exceptions, like being in a combat zone or affected by a federally declared disaster.
The application process typically involves submitting IRS Form 843, Claim for Refund and Request for Abatement, along with any supporting documentation. Remember, this form must be submitted within three years of the return due date or filing date, or within two years of the payment date. If the IRS denies your request for abatement, don’t lose hope; you can appeal the decision and inquire if the IRS will waive penalties and interest.
We understand that this process can be daunting, but taking these steps can lead you toward relief. You’re taking a positive step forward, and we’re here to help.
Comparing Pros and Cons of IRS Relief Options
When it comes to navigating IRS penalty relief options, we understand that it can feel overwhelming. It’s essential to weigh the advantages and disadvantages of each option to find the best fit for your situation:
-
First-Time Penalty Abatement:
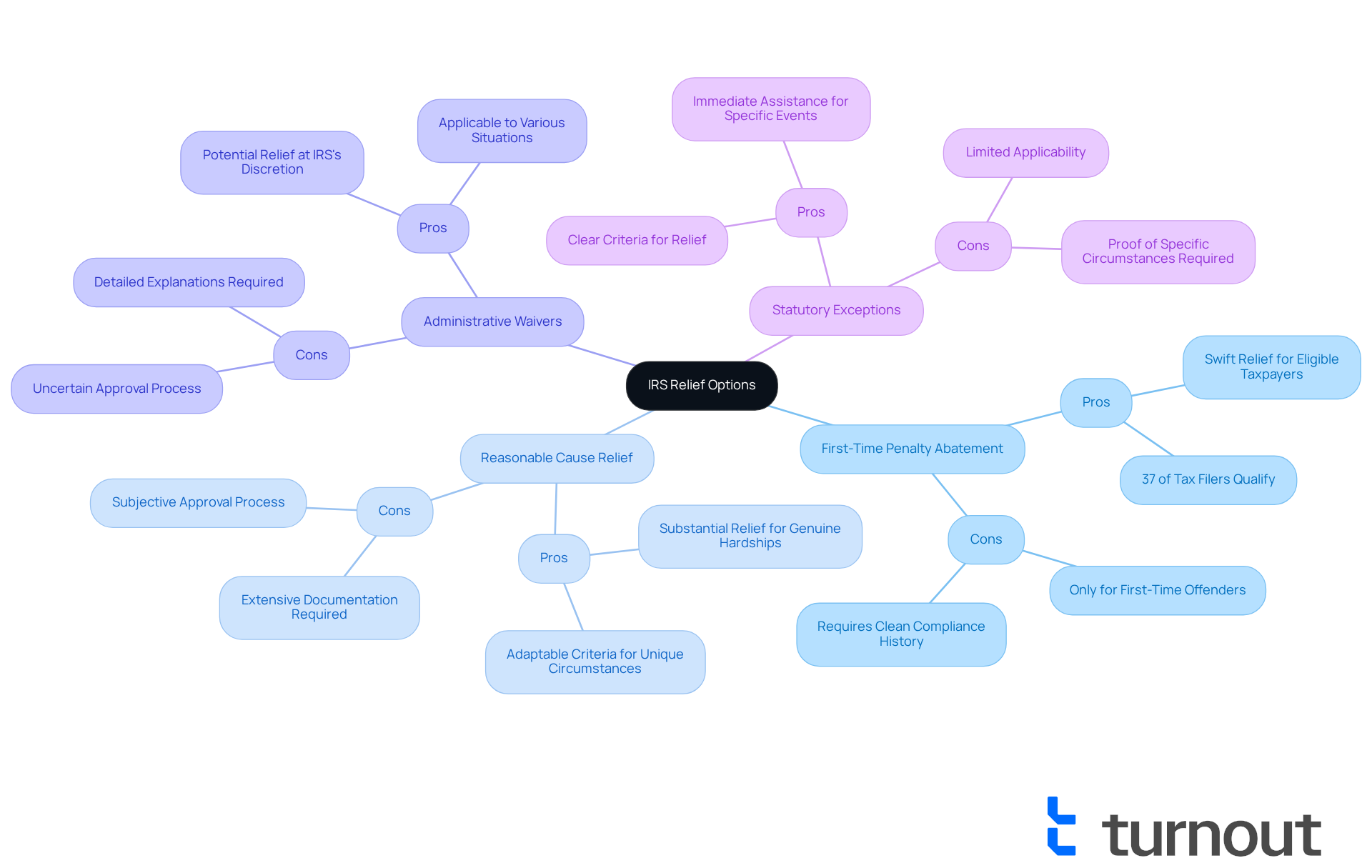
- Pros: This option offers swift relief for eligible taxpayers, allowing first-time offenders to avoid penalties. Did you know that about 37% of individuals who file taxes qualify for this option, no matter the fee amount? To be eligible, you must have submitted a tax return for at least three years before receiving a penalty.
- Cons: However, this relief is exclusively available to first-time offenders, which means you need a clean compliance history over the past three years.
-
Reasonable Cause Relief:
- Pros: This option provides substantial relief for individuals facing genuine hardships. The criteria can adapt to unique circumstances, making it particularly beneficial for those who can effectively document their situations.
- Cons: On the downside, it requires extensive documentation to support your claims, and approval can be subjective, leading to uncertainty in outcomes.
-
Administrative Waivers:
- Pros: These waivers offer potential relief at the IRS's discretion and can apply to various situations, which can be advantageous for taxpayers with unique challenges.
- Cons: However, approval is uncertain and may require detailed explanations of your circumstances.
-
Statutory Exceptions:
- Pros: This option features clear criteria for relief, providing immediate assistance for those impacted by disasters or specific events.
- Cons: Yet, it’s limited in applicability, requiring proof of specific circumstances that may not pertain to everyone.
By understanding these factors, you can make informed choices about the most appropriate assistance option for your specific situation. Remember, the IRS abated $50.9 billion in penalties during fiscal year 2022, highlighting the scale of relief available. If you’re feeling overwhelmed, seeking assistance from a tax professional can be a practical step to navigate these options effectively. You are not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of IRS penalties and interest can feel overwhelming. We understand that many taxpayers face these challenges alone, but there’s hope. By exploring the available relief options, you can find clarity and support. Options like:
- First-Time Penalty Abatement
- Reasonable Cause Assistance
- Administrative Waivers
are just a few avenues to consider.
It's essential to maintain a clean compliance history and keep thorough documentation for your claims. If your request is denied, remember that you have the right to appeal. Each relief option has its own criteria and processes, so take the time to assess your unique situation. Consulting with tax professionals can make a significant difference in navigating these waters.
Ultimately, this discussion is about empowering you to take proactive steps toward alleviating your financial burdens. Whether you’re dealing with penalties from late filings or unpaid taxes, exploring these relief options can pave a more manageable path forward. Stay informed and seek assistance when needed; the resources and support available can truly help you overcome IRS challenges. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Failure-to-File penalty?
The Failure-to-File penalty is 5% of the unpaid tax for each month your return is late, up to a maximum of 25%.
What is the Failure-to-Pay charge?
The Failure-to-Pay charge is typically 0.5% of the unpaid tax for each month it remains unpaid, also capping at 25%.
How does interest on unpaid taxes accumulate?
Interest on unpaid taxes accumulates daily and compounds at a rate set quarterly by the IRS. For 2025, this rate is 7%.
What is the minimum fine for late tax returns in 2025?
If individual taxpayers submit their returns more than 60 days late, the minimum fine is $525 in 2025, an increase from $510 in 2024.
What were the IRS's additional tax assessments for late filings in fiscal year 2024?
In fiscal year 2024, the IRS assessed $17.8 billion in additional taxes for returns not filed on time.
Can the IRS waive penalties and interest for tax year 2025?
The IRS has announced options for reducing penalties for tax year 2025, which may provide relief for those facing fines.
What should taxpayers do if they feel overwhelmed by penalties?
Prompt action can help lessen the consequences of penalties and prevent mounting financial obligations. It's important to seek assistance to navigate these challenges.




