Overview
Seniors, we understand that navigating tax obligations can be challenging. You may find relief in knowing that you can stop filing taxes when your income falls below certain thresholds set by the IRS. These thresholds vary based on your filing status and age, such as:
- $14,600 for single filers
- $30,750 for married couples in 2025
It's common to feel overwhelmed by these numbers, but understanding your financial situation is crucial.
Consider all sources of income, including Social Security, as they play a significant role in determining your tax obligations. Even if you're not required to file, there may be benefits to doing so. We're here to help you explore your options and ensure you make the best decision for your circumstances. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we're here to support you every step of the way.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of tax filing can feel overwhelming, especially for seniors who face unique financial situations during their transition into retirement. We understand that understanding the specific IRS guidelines for tax submissions is crucial. It can significantly impact your financial well-being.
This article will explore the essential thresholds and requirements that determine when you might stop filing taxes, shedding light on the relationship between income sources like Social Security and retirement benefits.
With so many variables at play, how can you confidently assess your tax obligations and make informed decisions about your filing needs? You're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help.
Understand Tax Filing Requirements for Seniors
To start, we understand that navigating tax submission requirements can feel overwhelming, especially for seniors. It's important to become acquainted with the general guidelines established by the IRS. Generally, individuals aged 65 and above may have varying levels of earnings that necessitate submitting a tax return. The IRS provides recommendations outlining the minimum earnings thresholds based on submission status, such as single or married filing jointly.
For the tax year 2025:
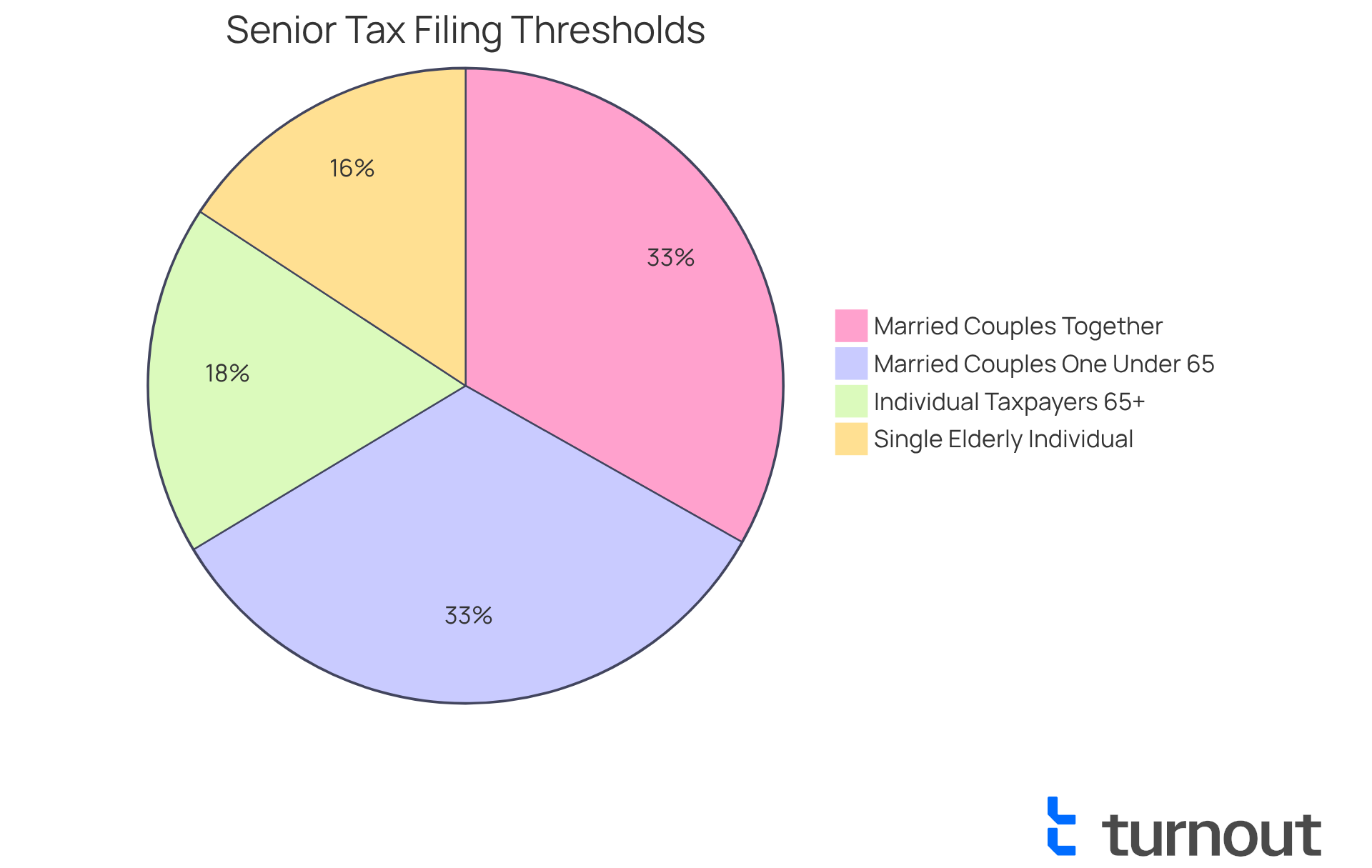
- A single elderly individual must submit if their gross earnings exceed $14,600.
- Married couples filing together need to report if their total gross earnings surpass $30,750, particularly if one partner is under 65.
- Additionally, individuals aged 65 and above are required to submit if their total income exceeds:
- $16,550 for individual taxpayers
- $30,750 for married couples filing together with one partner under 65
Understanding these requirements can help older adults determine when can you quit filing taxes.
Real-world examples illustrate how older adults navigate these guidelines. For instance, an older adult receiving Social Security benefits may be curious about when can you quit filing taxes if their total earnings remain below the threshold. However, if they have additional income sources, such as pensions or part-time work, they may exceed the limit and be required to file.
In the words of the Taxpayer Advocate Service, "TAS strives to protect taxpayer rights and ensure the IRS is administering the tax law in a fair and equitable way." By staying informed about the earnings limits and submission categories, older adults can make empowered choices regarding their tax responsibilities. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you navigate these important decisions.
Identify Age and Income Thresholds for Tax Filing
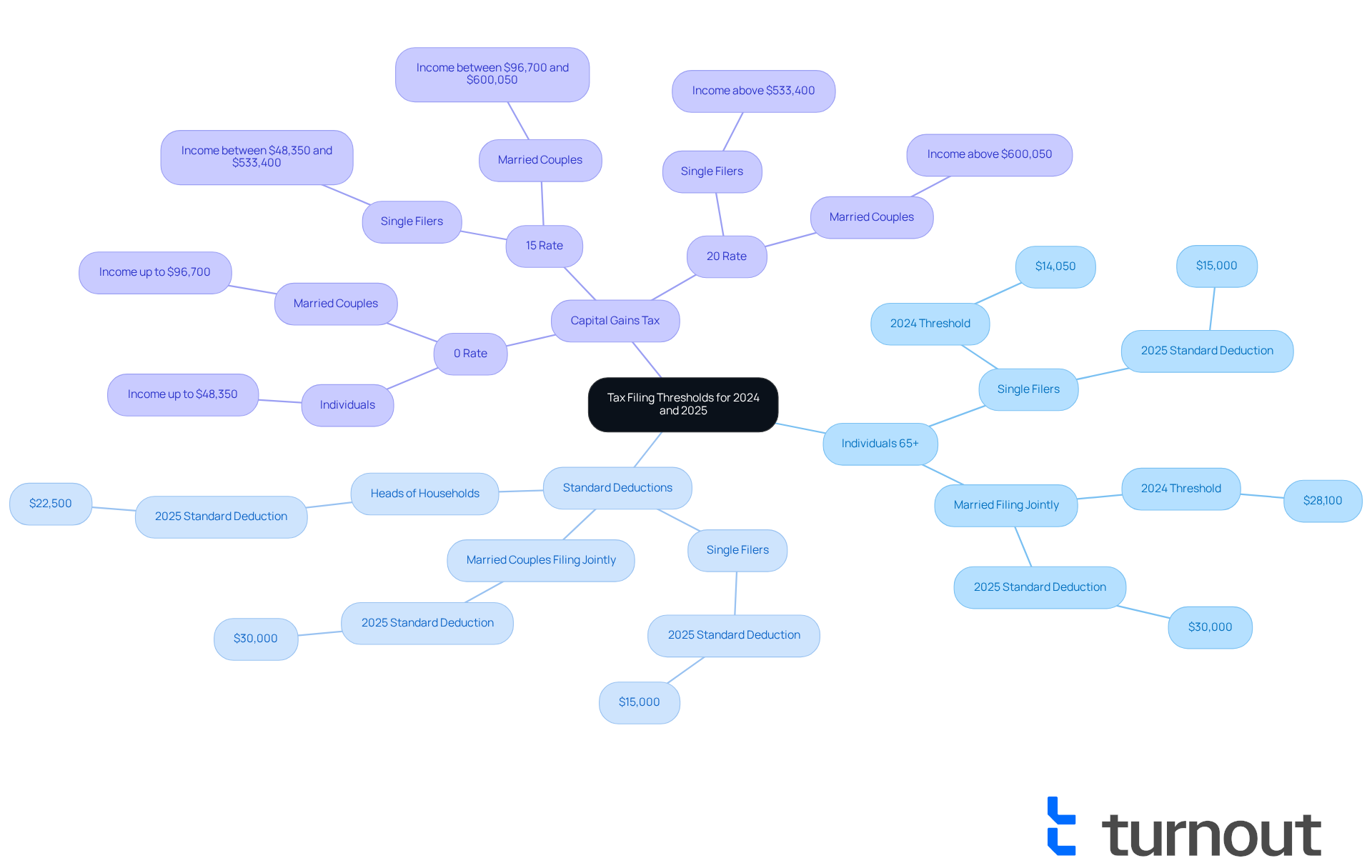
As we age, understanding the IRS guidelines for the current tax year becomes increasingly important. For the 2024 tax year, if you are 65 or older, it's essential to know that you must submit your tax return if your income exceeds $14,050. For married couples filing together, the threshold is $28,100. We understand that navigating these numbers can be overwhelming, but knowing them can greatly influence your tax responsibilities.
Moreover, individuals aged 65 and older may qualify for higher standard deductions. For instance, in 2025:
- Single filers and married couples filing separately will see the standard deduction rise to $15,000.
- Married couples filing jointly will benefit from an increase to $30,000.
- Heads of households will enjoy a standard deduction of $22,500 in 2025.
These adjustments underscore the importance of staying informed through IRS publications, ensuring compliance and optimizing your tax situation.
It's also crucial to be aware of the capital gains tax thresholds for 2025. Individuals earning up to $48,350 will qualify for a 0% tax rate on capital gains. We encourage you to maintain organized digital tax documents, as this practice can help in preparing an accurate tax return and identifying any overlooked deductions or credits. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we're here to help you navigate these complexities with confidence.
Evaluate the Impact of Social Security and Retirement Income on Taxes
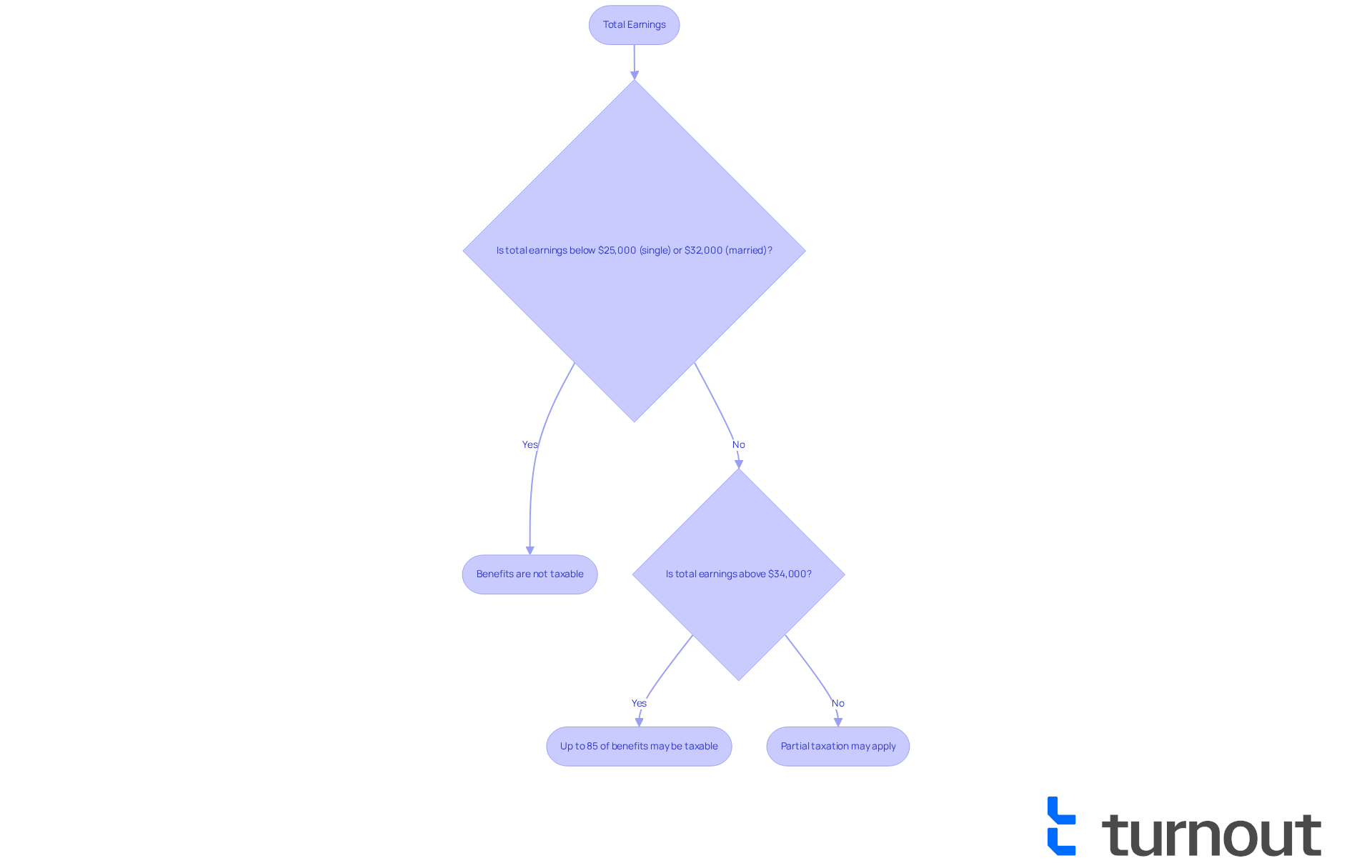
As seniors, it’s crucial to carefully assess how your revenue sources, including Social Security benefits and retirement accounts, impact your tax responsibilities. We understand that navigating these financial waters can feel overwhelming. Generally, your Social Security benefits may not be taxable if your overall earnings fall below specific thresholds. For instance, if your total earnings—calculated as adjusted gross earnings plus nontaxable interest plus half of your Social Security benefits—remain below $25,000 for single filers or $32,000 for married couples, your benefits are free from taxation.
However, it’s important to note that if your total earnings exceed $34,000, up to 85% of your Social Security benefits could become taxable. Grasping these nuances is essential, as they can significantly influence when you can quit filing taxes and how much you might owe. In 2025, projections suggest that approximately 57.4% of beneficiary families will owe income tax on their benefits. This highlights the importance of being aware of income thresholds.
For residents in Virginia, it’s reassuring to know that the state does not tax Social Security benefits, which can positively impact your overall tax responsibilities. We encourage you to consult tax authorities for any specific questions regarding your situation. For further guidance, Publication 915 offers comprehensive insights into the taxability of Social Security benefits, acting as a valuable resource for seniors managing their retirement funds and tax responsibilities. Remember, you are not alone in this journey—we're here to help.
Assess Your Personal Tax Situation and Filing Needs
As seniors, you may find it helpful to begin with a comprehensive assessment of your personal tax situation. This means taking a close look at all your sources of revenue while recognizing potential deductions and credits you might be eligible for. For the tax years 2025 through 2028, individuals aged 65 and older can claim an additional deduction of $6,000, bringing the total to $12,000 for married couples where both spouses qualify. However, it's important to understand that this additional deduction phases out for taxpayers with a modified adjusted gross income over $75,000 ($150,000 for joint filers).
We understand that navigating taxes can be overwhelming, but using tax preparation software can simplify this process. It provides clarity on submission requirements and highlights possible advantages. Consulting with a tax professional can also be beneficial, especially if you’re unsure about your obligations. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; help is available.
Furthermore, consider the option of submitting your taxes even if it’s not necessary. This could open the door to refunds or credits you may not have anticipated. By thoroughly evaluating your financial situation, you can make informed decisions about when can you quit filing taxes. We're here to help you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding when seniors can stop filing taxes can feel overwhelming. It's a complex landscape filled with income thresholds, filing requirements, and personal financial situations. This guide has highlighted the essential criteria seniors must consider, emphasizing the importance of being informed about IRS guidelines and income limits for the 2025 tax year. By recognizing these factors, older adults can make empowered decisions regarding their tax responsibilities.
We know that navigating these waters can be challenging. Key insights shared in this article include:
- The specific income thresholds for various filing statuses
- The impact of Social Security and retirement income on tax obligations
- The potential benefits of utilizing tax preparation resources
Staying updated on changes in tax laws and deductions is crucial, as is the advantage of consulting with tax professionals. These elements collectively contribute to a clearer understanding of when seniors may be able to cease filing taxes.
Ultimately, this journey of tax filing does not have to be daunting. Seniors are encouraged to assess their unique financial situations, remain proactive in seeking information, and consider filing even when not required. This could lead to unexpected refunds or credits. By taking these steps, seniors can navigate their tax responsibilities with confidence and clarity, ensuring they are well-informed and prepared for the future. Remember, you are not alone in this journey—we're here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the tax filing requirements for seniors aged 65 and above?
Seniors aged 65 and above must submit a tax return if their gross earnings exceed certain thresholds established by the IRS, which vary based on their filing status.
What is the gross earnings threshold for a single elderly individual to file taxes in 2025?
A single elderly individual must submit a tax return if their gross earnings exceed $14,600 for the tax year 2025.
What is the gross earnings threshold for married couples filing jointly in 2025?
Married couples filing jointly need to report if their total gross earnings surpass $30,750, particularly if one partner is under 65.
Are there specific income limits for elderly individuals that require them to file taxes?
Yes, individuals aged 65 and above must submit a tax return if their total income exceeds $16,550 for individual taxpayers or $30,750 for married couples filing together with one partner under 65.
How can Social Security benefits affect a senior's tax filing status?
An older adult receiving Social Security benefits may not need to file taxes if their total earnings remain below the threshold. However, if they have additional income sources, such as pensions or part-time work, they may exceed the limit and be required to file.
What resources are available to help seniors understand their tax responsibilities?
The Taxpayer Advocate Service (TAS) provides support to protect taxpayer rights and ensure fair administration of tax laws, helping seniors navigate their tax responsibilities effectively.




