Introduction
Understanding overtime pay is crucial for employees who want to maximize their earnings while navigating the complexities of tax implications. We understand that with new regulations on the horizon, including the potential to deduct significant amounts from taxable income, you might feel hopeful about your financial future. However, it’s common to feel uncertain about how overtime earnings can push you into higher tax brackets. What does this mean for you, and how can you ensure you’re making the most of your hard-earned income?
Let’s explore this together. By understanding the specific tax rates applied to these additional hours, you can take steps to protect your income. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you navigate these challenges and find the best path forward.
Define Overtime Pay: Understanding Its Basics
Overtime pay is more than just a number; it’s the extra compensation you earn for working beyond the standard 40-hour workweek, as outlined by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Typically, this means you’ll receive one and a half times (1.5x) your regular hourly wage for those additional hours. For example, if you earn $20 an hour, your pay for any hours over 40 in a week would be $30 per hour.
Understanding this is crucial. It ensures you’re fairly rewarded for your hard work and helps you navigate the complexities of tax implications tied to those extra earnings, including what rate is overtime taxed at. We understand that keeping track of these details can be overwhelming, especially with changes on the horizon. As of 2025, the IRS has introduced new guidelines for reporting and deducting qualified extra pay, although formal guidance on implementation is still pending. Staying informed about these regulations is essential to maximize your benefits and avoid potential penalties.
Additionally, the salary limit for extra pay eligibility has significantly increased. This change affects how you should approach your compensation and tax reporting. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you understand your rights and ensure you receive what you deserve.
Explore Overtime Tax Rates: How Overtime Is Taxed
Overtime compensation often leads to confusion, especially when people wonder what rate is overtime taxed at. We understand that navigating these financial waters can be challenging. Just like regular wages, overtime pay is taxed at the same federal earnings tax rates, which raises the question of what rate is overtime taxed at, meaning it falls under your normal tax bracket. But here’s some good news: the recent 'No Tax on Extra Hours' provision from the One Big Beautiful Bill Act allows eligible taxpayers to deduct up to $12,500 of qualified extra hours compensation from their taxable earnings for the years 2025 through 2028.
This change can significantly lighten your tax burden. By deducting this amount, you can lower your taxable income, which is a relief many employees will appreciate. It’s important to note that this deduction applies only to the portion of your extra pay that exceeds your standard rate. For instance, if you earn 'time-and-a-half' for those extra hours, only the additional amount beyond your regular salary qualifies for this reduction.
To take advantage of this benefit, you’ll need a valid Social Security number for work. However, keep in mind that the tax benefit phases out for individuals with Modified Adjusted Gross Incomes (MAGI) above $150,000 for single filers and $300,000 for joint filers. If you’re filing as Married Filing Separately, unfortunately, you won’t be eligible for this deduction.
This provision is designed to provide greater financial relief during tax season, and we hope it helps many workers like you. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and understanding these changes can empower you to make the most of your earnings.
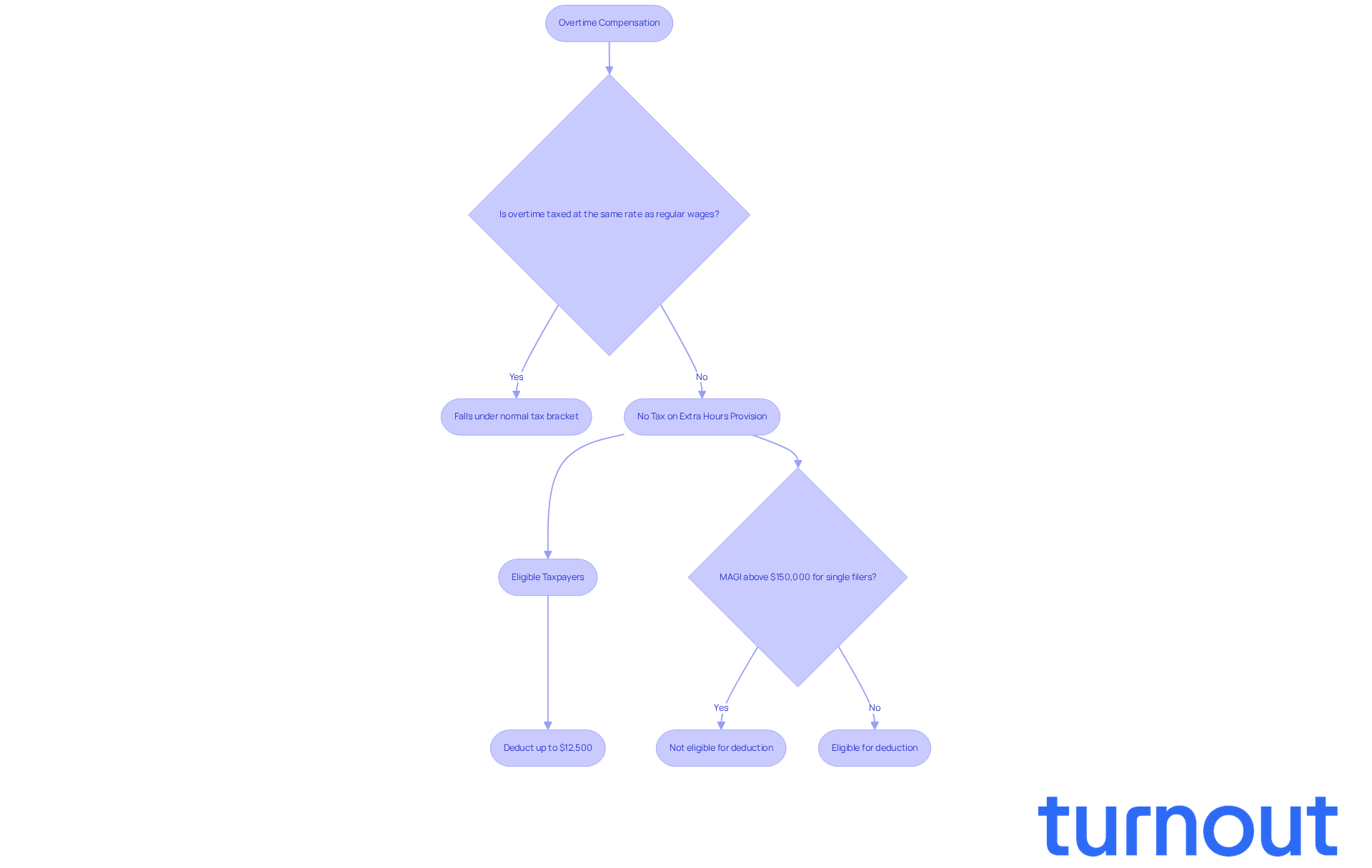
Analyze Tax Bracket Implications: The Impact of Overtime Earnings
Receiving extra hours can significantly impact your overall earnings, and it might even push you into a higher tax bracket. For example, if you typically earn $40,000 and then receive an additional $10,000 from extra hours, your total earnings would rise to $50,000. This increase could mean that part of your income is taxed at a higher rate, leading to the inquiry of what rate is overtime taxed at, depending on the tax brackets for that year.
But here’s some good news: starting in 2025 and lasting until 2028, there’s a new allowance for extra pay that can help you lower your taxable earnings. You can deduct up to $12,500 for eligible additional compensation, which can ease the tax burden that comes with increased earnings. This tax benefit is available for both itemizers and non-itemizers, making it especially helpful for those whose modified adjusted gross earnings are under $150,000, as it gradually decreases for higher incomes.
As Nate J. Kowalski, a partner at AALRR, points out, "The OBBBA established a substantial new tax relief for workers who receive extra hours mandated by federal law, intended to reduce taxable earnings for employees." It is crucial for effective financial planning and tax preparation to understand what rate is overtime taxed at, along with the benefits of this new deduction.
We’re here to help you navigate these changes, ensuring you can make informed decisions about your income and potential deductions. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey.
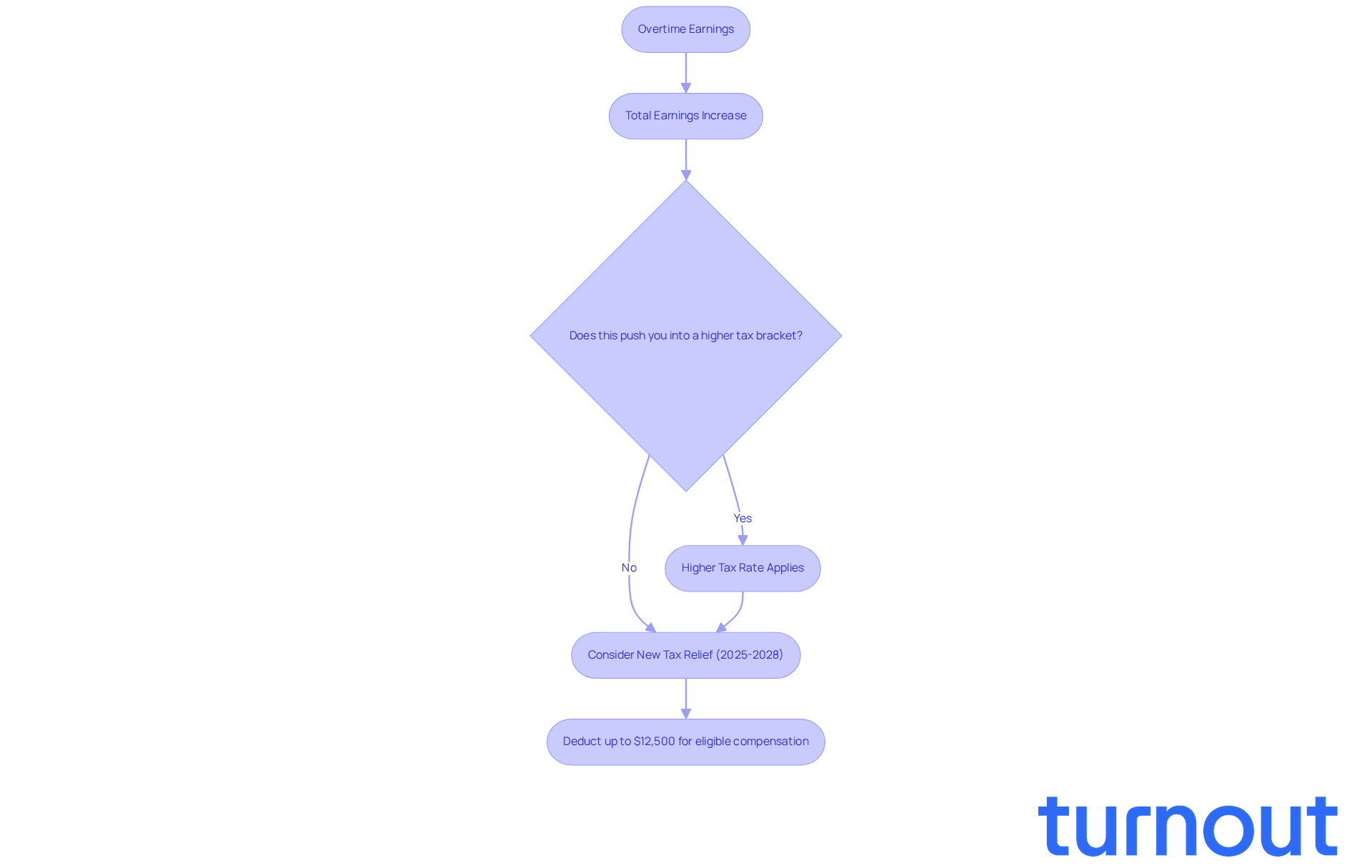
Illustrate with Examples: Real-World Scenarios of Overtime Taxation
Imagine a nurse who typically earns $30 per hour and puts in 10 extra hours in a week. Her regular pay for that week would be $1,200 (40 hours x $30), and her overtime pay would amount to $450 (10 hours x $45). If she qualifies for the 'No Tax on Overtime' exemption, which took effect on January 1, 2025, she can subtract $4,500 from her taxable income. This can significantly lighten her tax burden.
This deduction is available until December 31, 2028, with a maximum deductible amount of $12,500 for single filers and $25,000 for joint filers. Now, consider a construction worker earning $25 per hour who works 15 additional hours. His regular pay would be $1,000, and his additional pay would be $562.50. By understanding how to calculate these amounts and apply the new tax rules, including what rate is overtime taxed at, workers can navigate their financial situations more effectively and maximize their earnings.
It's essential for employees to keep precise records to support their claims for these reductions. For instance, a manufacturing worker earning $25 per hour and working 15 overtime hours weekly can deduct $9,750 in qualified overtime. This could potentially save him $1,072 in federal taxes at an 11% tax bracket. This illustrates how important accurate calculations and a solid understanding of what rate is overtime taxed at can be for overall financial well-being.
We understand that tax regulations can be overwhelming. It's also important to note that the deduction begins to phase out for individuals with modified adjusted gross incomes (MAGI) exceeding $150,000 for single filers and $300,000 for married couples filing jointly. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we're here to help you make sense of it all.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of overtime pay and its tax implications is vital for maximizing your earnings and ensuring fair compensation. Overtime pay, which is the extra compensation for hours worked beyond the standard workweek, not only rewards your hard work but also brings about some tax complexities. Recent changes have introduced deductions for qualified extra hours compensation, which can significantly ease the tax burden for many workers, especially from 2025 to 2028.
We know that navigating these regulations can feel overwhelming. Key insights have emerged, such as:
- The fundamental definition of overtime pay
- The tax rates applied to these earnings
- The potential for increased tax deductions under the new provisions
It's important to be aware that overtime earnings could push you into higher tax brackets. Understanding these regulations can lead to financial benefits that empower you to manage your financial situation more effectively.
As these developments unfold, staying informed and proactive about your earnings and tax implications is crucial. By grasping the current overtime tax laws and utilizing available deductions, you can enhance your financial well-being. Remember, as the landscape of overtime taxation evolves, taking these steps can lead to significant savings and a clearer path toward financial security. You're not alone in this journey; we're here to help you navigate it.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is overtime pay?
Overtime pay is the extra compensation earned for working beyond the standard 40-hour workweek, as defined by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA).
How is overtime pay calculated?
Overtime pay is typically calculated at one and a half times (1.5x) your regular hourly wage for any hours worked over 40 in a week. For example, if your regular wage is $20 per hour, your overtime rate would be $30 per hour.
Why is it important to understand overtime pay?
Understanding overtime pay is crucial to ensure fair compensation for your work and to navigate the tax implications associated with those extra earnings.
What changes regarding overtime pay are expected in 2025?
As of 2025, the IRS will introduce new guidelines for reporting and deducting qualified extra pay, although formal guidance on implementation is still pending.
How have salary limits for extra pay eligibility changed?
The salary limit for extra pay eligibility has significantly increased, affecting how individuals should approach their compensation and tax reporting.
Where can I find help regarding my rights and compensation related to overtime pay?
There are resources available to help you understand your rights and ensure you receive the compensation you deserve for overtime work.




