Introduction
Understanding tax obligations can feel overwhelming, especially when you're dealing with significant debt. We understand that this can be a heavy burden to carry. An Offer in Compromise (OIC) might be a solution worth considering, as it allows individuals to settle their tax debts for less than what they owe. However, navigating the path to securing an OIC can be complex, with strict eligibility criteria that may leave you wondering if you qualify.
What are the key factors that determine whether you can successfully navigate this process? And what common pitfalls should you avoid to enhance your chances of acceptance? It's common to feel uncertain, but you're not alone in this journey. We're here to help you understand the steps you can take.
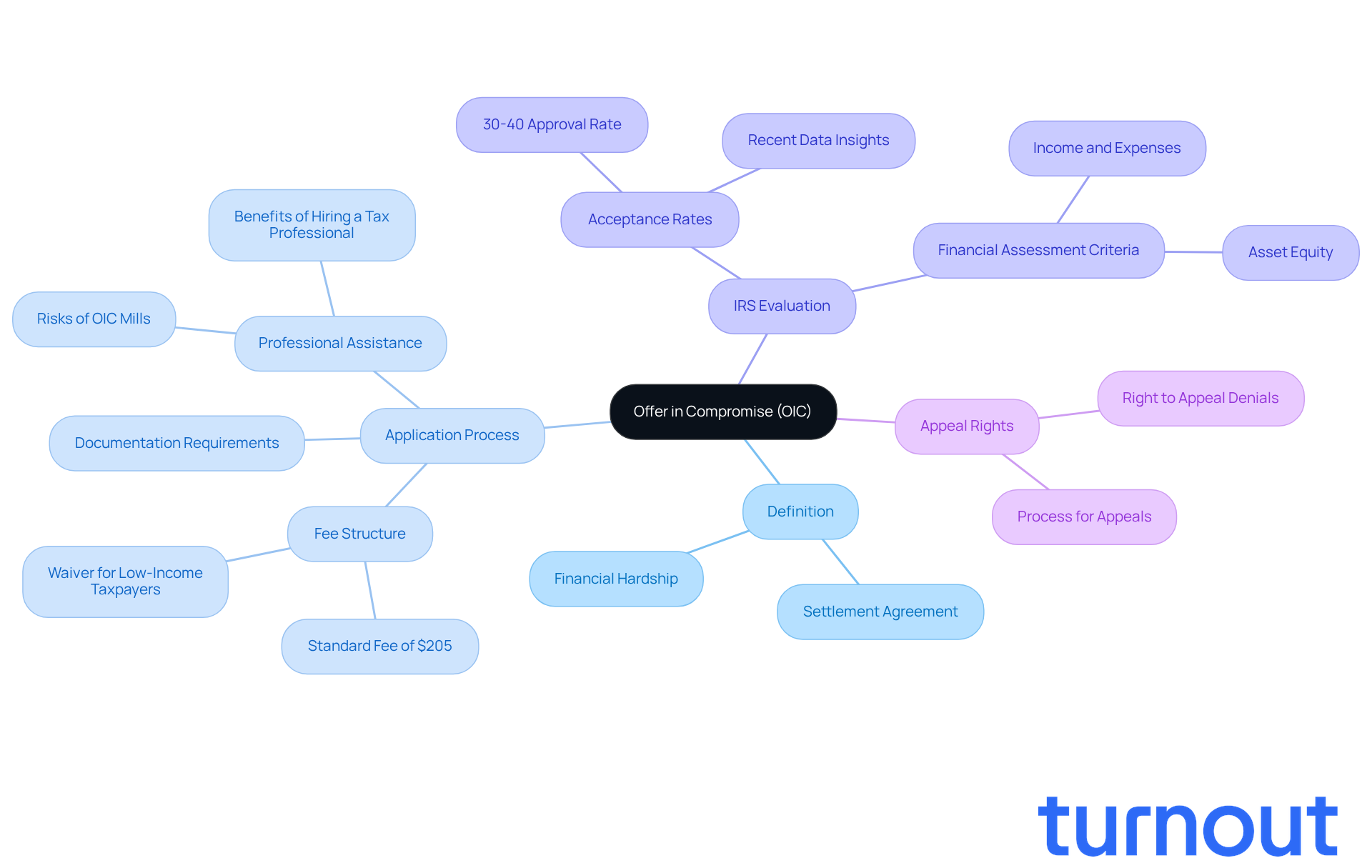
Define Offer in Compromise: Understanding the Basics
For those struggling with tax debt, understanding what is an offer in compromise can be a lifeline. What is an offer in compromise? It’s a settlement agreement between you and the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) that allows you to resolve your tax obligations for less than what you owe. If you’re facing financial hardship and can’t pay your tax liabilities in full, you may be wondering what is an offer in compromise and how it could help you.
Imagine negotiating a lower payment based on your unique financial situation. For those burdened by tax debt, understanding what is an offer in compromise can provide a potential fresh start through the OIC process. In 2025, around 50,000 OIC applications were submitted, with acceptance rates ranging from 30 to 40%. To understand what is an offer in compromise, it's important to know that the IRS carefully evaluates each offer by looking at your individual financial circumstances, including your income, expenses, and asset equity. This thorough assessment helps determine if your proposal is viable.
Applying for an OIC does come with a fee of $205, but don’t worry - if you have a low income, you may qualify for a waiver. Engaging a tax professional can significantly boost your chances of approval. As QMK Consulting wisely states, "A professional ensures your offer is realistic, complete, and compliant, increasing your chances of approval."
If the IRS denies your OIC, remember that you have the right to appeal. This gives you options to advance your case. However, it’s crucial to be cautious of OIC mills that may mislead you about what is an offer in compromise, which could potentially lead to unnecessary expenses and frustration.
You are not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you navigate these challenges and find the best path forward.
Eligibility Requirements for an Offer in Compromise
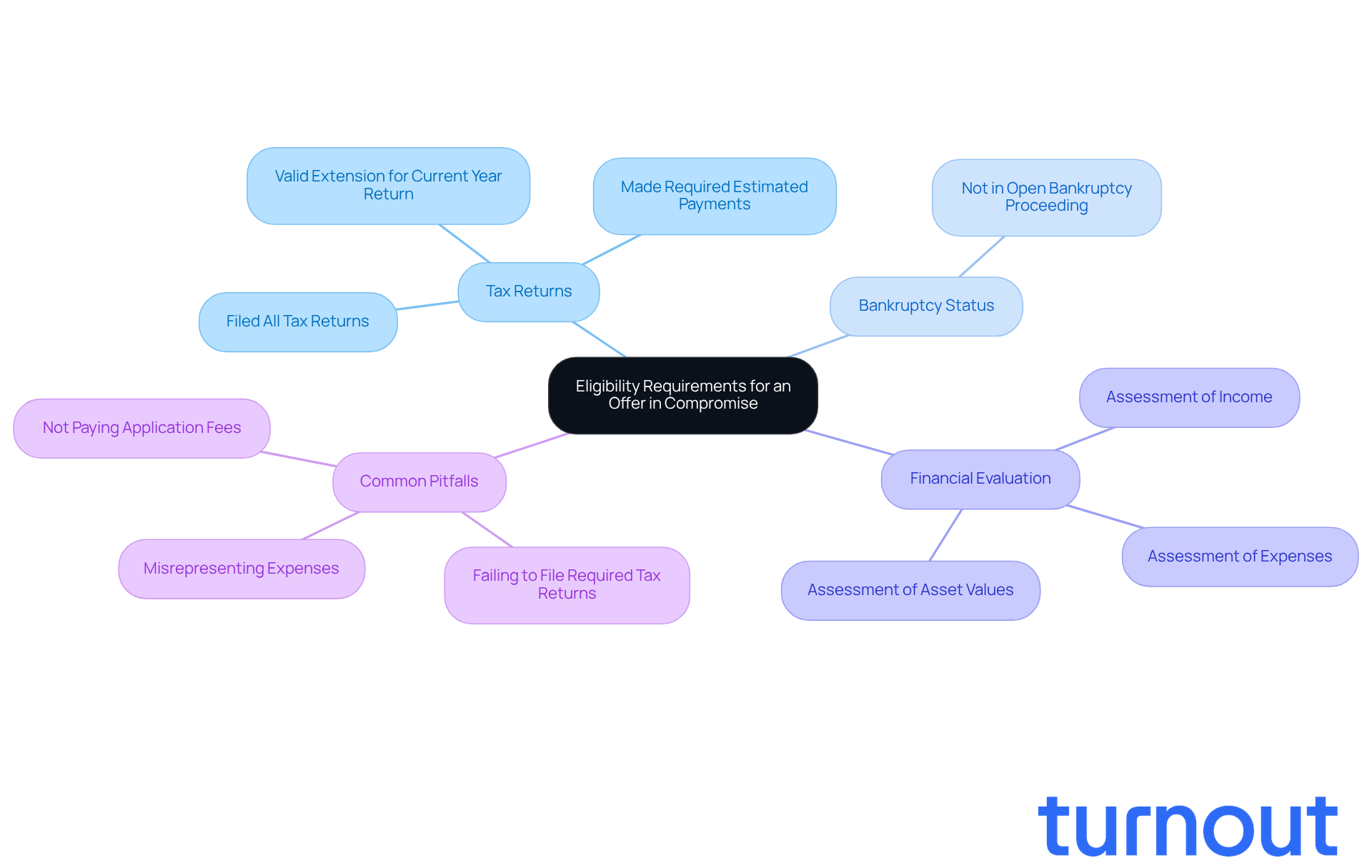
Navigating the process of what is an offer in compromise (OIC) can feel overwhelming, but understanding the eligibility criteria is a crucial first step. To understand what is an offer in compromise, individuals must meet several key requirements. First, it’s essential to have filed all necessary tax returns and made any required estimated tax payments. Additionally, applicants should not be in an open bankruptcy proceeding. The IRS carefully evaluates each person’s financial situation, including income, expenses, and asset values, to assess their ability to pay the full tax obligation. If it appears that an individual can meet their obligations through an installment agreement or other means, the OIC may be denied.
In 2025, it’s estimated that around 30% of individuals will meet the eligibility requirements for an OIC. This statistic highlights the stringent criteria set by the IRS. Tax professionals often stress the importance of thorough documentation and compliance with tax obligations to improve the chances of acceptance. For instance, ensuring that there are no pending tax returns and that all estimated payments are current can make a significant difference. As the IRS advises, confirm you're eligible and prepare a preliminary proposal to understand what is an offer in compromise using the Offer in Compromise Pre-Qualifier Tool.
Understanding these requirements is vital as you assess your likelihood of acceptance. By confirming your eligibility and preparing a preliminary proposal using the IRS Offer in Compromise Pre-Qualifier Tool, you can navigate the complexities of the OIC process with greater confidence. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. It’s also important to be aware of common pitfalls that could lead to rejection, such as failing to file required tax returns or misrepresenting expenses.
We’re here to help you through this process. Take the time to gather your documents and ensure everything is in order. You deserve a chance to find a solution that works for your financial situation.
Determining the Offer Amount: Financial Considerations
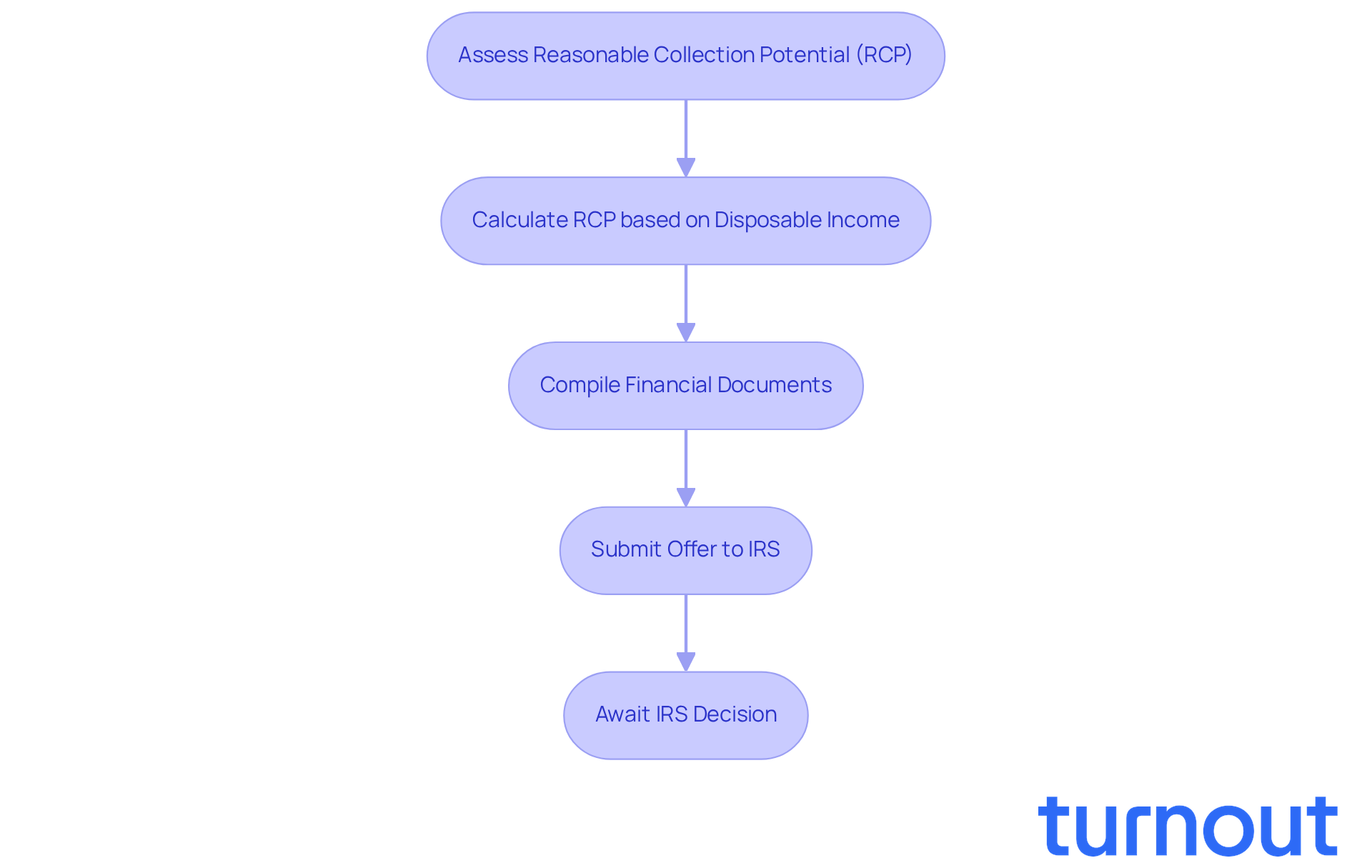
Determining what is an offer in compromise and the right offer amount can feel overwhelming. We understand that navigating this process is challenging, but you’re not alone. To start, it’s essential to assess your 'Reasonable Collection Potential' (RCP), which reflects what the IRS could realistically collect from you. This assessment involves looking at your disposable income and the value of your assets, while allowable expenses are determined by IRS national and local standards.
The IRS generally expects your offer to meet or exceed the RCP. This is calculated by multiplying your monthly disposable income by a specific number of months - 12 for a lump sum offer or 24 for a periodic payment offer. For example, if your monthly disposable income is $1,000, your RCP for a lump sum offer would be $12,000.
It’s crucial to compile all relevant financial documents, such as income statements, asset valuations, and liabilities, to support your offer. The IRS will also consider your individual assets, future income, and allowable expenses when calculating RCP. This includes factors like bank account balances, real estate values, and retirement accounts.
Understanding these financial considerations is vital. Offers that fall below the calculated RCP often lead to discussions about what is an offer in compromise and are likely to be rejected. The competitive nature of the OIC program means that having a well-substantiated case can significantly improve your chances of acceptance, which typically ranges from 30 to 40%. Engaging with tax professionals can greatly enhance your chances of a successful application. They can help ensure that your offers are realistic, complete, and compliant with IRS expectations.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you navigate these complexities with care and support.
Applying for an Offer in Compromise: Step-by-Step Guide
Applying for what is an offer in compromise can feel overwhelming, but we're here to help you navigate this journey. By following these essential steps, you can improve your chances of a successful outcome:
-
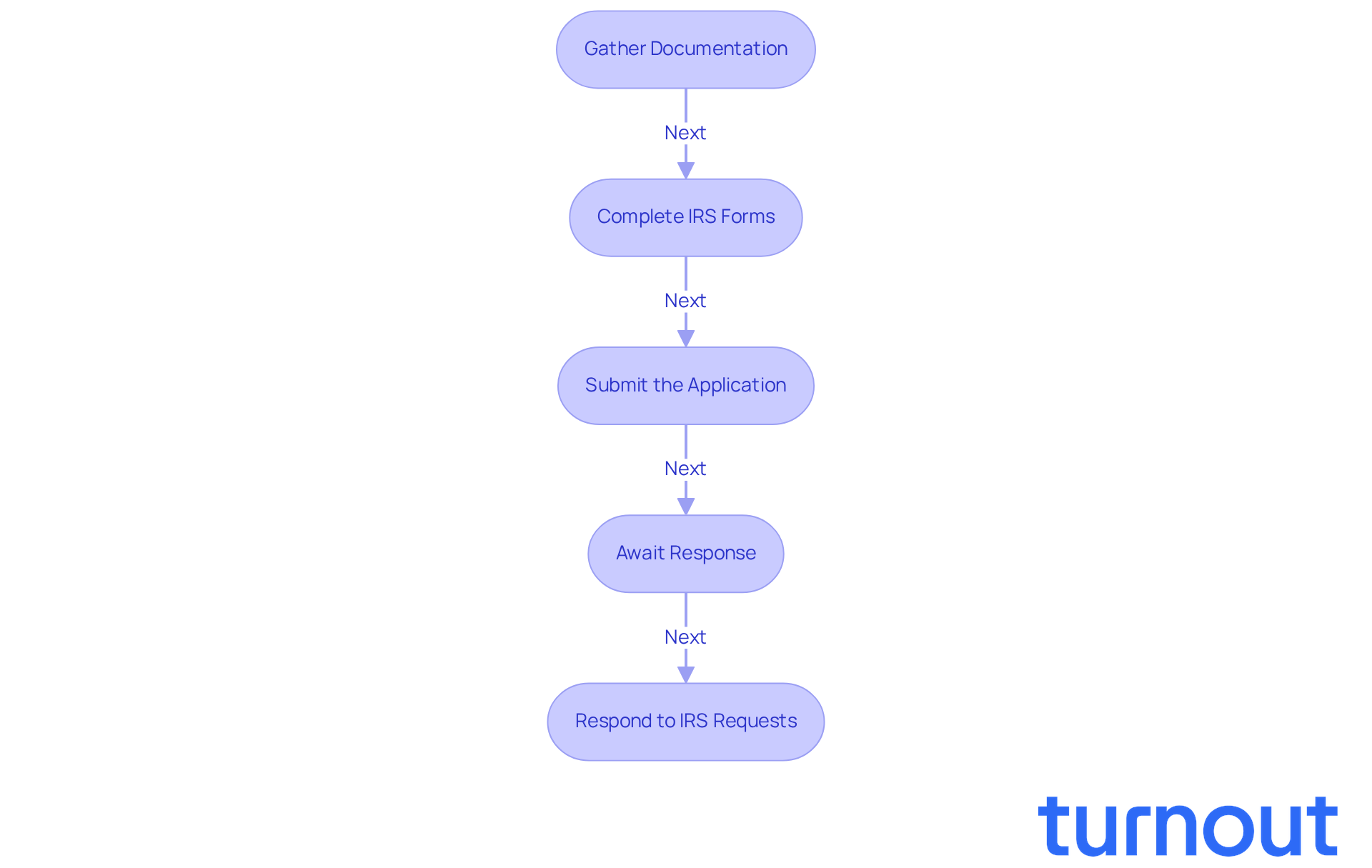
Gather Documentation: Start by collecting all necessary financial documents, such as tax returns, income statements, and asset valuations. Accurate and thorough reporting is crucial, as the IRS closely examines your ability to pay. Many OIC applications are rejected due to incomplete or inaccurate information, so make sure everything is in order.
-
Complete IRS Forms: Next, fill out IRS Form 656 (Offer in Compromise) and Form 433-A (OIC) for individuals or Form 433-B (OIC) for businesses. These forms require detailed financial disclosures, including your monthly income, living expenses, and assets. Remember, you must have filed all required tax returns for the past five years to qualify for the OIC program.
-
Submit the Application: Once your forms are complete, send them along with the required application fee, typically $205 (which may be waived for low-income applicants), to the IRS. Double-check all forms for accuracy to avoid delays or rejections. Keep in mind that the IRS accepts around 30-40% of OIC applications, so careful preparation is key.
-
Await Response: After submission, the IRS will review your application, which usually takes between 6 to 9 months, though it can extend up to 24 months for automatic acceptance. During this time, the IRS may request additional information or clarification, and it’s common to feel anxious while waiting.
-
Respond to IRS Requests: Be ready to provide any further documentation or information the IRS may ask for to support your offer. Prompt and thorough responses can significantly enhance your chances of approval. If your OIC is rejected, remember that you have the option to appeal the decision.
By diligently following these steps, you can improve your likelihood of understanding what is an offer in compromise for a successful application. This process can help you settle your tax debt for less than the full amount owed, giving you a fresh start. You're not alone in this journey, and with the right support, you can find relief.
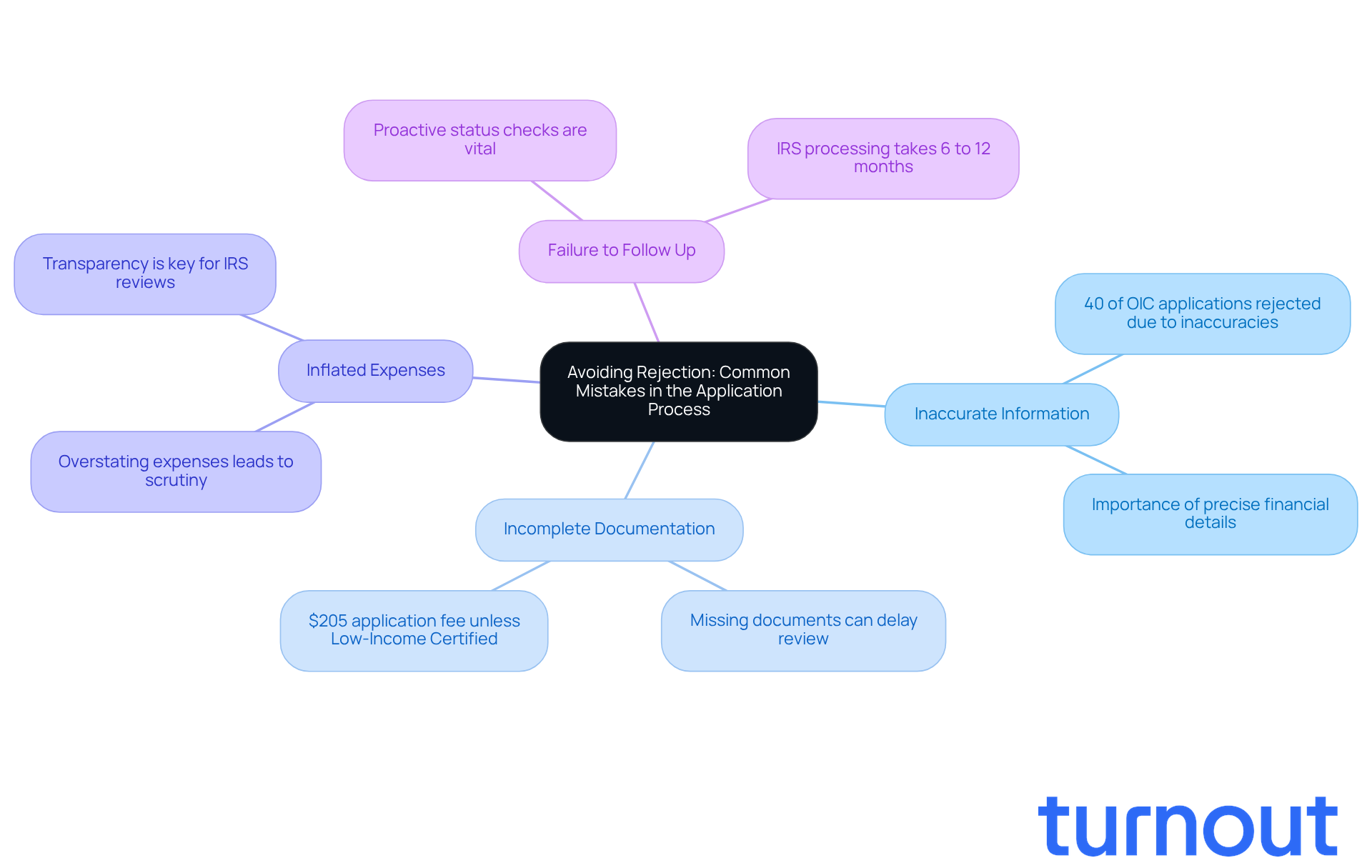
Avoiding Rejection: Common Mistakes in the Application Process
Navigating the process of what is an offer in compromise (OIC) can feel overwhelming, but you’re not alone. To enhance your chances of acceptance, it’s essential to avoid some common pitfalls:
-
Inaccurate Information: Providing precise and complete financial details is crucial. Did you know that in 2025, nearly 40% of OIC applications were rejected due to inaccuracies? This highlights just how important thoroughness is. Remember, less than half of all OIC applications are accepted, so being meticulous can make a real difference.
-
Incomplete Documentation: Make sure you submit all required documents and forms. Missing information can significantly delay the review process or even lead to outright rejection. The IRS requires a $205 application fee unless you qualify for Low-Income Certification, which is an important consideration for many taxpayers.
-
Inflated Expenses: It’s tempting to overstate expenses or hide assets, but this can lead to increased scrutiny from the IRS. Transparency is key; the IRS conducts thorough reviews to verify financial claims, so honesty is the best policy.
-
Failure to Follow Up: After submitting your application, it’s vital to stay proactive. Checking in with the IRS about your application’s status can help keep things on track. Timeliness is critical; missing deadlines can jeopardize your chance for tax relief. The IRS typically takes 6 to 12 months to process an OIC, so understanding this timeline can help set realistic expectations.
By being diligent and meticulous, you can significantly improve your chances of a successful application by understanding what is an offer in compromise. We understand that the process can be frustrating, but with careful attention to detail, you can avoid the disappointment of rejection and the need for reapplication. Remember, we’re here to help you through this journey.
Conclusion
Understanding what an offer in compromise (OIC) entails is crucial for anyone grappling with tax debt. We know how overwhelming this situation can feel. This settlement agreement with the IRS offers a potential pathway to resolve tax obligations for less than the total amount owed, providing a chance for a fresh financial start. By grasping the intricacies of the OIC process, you can better navigate your options and seek relief from those burdensome tax responsibilities.
Throughout this article, we’ve highlighted key points that matter to you. These include:
- The eligibility requirements
- The importance of accurately assessing your financial situation
- The steps involved in applying for an OIC
It’s essential to file all necessary tax returns, provide complete documentation, and ensure that your financial claims are truthful. This honesty can help you avoid common pitfalls that might lead to rejection. Engaging a tax professional can significantly enhance your chances of approval, given their expertise in navigating the complexities of the IRS's evaluation process.
Ultimately, the offer in compromise serves as a vital tool for those facing financial hardship. It’s not just a means of settling tax debt; it’s a significant opportunity for you to reclaim control over your financial future. Taking proactive steps to understand and engage with the OIC process can lead to a more manageable financial situation. If you’re considering this option, remember that thorough preparation and honest representation of your financial circumstances are essential for success. You are not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an offer in compromise (OIC)?
An offer in compromise is a settlement agreement between you and the IRS that allows you to resolve your tax obligations for less than the total amount owed, particularly if you are facing financial hardship.
How does the IRS evaluate an offer in compromise?
The IRS evaluates each offer by examining your individual financial circumstances, including your income, expenses, and asset equity, to determine if your proposal is viable.
What are the costs associated with applying for an offer in compromise?
Applying for an offer in compromise comes with a fee of $205, but individuals with low income may qualify for a fee waiver.
How can a tax professional assist with an offer in compromise?
Engaging a tax professional can significantly increase your chances of approval by ensuring that your offer is realistic, complete, and compliant with IRS requirements.
What should I do if my offer in compromise is denied?
If your offer in compromise is denied, you have the right to appeal the decision, which provides options to advance your case.
What are the eligibility requirements for an offer in compromise?
To be eligible for an offer in compromise, you must have filed all necessary tax returns, made required estimated tax payments, and not be in an open bankruptcy proceeding.
What percentage of individuals are estimated to meet the eligibility requirements for an OIC in 2025?
It is estimated that around 30% of individuals will meet the eligibility requirements for an offer in compromise in 2025.
How can I prepare for the offer in compromise process?
Confirm your eligibility, ensure all tax returns are filed and payments are current, and consider using the IRS Offer in Compromise Pre-Qualifier Tool to prepare a preliminary proposal.
What common pitfalls should I avoid when applying for an offer in compromise?
Common pitfalls include failing to file required tax returns and misrepresenting expenses, which could lead to rejection of your application.




