Introduction
Navigating the complexities of tax penalties can be daunting for many taxpayers. We understand that these penalties not only serve as a deterrent against non-compliance but also underscore the importance of following tax regulations. Ignoring these can significantly impact your financial health. As the tax code evolves, the stakes get higher. You might be wondering: how can you effectively manage your tax responsibilities to avoid the growing consequences of penalties?
It's common to feel overwhelmed by the intricacies of tax laws. But remember, you're not alone in this journey. There are ways to navigate these challenges with confidence. By staying informed and proactive, you can protect your financial well-being and avoid unnecessary penalties.
We’re here to help you understand your options and take control of your tax situation. Together, we can work towards a more secure financial future.
Define Tax Penalty: Understanding the Basics
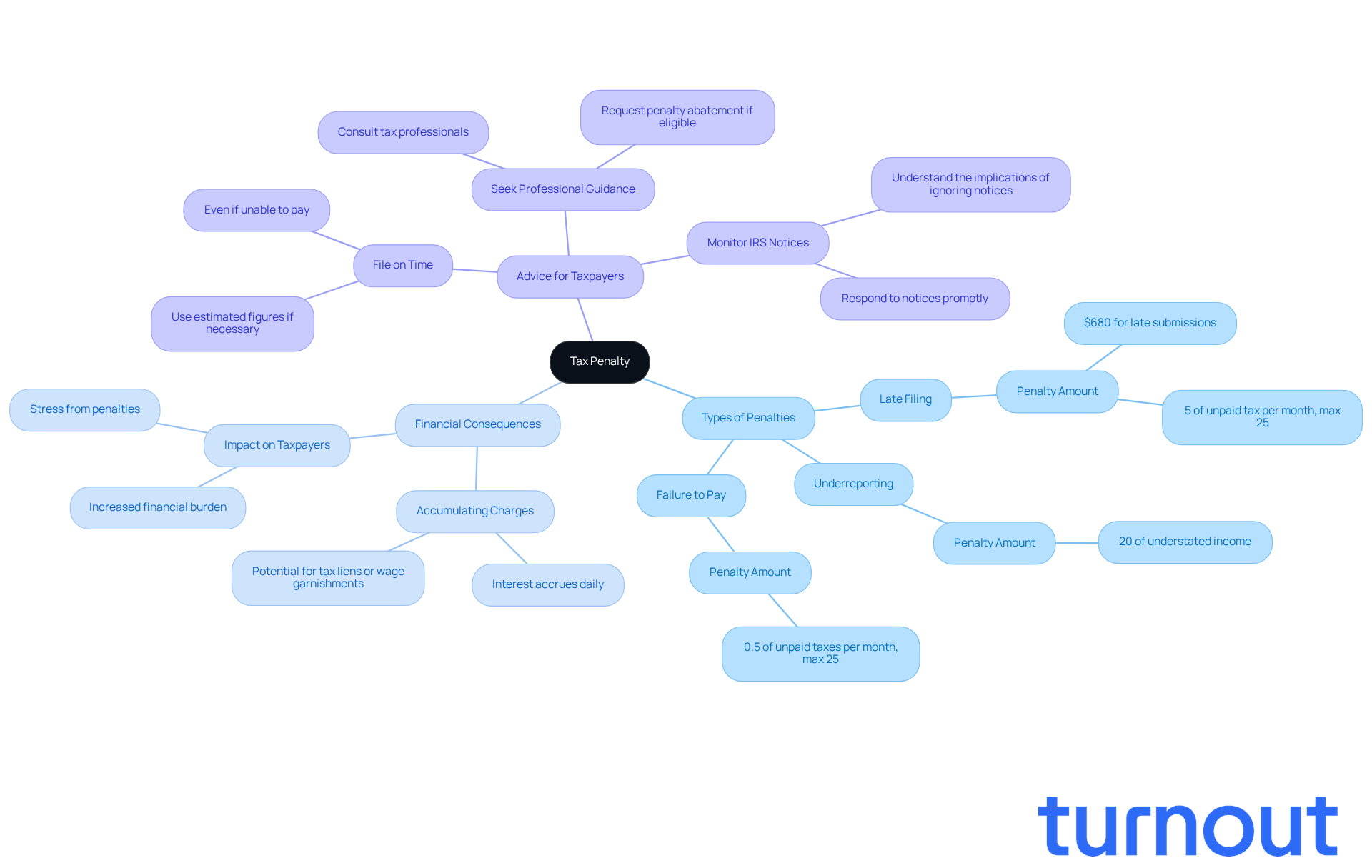
A tax charge can feel overwhelming, can't it? When individuals don’t follow tax regulations, a tax penalty is the financial consequence imposed by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or state tax authorities. This might happen if you miss the deadline to file your tax return, fail to pay what you owe, or underreport your income. These fines are meant to encourage compliance, but they can also add stress to your financial situation.
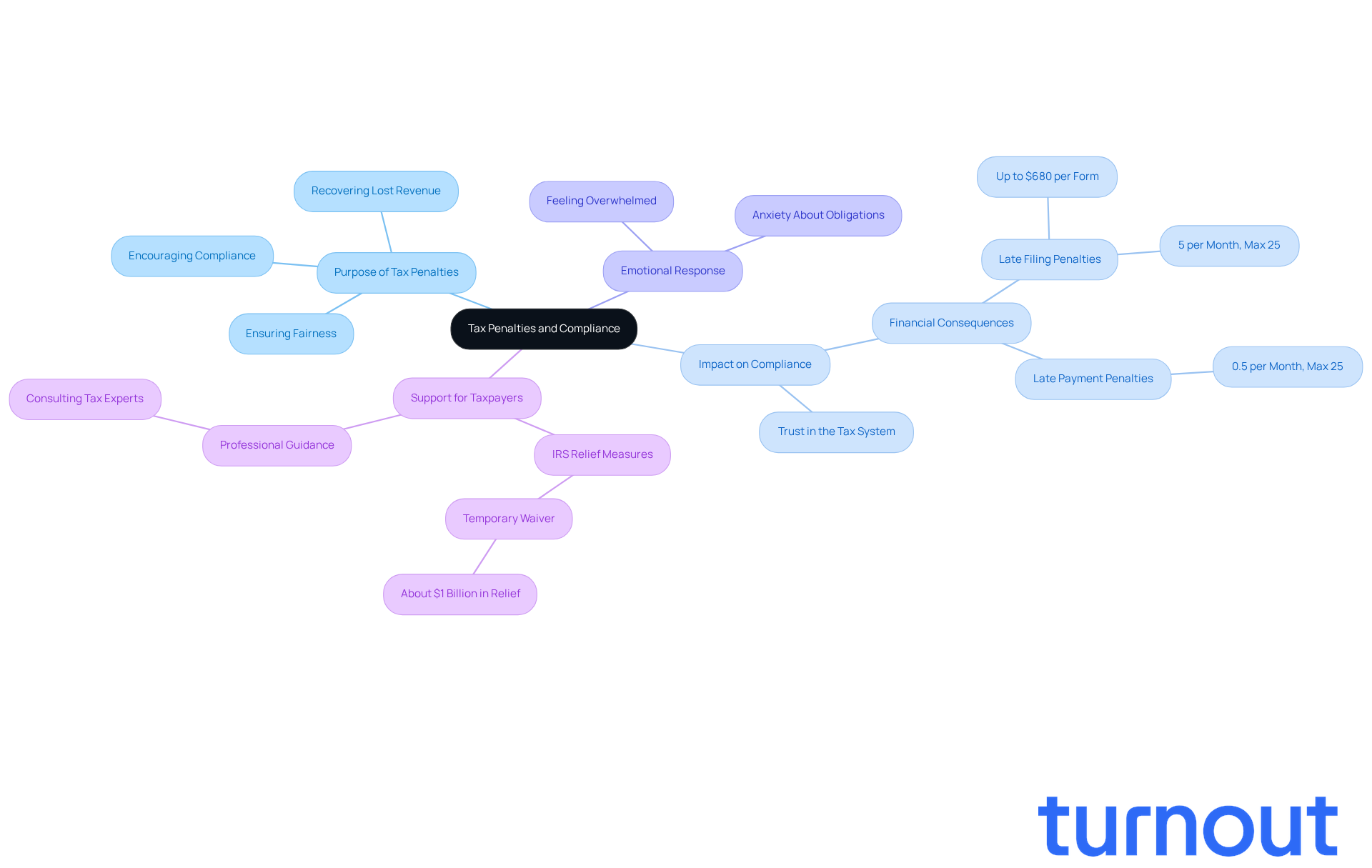
The seriousness of these sanctions varies. For instance, during the 2026 tax-filing season, the IRS may impose fines of up to $680 per form for late submissions. If you underreport your income, the charges can reach as high as 20% of the amount you understated. Additionally, if you fail to file on time, you could face a fee of 5% of the unpaid tax for each month your return is overdue, capping at 25%. These fines can accumulate quickly, leading to significant financial repercussions.
For anyone who pays taxes, understanding what a tax penalty is crucial. The financial burden can grow rapidly, resulting in larger sums owed due to accumulating charges and interest. Imagine delaying your submission and watching your bill increase significantly because of fines. It really highlights the importance of timely action.
We understand that navigating these complexities can be daunting. Seeking guidance from tax professionals, like enrolled agents such as Josh Youngblood, can make a difference. They can help you understand your obligations and mitigate potential financial burdens. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Contextualize Tax Penalties: Importance in Tax Compliance
Tax sanctions are more than just penalties; they help us understand what is a tax penalty and play a vital role in our tax compliance landscape. We understand that navigating tax laws can be overwhelming, and to clarify what is a tax penalty, these sanctions are designed to encourage compliance, helping you meet your obligations with confidence.
To understand what is a tax penalty, one must recognize that the IRS imposes fines not only to recover lost revenue but also to ensure fairness within our tax system. When individuals don’t adhere, it can lead to a loss of trust in the system and unfair advantages for those who evade their responsibilities.
It’s common to feel anxious about tax obligations, but recognizing the significance of these sanctions can help you appreciate the importance of compliance. By understanding what is a tax penalty related to overlooking your tax duties, you can take proactive steps to stay on track. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you navigate these challenges and ensure you meet your obligations with ease.
Trace the Origins: Evolution of Tax Penalties
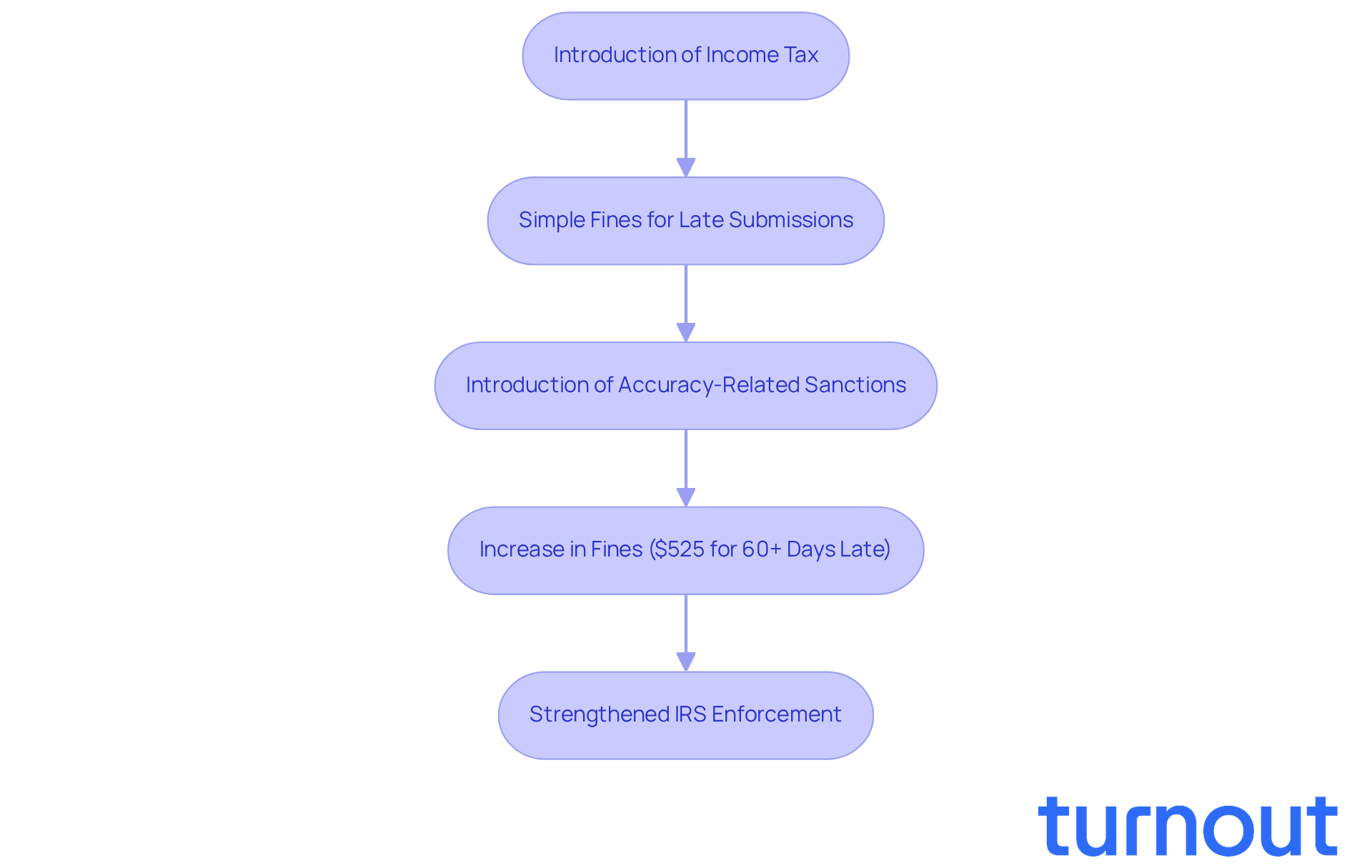
The landscape of tax consequences has changed quite a bit since income tax was first introduced in the United States. Initially, fines were straightforward, mainly focusing on late submissions and payments. But as the tax code grew more complex, so did the consequences for non-compliance.
We understand that navigating these changes can be overwhelming. Over the years, the IRS has rolled out various sanctions, like accuracy-related and underpayment sanctions, to tackle specific compliance issues. For instance, did you know that the lowest fine for individual filers who submit returns more than 60 days late has jumped to $525 in 2025? This increase highlights the growing scrutiny on tax responsibilities.
It's common to feel anxious about these evolving tax laws. This evolution reflects the government's commitment to ensuring individuals comply with tax laws while adapting to the complexities of modern financial systems. The IRS's enforcement capabilities have also been strengthened by significant funding increases from the Inflation Reduction Act in 2022, allowing for more thorough compliance measures.
Moreover, when considering non-compliance, it is important to understand what is a tax penalty, as the implications can be serious. Sanctions for tax preparers and the potential for criminal prosecution for tax evasion under USC §7201 further emphasize the importance of understanding these evolving tax consequences. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. We're here to help you navigate these complexities.
Identify Key Characteristics: Types and Scenarios of Tax Penalties
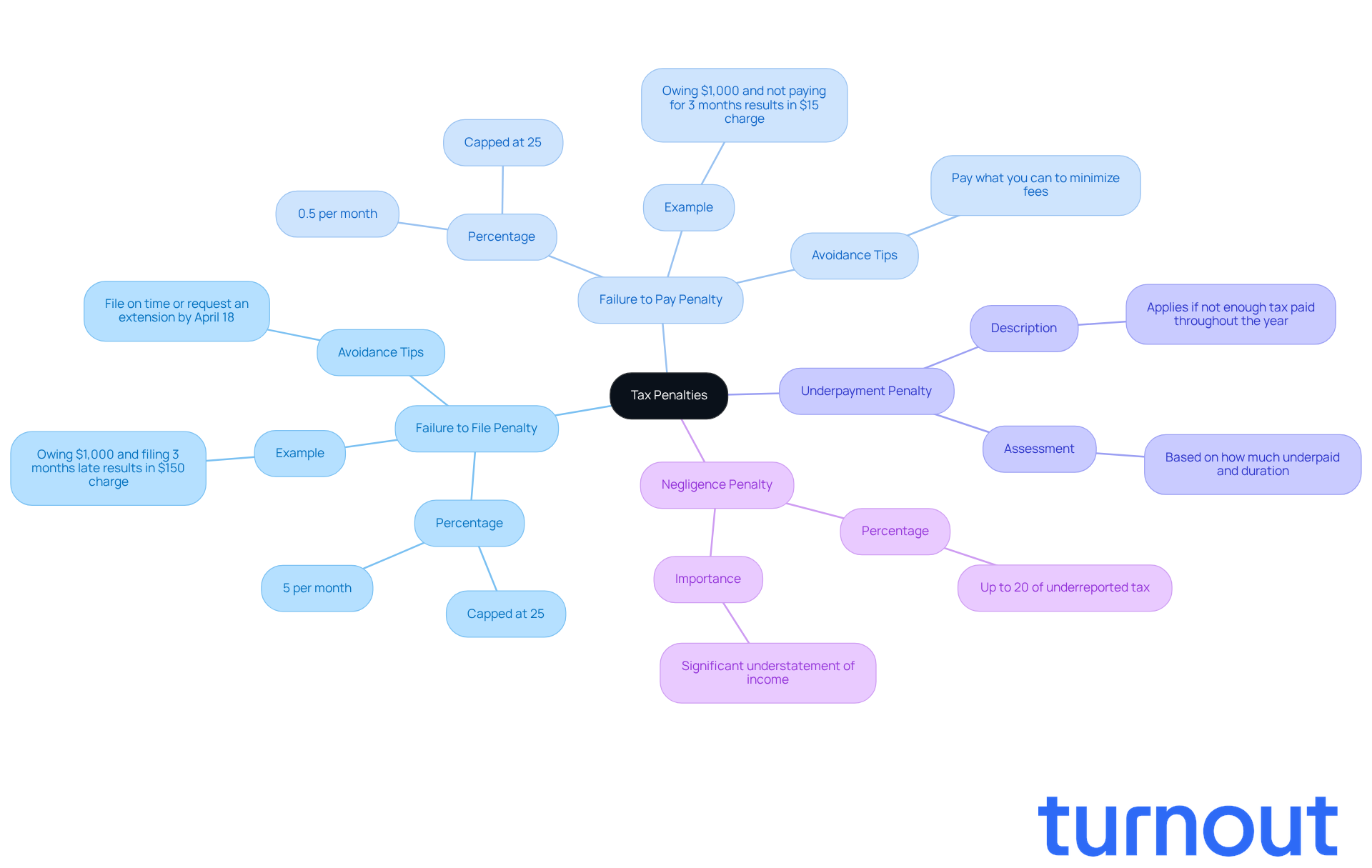
Tax fines can feel overwhelming, and understanding what is a tax penalty is crucial for effectively managing your responsibilities. Let’s break down the key types of penalties you might encounter:
-
Failure to File Penalty: If you miss the deadline to file your tax return, you could face a penalty of 5% of the unpaid tax for each month your return is late, up to a maximum of 25%. For example, if you owe $1,000 and file three months late, that’s a $150 charge. To avoid this, make sure to file your return or request an extension by April 18.
-
Failure to Pay Penalty: This occurs when you don’t pay your taxes by the due date. It’s typically 0.5% of the unpaid tax for each month it remains unpaid, also capped at 25%. So, if you owe $1,000 and don’t pay for three months, you’ll incur an additional $15. If you can’t pay your full tax amount by April 18, try to pay what you can to minimize fees and interest.
-
Underpayment Penalty: This applies if you haven’t paid enough tax throughout the year, often due to insufficient withholding or estimated payments. The IRS assesses this based on how much you underpaid and for how long.
-
Negligence Penalty: If you significantly understate your income or are negligent in reporting, it is important to understand what is a tax penalty, which could be up to 20% of the underreported tax.
We understand that navigating these fines can be stressful. Recent IRS updates emphasize the importance of timely filing and payment to help reduce what is a tax penalty. Even if you can’t pay in full, filing on time is essential to avoid additional costs. Remember, if you can demonstrate reasonable cause for not meeting your tax obligations, you may qualify for penalty relief.
You are not alone in this journey. The Taxpayer Advocate Service is here to help you through these challenges. Don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance.
Conclusion
Understanding tax penalties is crucial for anyone navigating the financial landscape. These penalties aren’t just consequences for non-compliance; they’re also mechanisms to encourage adherence to tax laws. We understand that the implications of failing to meet tax obligations can be severe, leading to financial burdens that can quickly spiral out of control. Recognizing the importance of timely filing and payment can help ease the stress and consequences associated with tax penalties.
Throughout this article, we’ve highlighted key points, including various types of tax penalties like:
- Failure to file
- Failure to pay
- Underpayment penalties
The evolution of these penalties reflects the increasing complexity of tax laws and the IRS's commitment to ensuring compliance. By understanding these aspects, you empower yourself to take proactive measures, such as seeking professional assistance, to navigate your responsibilities effectively.
It’s essential to stay informed about your tax obligations and the potential penalties for non-compliance. By prioritizing timely action and seeking guidance when needed, you can avoid unnecessary financial strain and contribute to a fairer tax system. Engaging with resources like the Taxpayer Advocate Service can provide support and clarity, ensuring that you can meet your obligations with confidence and ease. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a tax penalty?
A tax penalty is a financial consequence imposed by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) or state tax authorities when individuals do not follow tax regulations, such as missing the deadline to file a tax return, failing to pay owed taxes, or underreporting income.
What are common reasons for incurring a tax penalty?
Common reasons for incurring a tax penalty include late filing of tax returns, failure to pay taxes owed, and underreporting income.
How serious can tax penalties be?
Tax penalties can be significant; for example, the IRS may impose fines of up to $680 per form for late submissions during the 2026 tax-filing season. Underreporting income can lead to charges as high as 20% of the understated amount, and failing to file on time can result in a fee of 5% of the unpaid tax for each month the return is overdue, capped at 25%.
How quickly can tax penalties accumulate?
Tax penalties can accumulate quickly, leading to significant financial repercussions as fines and interest increase over time.
Why is it important to understand tax penalties?
Understanding tax penalties is crucial because the financial burden can grow rapidly, resulting in larger sums owed due to accumulating charges and interest, emphasizing the importance of timely action.
How can individuals navigate tax penalties effectively?
Individuals can navigate tax penalties effectively by seeking guidance from tax professionals, such as enrolled agents, who can help them understand their obligations and mitigate potential financial burdens.




