Overview
Not filing your taxes can lead to significant penalties, and we understand how overwhelming that can feel. Fines may accumulate to 25% of the tax owed, and you could potentially lose refunds or credits that you rely on. It's important to know that the IRS not only imposes these financial penalties but may also file a substitute return on your behalf. This could result in higher tax liabilities, which can have long-term impacts on your financial health. You might face difficulties in obtaining loans and increased scrutiny on future filings.
We want you to know that you're not alone in this journey. Many people experience similar challenges, and there are solutions available. Taking action now can help you regain control of your financial situation. If you're feeling uncertain, remember that seeking assistance can make a significant difference. We're here to help you navigate these complexities and find a path forward.
Introduction
Neglecting to file taxes can lead to serious implications that go beyond financial penalties. We understand that the thought of dealing with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) can be daunting. The IRS imposes hefty fines and interest on unpaid taxes, which can quickly spiral out of control, leaving you in a precarious financial situation.
This article delves into the critical consequences of failing to file taxes. It highlights:
- Potential loss of refunds
- Increased scrutiny on future filings
- Long-term impact on your credit score and financial stability
What happens if you simply forget to file your taxes? The answer may reveal unexpected challenges that could haunt you for years to come. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help you navigate these challenges.
Define the Consequences of Not Filing Taxes
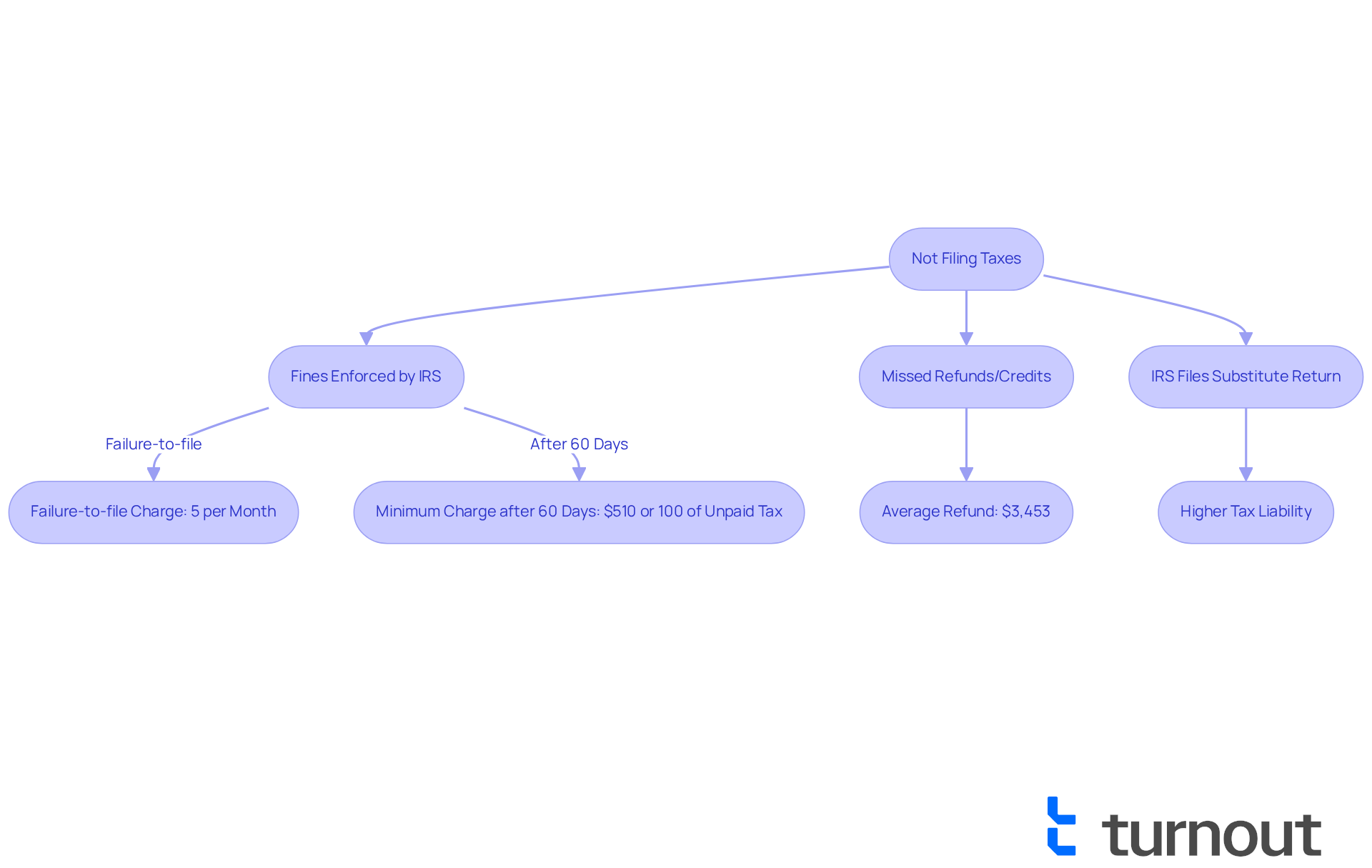
Not filing taxes can lead to serious consequences, and we understand what happens if you forgot to file taxes can be quite overwhelming. Primarily, fines enforced by the IRS can weigh heavily on your mind. The failure-to-file charge is typically 5% of the outstanding tax for each month or part of a month that the return is delayed, with a maximum limit of 25% of the total tax due. If you find yourself unable to submit your return for over 60 days after the deadline, you might be concerned about what happens if you forgot to file taxes, as the minimum charge can rise to $510 or 100% of the unpaid tax, whichever is lower.
For instance, if you owe $1,000 and submit your return two months late, you could face a fee of $100, which could increase to $250 if you remain unfiled for five months. Additionally, it’s important to recognize what happens if you forgot to file taxes, as you may miss out on potential refunds or credits that could have been claimed had you filed on time. The average refund amount American taxpayers received in the 2025 filing season is $3,453, a significant amount that highlights what you might forfeit by not filing promptly.
The IRS typically issues more than 90% of refunds within 21 days, but this process can be delayed for non-filers. Furthermore, what happens if you forgot to file taxes is that the IRS may file a substitute return on your behalf, often disregarding deductions or credits, resulting in a higher tax liability than necessary. This can lead to further financial strain, especially if you are already facing challenges in navigating the tax system.
It's essential to know that you can avoid fines by submitting and paying your taxes by the deadline. If there are valid reasons for your delayed submission, the IRS may waive the fines. Additionally, you can seek a six-month extension to submit, which can alleviate some of the urgent worries regarding fines. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help you navigate these challenges.
Examine Penalties and Interest for Late Filing
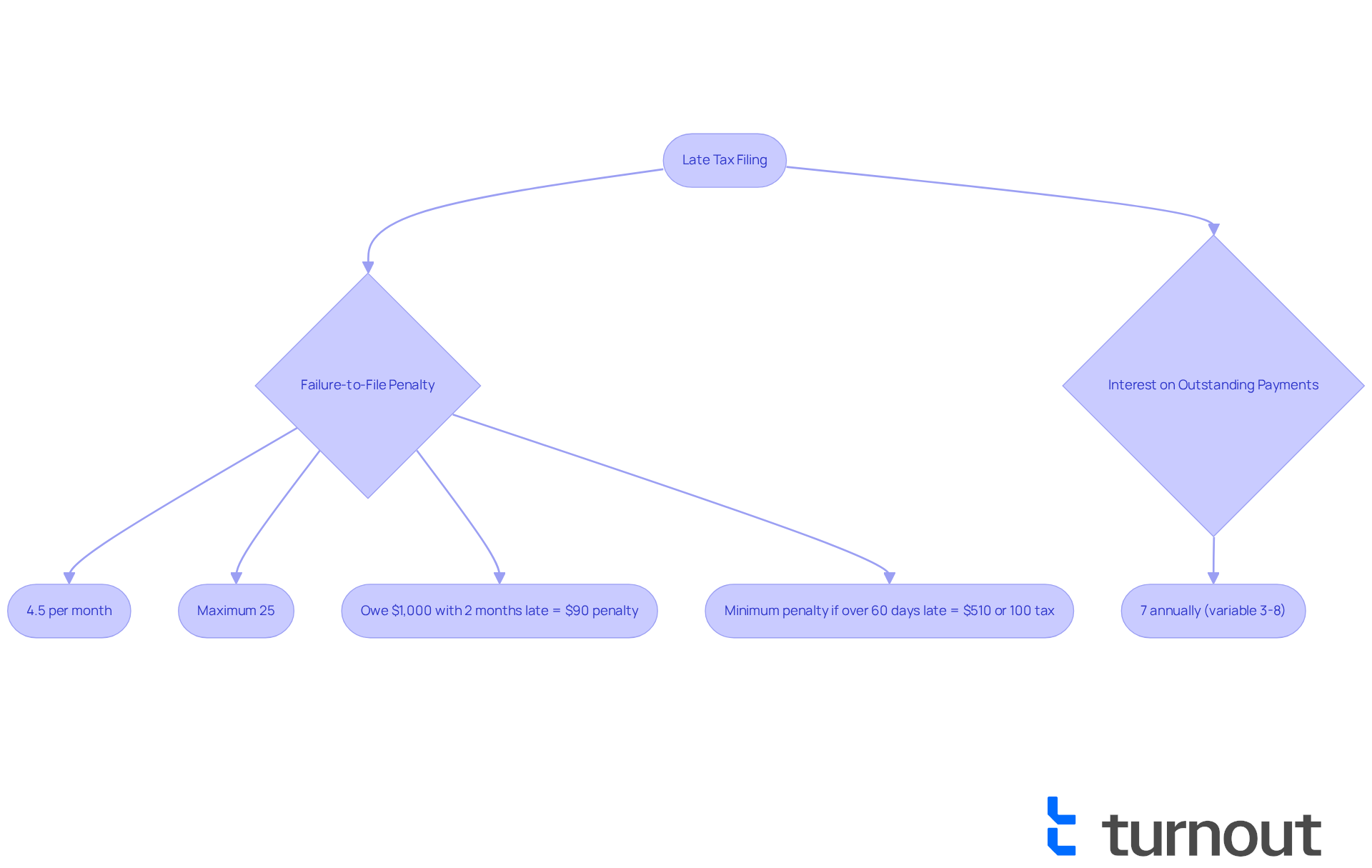
We understand that dealing with tax filings can be overwhelming, particularly when you think about what happens if you forgot to file taxes. When thinking about what happens if you forgot to file taxes, it's crucial to understand that the IRS enforces both fees and interest on the outstanding sum after the deadline, which can add to your worries. The failure-to-file penalty starts at 4.5% of the unpaid tax for each month the return is late, capping at a maximum of 25%. Moreover, the IRS imposes interest on any outstanding payments, compounded daily, which can significantly increase your financial burden.
Starting in 2025, the interest rate for outstanding payments is set at 7% annually, but it may vary between 3% and 8%. This means that taxpayers not only face fines but also see their owed amounts grow due to accumulating interest. For instance, if you owe $1,000 and submit your filing two months overdue, you would incur a charge of $90 (4.5% for the first month and 4.5% for the second month) along with interest. This leads to a total obligation that exceeds the initial amount due.
If your return is over 60 days late, the minimum penalty is $510 or 100% of the tax required to be shown on the return, whichever is less. Understanding these financial implications is crucial to avoid falling into a cycle of debt with the IRS, particularly in light of what happens if you forgot to file taxes. Remember, the IRS imposes interest on outstanding amounts from the due date until the obligation is fully settled. This highlights the importance of prompt filing and payment. You're not alone in this journey; we're here to help you navigate these challenges.
Impact on Future Tax Filings
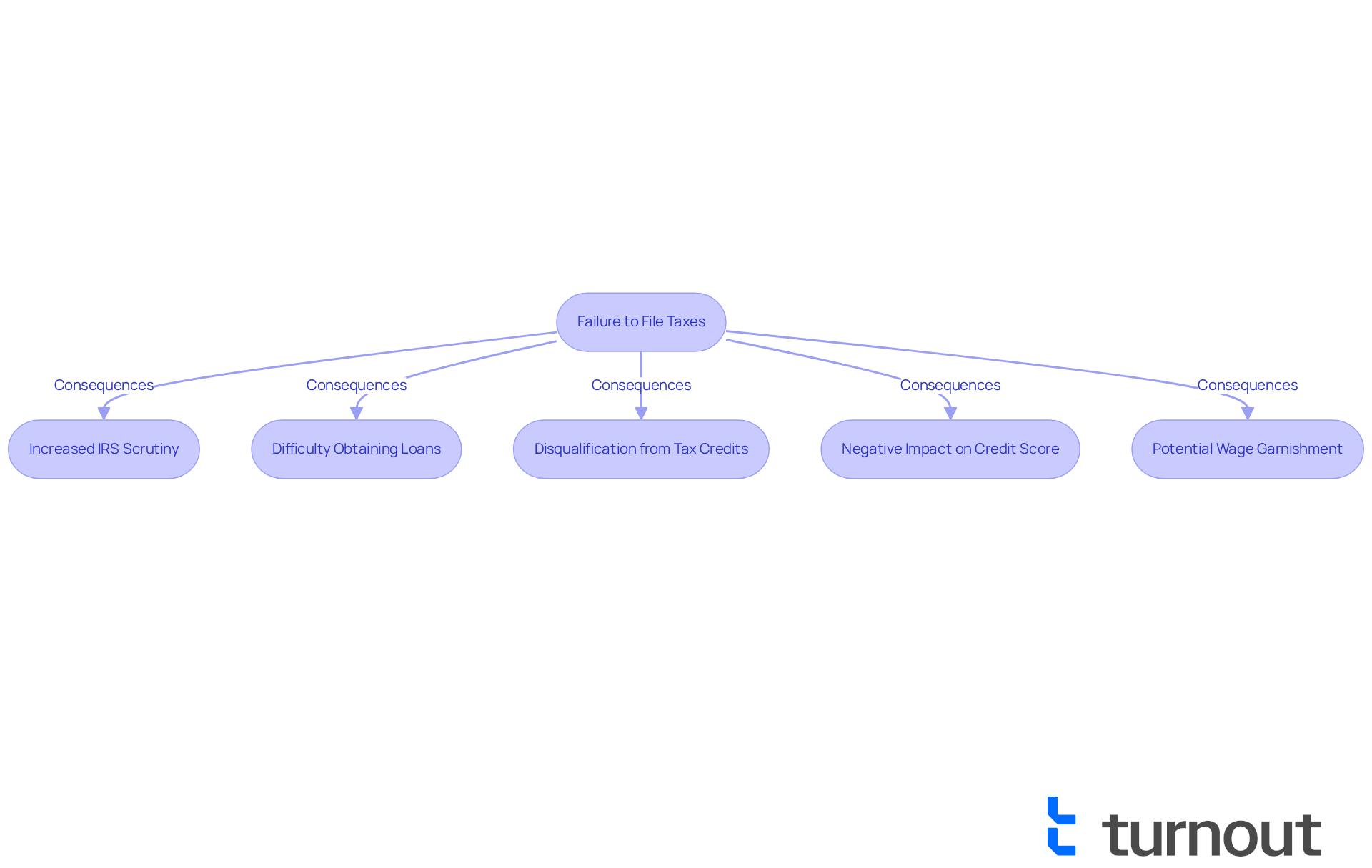
If you are wondering what happens if you forgot to file taxes, it can lead to significant and lasting repercussions on your future tax obligations. We understand that navigating tax responsibilities can be overwhelming. Once a pattern of non-filing is established, the IRS is likely to examine subsequent submissions more rigorously. This heightened scrutiny may result in audits or additional penalties if any discrepancies are identified.
Moreover, individuals with unsubmitted filings often face challenges in obtaining financial products, such as loans or mortgages. Lenders typically require evidence of tax compliance. For instance, small business proprietors may find that banks and SBA lenders view unfiled tax documents as a sign of mismanagement, which can hinder their ability to secure essential funding for expansion.
Additionally, unsubmitted filings can disqualify taxpayers from specific tax credits or benefits in future years, complicating their financial situation even further. It's crucial to recognize what happens if you forgot to file taxes, as the ramifications can extend beyond immediate penalties and potentially impact your financial stability for years to come.
To restore good standing, the IRS usually requires individuals to submit the last six years of financial submissions. Unfiled obligations can also adversely affect personal credit, as IRS liens become part of public records, leading to higher interest rates and lower credit limits. Ignoring tax issues can result in wage garnishment or bank account levies, further disrupting your financial stability.
As Joe Serrone pointed out, outstanding tax obligations can significantly harm your financial future. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. It's vital to resolve unsubmitted tax filings swiftly. We're here to help you navigate these challenges and find a way forward.
Options for Addressing Unfiled Taxes
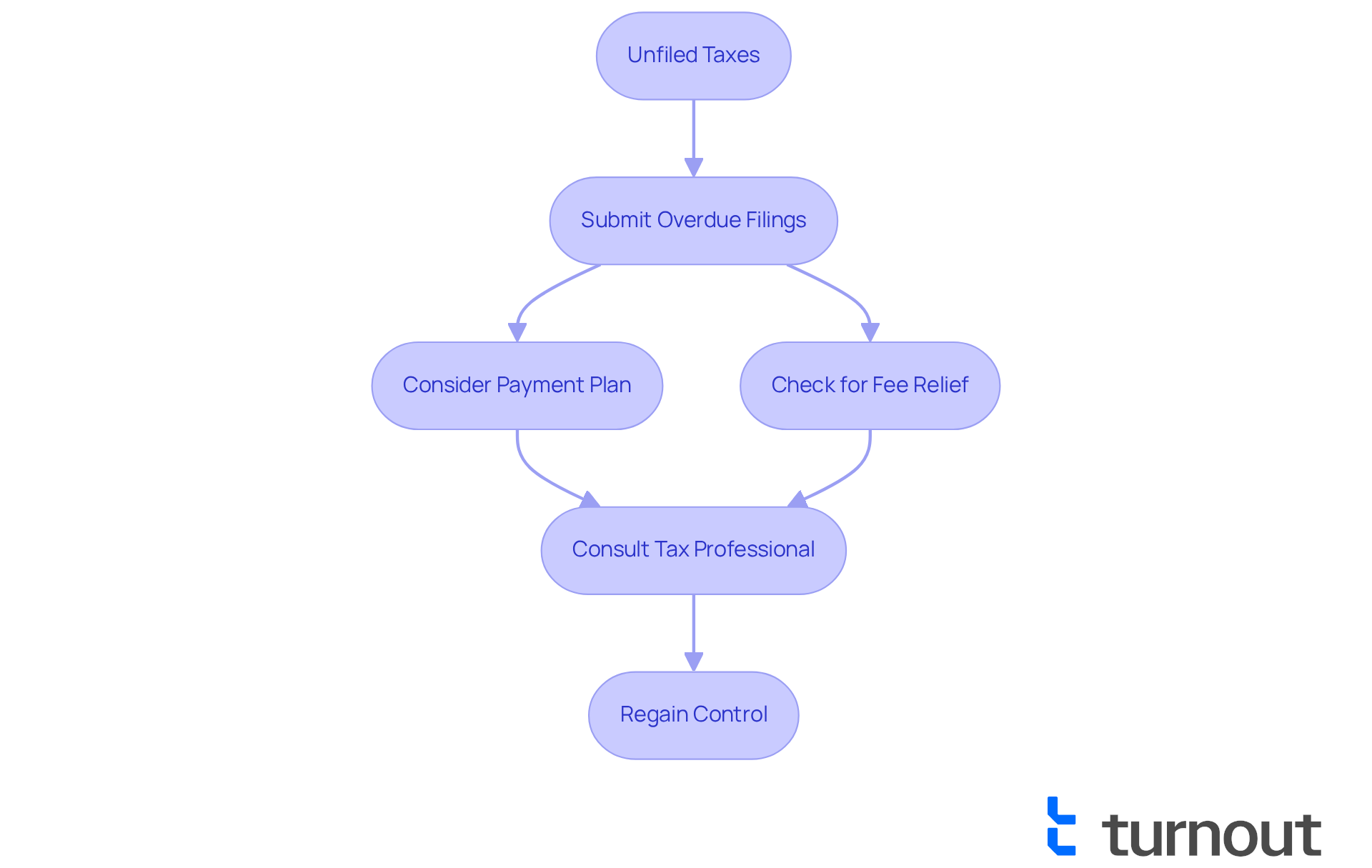
If you haven't filed your taxes, it's crucial to consider what happens if you forgot to file taxes, as you have several options to effectively address this situation. The first step is to submit your overdue filings as quickly as possible, even if you can't pay the total amount owed right now. Filing a return can significantly reduce fines and interest, as the failure-to-file penalty is usually harsher than the failure-to-pay fee. In fact, the IRS imposes a late-filing fee of 5% per month, with a maximum charge of 25%.
We understand that managing tax debt can be overwhelming, which is why it's important to consider setting up a payment plan with the IRS. They offer various installment agreements that allow you to pay your tax liabilities in manageable monthly payments, helping you avoid unwanted collection actions. For instance, if you owe $100,000 or less, you can request a short-term payment plan that allows you to pay within 180 days.
Additionally, you may qualify for fee relief under certain circumstances, such as being a first-time noncompliant taxpayer or facing financial hardship. If you have consistently filed and paid your taxes on time in the past, you might be eligible for initial fee relief, which can ease some of the financial burden you're experiencing.
Seeking assistance from knowledgeable advocates can also provide valuable support in navigating the complexities of tax compliance and addressing any outstanding issues. We encourage you to consult with a tax professional who can help you explore your options and ensure your filings are accurate.
It's crucial to remember what happens if you forgot to file taxes, since neglecting state filings can lead to penalties, even if a refund is due. If you don't file your taxes within three years of the due date, what happens if you forgot to file taxes is that you risk losing any potential tax refund. Taking action sooner rather than later can save you money and prevent unnecessary legal headaches. The IRS is generally more lenient with voluntary filings of past-due returns.
By filing promptly and exploring available options, you can regain control over your tax situation and avoid further complications. Remember, you're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help.
Conclusion
Not filing taxes can lead to serious repercussions that go beyond immediate financial penalties. We understand that navigating tax responsibilities can be overwhelming, and recognizing the consequences of forgetting to file is crucial. This article highlights how failing to submit tax returns on time can result in significant fines, missed refunds, and long-term financial challenges that may affect your overall stability.
The key points discussed include:
- The escalating penalties imposed by the IRS, which can accumulate quickly, resulting in a heavier financial burden due to both fines and interest.
- It's common to feel anxious about your situation, but it's important to file even if payment cannot be made immediately. Doing so can help mitigate harsher penalties.
- The potential impact on future tax filings, credit scores, and access to financial products underscores the need for timely compliance.
Ultimately, addressing unfiled taxes promptly is essential to avoid further complications and regain control over your financial situation. Seeking assistance from tax professionals can provide valuable guidance in navigating these challenges. Remember, taking proactive steps not only helps in resolving current issues but also paves the way for a more secure financial future. You are not alone in this journey, and staying on top of your tax obligations is key to achieving peace of mind.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the consequences of not filing taxes?
Not filing taxes can lead to serious consequences, including fines enforced by the IRS. The failure-to-file charge is typically 5% of the outstanding tax for each month or part of a month that the return is delayed, with a maximum limit of 25% of the total tax due.
How much can the fines increase if I delay filing my taxes for more than 60 days?
If you delay filing your return for over 60 days after the deadline, the minimum charge can rise to $510 or 100% of the unpaid tax, whichever is lower.
Can you provide an example of how fines accumulate for late tax filing?
For instance, if you owe $1,000 and submit your return two months late, you could face a fee of $100. If you remain unfiled for five months, the fee could increase to $250.
What potential losses might I face by not filing my taxes on time?
By not filing on time, you may miss out on potential refunds or credits. The average refund amount for American taxpayers in the 2025 filing season was $3,453.
How does the IRS handle refunds for non-filers?
The IRS typically issues more than 90% of refunds within 21 days, but this process can be delayed for those who do not file.
What happens if the IRS files a substitute return for me?
If you do not file, the IRS may file a substitute return on your behalf, often disregarding deductions or credits, which can result in a higher tax liability than necessary.
Are there ways to avoid fines for late tax filing?
You can avoid fines by submitting and paying your taxes by the deadline. If there are valid reasons for your delayed submission, the IRS may waive the fines.
Is it possible to get an extension on filing taxes?
Yes, you can seek a six-month extension to submit your taxes, which can help alleviate some of the urgency regarding fines.




