Introduction
Ignoring tax obligations can lead to serious financial consequences that many people might not fully grasp. We understand that as penalties and interest pile up, the stakes can feel overwhelming. This could mean hefty fines or even legal actions.
So, what happens if you choose not to file your taxes? It’s a question that reveals a complex web of consequences. From missing out on refunds to facing the threat of criminal charges, it’s a daunting reality that many taxpayers must confront.
Understanding these implications is crucial for anyone looking to manage their financial responsibilities effectively. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you navigate these challenges.
Define the Consequences of Not Filing Taxes
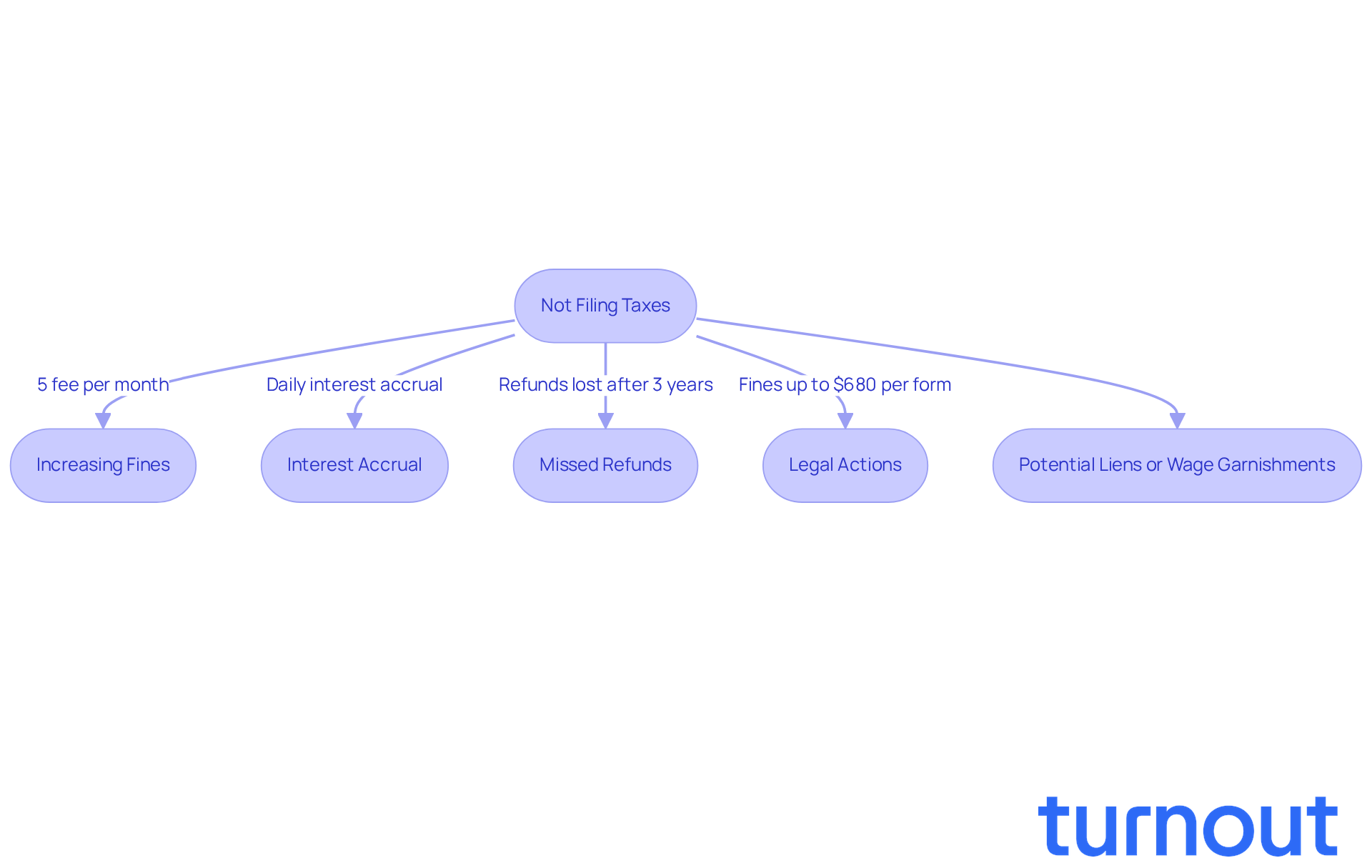
We understand that if you don't file your taxes what happens can lead to serious financial consequences, which is a concern many people share. Ignoring this responsibility can result in increasing fines and interest fees that can feel overwhelming, particularly if you consider what happens if you don't file your taxes. The IRS imposes a failure-to-file fee of 5% of the unpaid tax amount for each month the return is overdue, with a maximum limit of 25%. For instance, if you owe $3,000 and delay filing for six months, you could see fees and interest add up to over $500. Plus, interest on unpaid taxes accrues daily, compounding the financial burden over time.
It’s common to feel anxious about neglecting to submit your taxes, not just because of the fines but also due to the risk of missing out on potential refunds or credits. Many taxpayers miss out on refunds each year simply because they haven’t filed their returns, which can only be claimed within three years. After that, the IRS retains those funds. Remember, the IRS keeps track of income through W-2s and 1099s, so unfiled returns don’t go unnoticed. If you intentionally disregard filing rules, the IRS can impose a fine of $680 per information return, with no maximum limit. This highlights just how serious non-compliance can be.
The consequences of inaction can escalate quickly, and it’s important to understand what happens if you don't file your taxes. If you don't file your taxes what happens is that you may face accumulating fines and even legal actions from the IRS, such as liens on property or wage garnishments. Specific fines for delayed information submissions can rise from $60 to $680 per form, showing the monetary consequences of not meeting deadlines.
But you’re not alone in this journey. Seeking assistance from tax professionals can help you navigate these complexities and mitigate risks. They can provide the support you need to ensure better financial outcomes. Remember, we’re here to help you through this process.
Differentiate Between Late Filing and Non-Filing
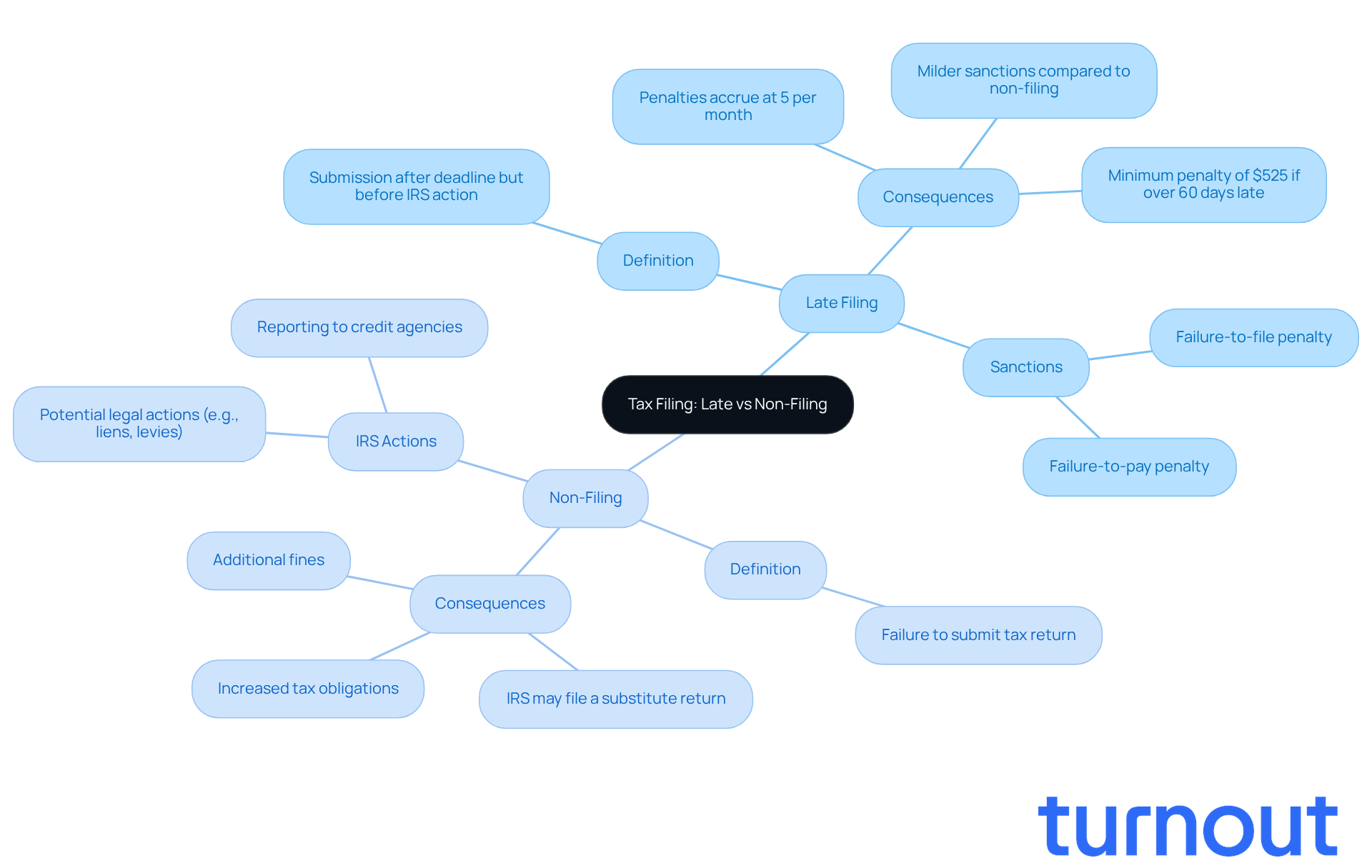
We understand that dealing with tax deadlines can be stressful. Late filing happens when a taxpayer submits their tax return after the deadline but before the IRS takes further action. While there are sanctions for this, they tend to be milder than those for non-filing.
On the other hand, the question of if you don't file your taxes what happens can lead to more serious consequences. If you don't file your taxes, what happens is that the IRS might file a substitute return on your behalf, which may not accurately reflect your income or deductions. This can result in increased tax obligations and additional fines.
It's common to feel overwhelmed by these situations, but understanding this distinction is vital. By recognizing the differences between late filing and non-filing, you can navigate your obligations more effectively. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we're here to help.
Examine Legal Ramifications of Tax Evasion
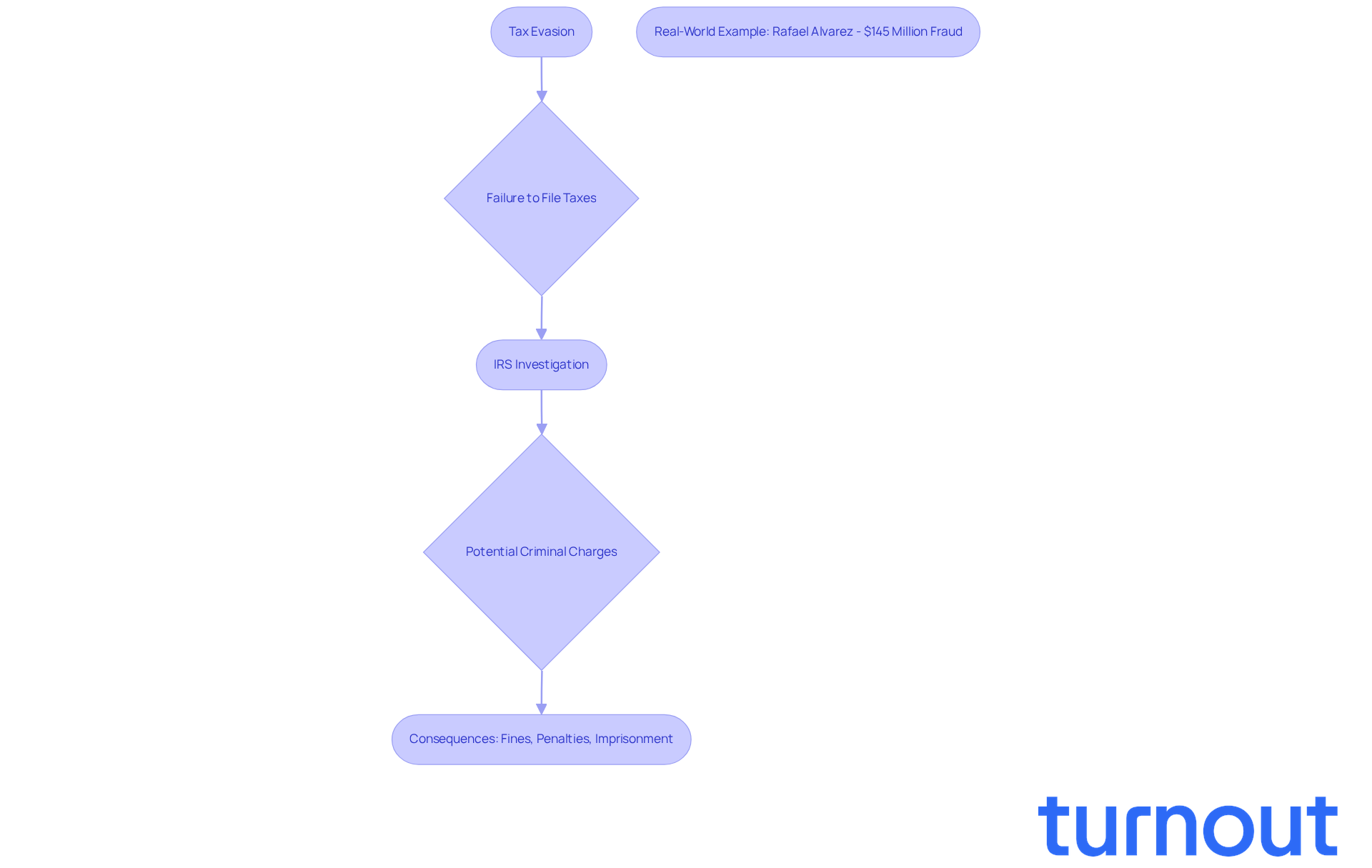
Tax evasion is a serious issue that many individuals may face, defined as the illegal act of not reporting or underreporting income to avoid paying taxes. We understand that the thought of dealing with the IRS can be overwhelming. If you don't file your taxes, what happens is that the IRS may determine that someone has willfully failed to file, which could result in criminal charges under Section 7203 of the Internal Revenue Code. Convictions can lead to hefty fines, penalties, and even imprisonment.
The IRS actively pursues cases of tax evasion, especially focusing on high-income non-filers. It’s crucial to catch up on tax filings rather than hoping the issue will resolve itself. In FY 2025, the IRS Criminal Investigation division identified a staggering $10.59 billion in monetary crimes, with a significant portion linked to tax fraud. The median losses from tax fraud offenses reached a five-year peak of $358,827 in 2024, underscoring the economic stakes involved.
Real-world examples highlight the severity of these consequences. For instance, Rafael Alvarez faced sentencing for submitting false tax returns, resulting in $145 million in fraud. This serves as a stark reminder of the risks associated with tax evasion. Additionally, the IRS has made it clear that intentionally failing to report income can trigger criminal investigations. It’s essential for taxpayers to remain compliant.
With revenue evasion costing the U.S. an estimated $1 trillion each year, it is vital for everyone liable for payment to understand the consequences of if you don't file your taxes, what happens. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you navigate these challenges and ensure you stay on the right path.
Outline Financial Penalties for Non-Filing
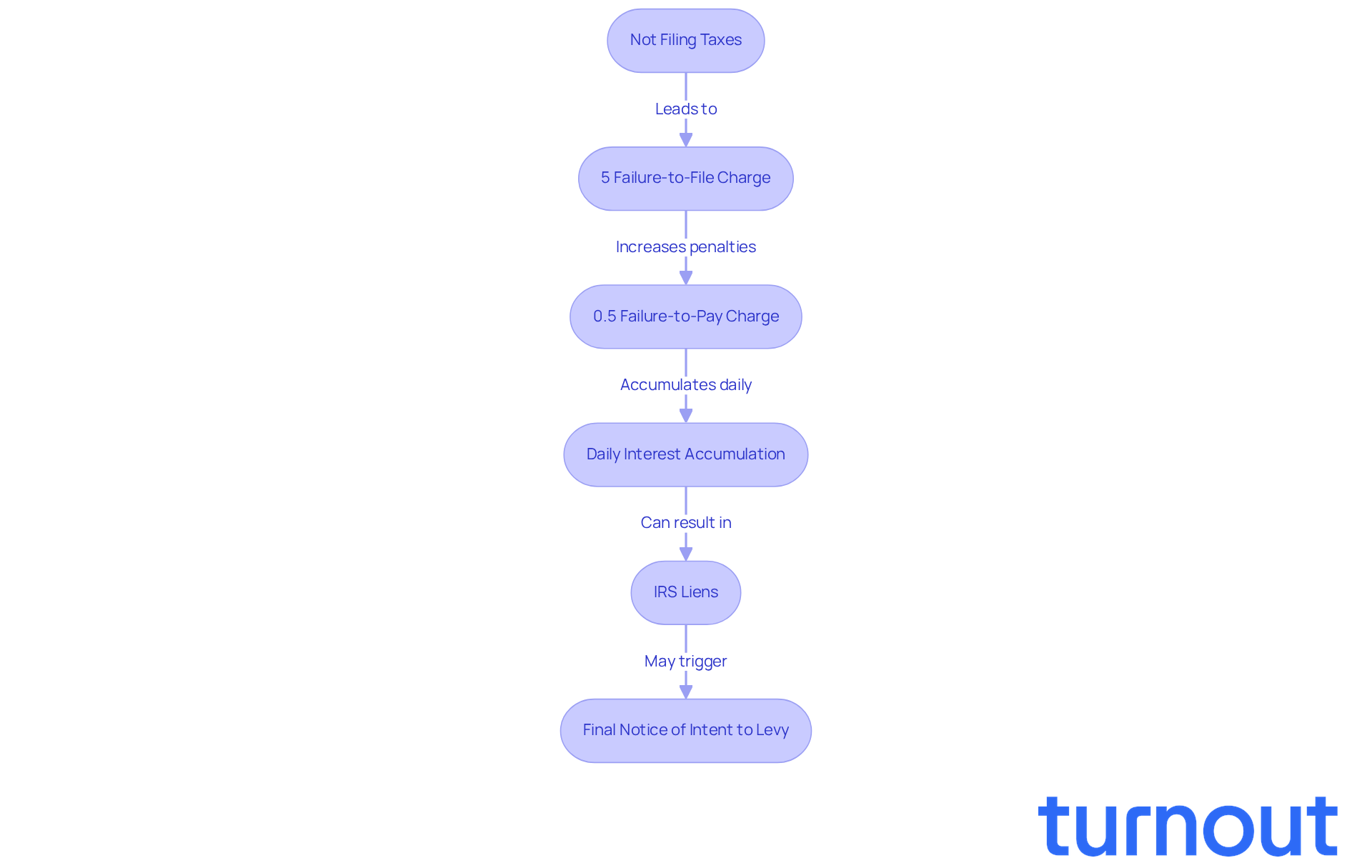
If you don't file your taxes, what happens is that it can lead to significant financial burdens that can pile up quickly. We understand that life can get overwhelming, and sometimes things slip through the cracks. However, it’s important to know that the IRS imposes a failure-to-file charge of 5% of the unpaid tax amount for each month your return is late, capped at a maximum of 25%. For example, if you owe $1,000 and file three months late, you could face a fee of $150, plus daily interest on the unpaid balance.
It’s common to feel anxious about these financial obligations. If dues remain unsettled, a failure-to-pay charge of 0.5% per month also applies, again capped at 25%. This means that the longer you wait to file, the heavier your financial load becomes, as interest accumulates daily on both penalties and unpaid dues. If you don't file your taxes, what happens is that ignoring these responsibilities can lead to serious consequences, such as the IRS placing liens on your property or even seizing your bank accounts and wages to recover what you owe.
Additionally, the IRS may send a 'Final Notice of Intent to Levy,' which emphasizes the urgency of addressing unpaid taxes. Understanding these penalties is crucial to avoid unnecessary economic strain and potential legal issues. But remember, you are not alone in this journey. The IRS offers installment agreements to help manage tax bills that cannot be paid in full, providing potential solutions for those facing financial difficulties. We're here to help you navigate this challenging situation.
Conclusion
Neglecting to file taxes can lead to a cascade of financial and legal repercussions that may feel overwhelming for any taxpayer. We understand that the gravity of these consequences can be daunting. Failing to meet tax obligations can result in escalating fines, lost refunds, and even legal action from the IRS. The implications of not filing extend beyond monetary penalties; they can impact your overall financial well-being and future stability.
Throughout this article, we’ve highlighted key points, including the significant penalties imposed by the IRS for both late and non-filing. It’s crucial to recognize that while late filing incurs fines, non-filing can lead to even more severe consequences. The IRS may file a substitute return on your behalf, which might not accurately reflect your financial situation. Furthermore, the threat of tax evasion charges looms large for those who willfully ignore their tax responsibilities, underscoring the importance of compliance.
Ultimately, the stakes are high when it comes to tax filing. It’s imperative for taxpayers to take proactive steps in managing their tax obligations to avoid unnecessary financial strain and legal issues. Seeking guidance from tax professionals can provide the necessary support to navigate these complexities. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Taking action now can prevent future complications and pave the way for a more secure financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the consequences of not filing taxes?
Not filing taxes can lead to serious financial consequences, including increasing fines and interest fees imposed by the IRS.
What is the failure-to-file fee imposed by the IRS?
The IRS imposes a failure-to-file fee of 5% of the unpaid tax amount for each month the return is overdue, with a maximum limit of 25%.
How much could I owe if I delay filing my taxes?
For example, if you owe $3,000 and delay filing for six months, you could see fees and interest add up to over $500.
How does interest on unpaid taxes work?
Interest on unpaid taxes accrues daily, compounding the financial burden over time.
What happens if I miss out on filing my taxes?
If you don't file your taxes, you risk missing out on potential refunds or credits, which can only be claimed within three years. After that, the IRS retains those funds.
Does the IRS track unfiled returns?
Yes, the IRS keeps track of income through W-2s and 1099s, so unfiled returns do not go unnoticed.
What are the penalties for intentionally disregarding filing rules?
If you intentionally disregard filing rules, the IRS can impose a fine of $680 per information return, with no maximum limit.
What legal actions can the IRS take if I don't file my taxes?
The IRS may take legal actions such as placing liens on property or garnishing wages if taxes are not filed.
What are the fines for delayed information submissions?
Fines for delayed information submissions can rise from $60 to $680 per form.
How can I get help with my taxes?
Seeking assistance from tax professionals can help you navigate the complexities of tax filing and mitigate risks.




