Overview
Understanding payroll tax deposit schedules can feel overwhelming, especially when it comes to navigating your responsibilities as an employer. We understand that the classification of your tax obligations—whether you're a monthly or semi-weekly contributor—depends largely on your total tax liability during a specific lookback period. If your obligations exceed $50,000, it's crucial to be aware of these classifications to avoid potential penalties.
It's common to feel uncertain about these requirements, but accurate assessments and timely payments are essential for maintaining compliance with IRS regulations. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Many employers share similar concerns, and there are resources available to help you manage these obligations effectively.
By staying informed and proactive, you can ensure that your payroll tax responsibilities are met with confidence. We're here to help guide you through this process, so you can focus on what truly matters—your business and your employees.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of payroll tax deposit schedules can feel overwhelming for many employers. We recognize that navigating the complexities of federal tax obligations is no small feat. These schedules dictate not only when payments are due but also significantly impact your cash flow and compliance.
The IRS categorizes employers into monthly or semi-weekly contributors based on their tax liabilities. The stakes are high—failure to adhere can lead to costly penalties, which can add to your stress. What factors truly determine your payroll tax deposit schedule? How can you ensure compliance while effectively managing your financial health?
You're not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you understand these crucial aspects, so you can focus on what matters most—your business.
Define Payroll Tax Deposit Schedule
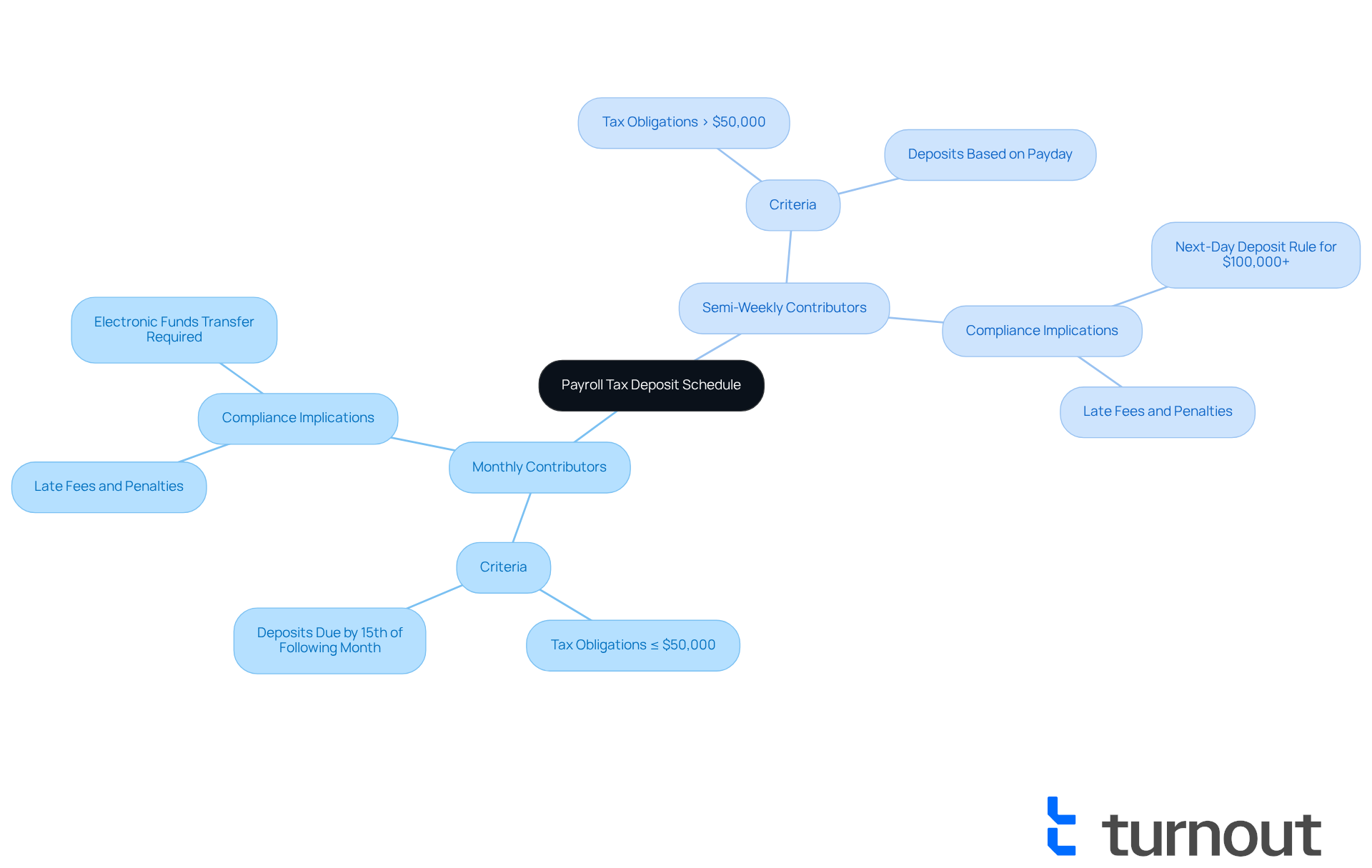
A payroll contribution schedule is more than just a timetable; it’s a lifeline set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) that helps employers navigate the complexities of federal payroll withholdings from employee earnings. These taxes typically include federal income tax, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax. We understand that managing these obligations can feel overwhelming, particularly when considering what determines an employer's payroll tax deposit schedule, as employers are categorized as either monthly or semi-weekly contributors based on their total tax liability during a specific lookback period. For the 2025 contribution schedules, this period runs from July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024.
For instance, if your company’s tax obligations exceed $50,000 during this timeframe, this situation illustrates what determines an employer's payroll tax deposit schedule, requiring you to follow a semi-weekly payment schedule. On the other hand, those with obligations of $50,000 or less will be classified as monthly contributors, which is part of what determines an employer's payroll tax deposit schedule. It’s important to remember that all federal tax payments must be made using electronic funds transfer (EFT). Adhering to this schedule is crucial for compliance; we know that failure to do so can lead to late fees, penalties, and interest from the IRS, which can range from 2% to 15% depending on the delay.
It's common to feel anxious about meeting these deadlines. Data suggests that many organizations face challenges with timely payments, highlighting the need for efficient compensation management systems to ensure compliance. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Organizations are also required to keep tax records for four years after submission, and they must report their tax obligations using designated forms, such as Form 941.
Quotes from tax professionals emphasize the importance of understanding these requirements to avoid penalties and maintain compliance. We’re here to help you navigate these complexities, ensuring that you can focus on what truly matters—your business and your employees.
Identify Key Factors Influencing Deposit Schedules
Understanding the complexities of tax payment timelines can be overwhelming for employers. We recognize that navigating these obligations is not always easy, especially when it comes to ensuring compliance and avoiding penalties. Several essential elements play a significant role in understanding what determines an employer's payroll tax deposit schedule, primarily revolving around the total tax obligation documented during the lookback period and the frequency of wage disbursements.
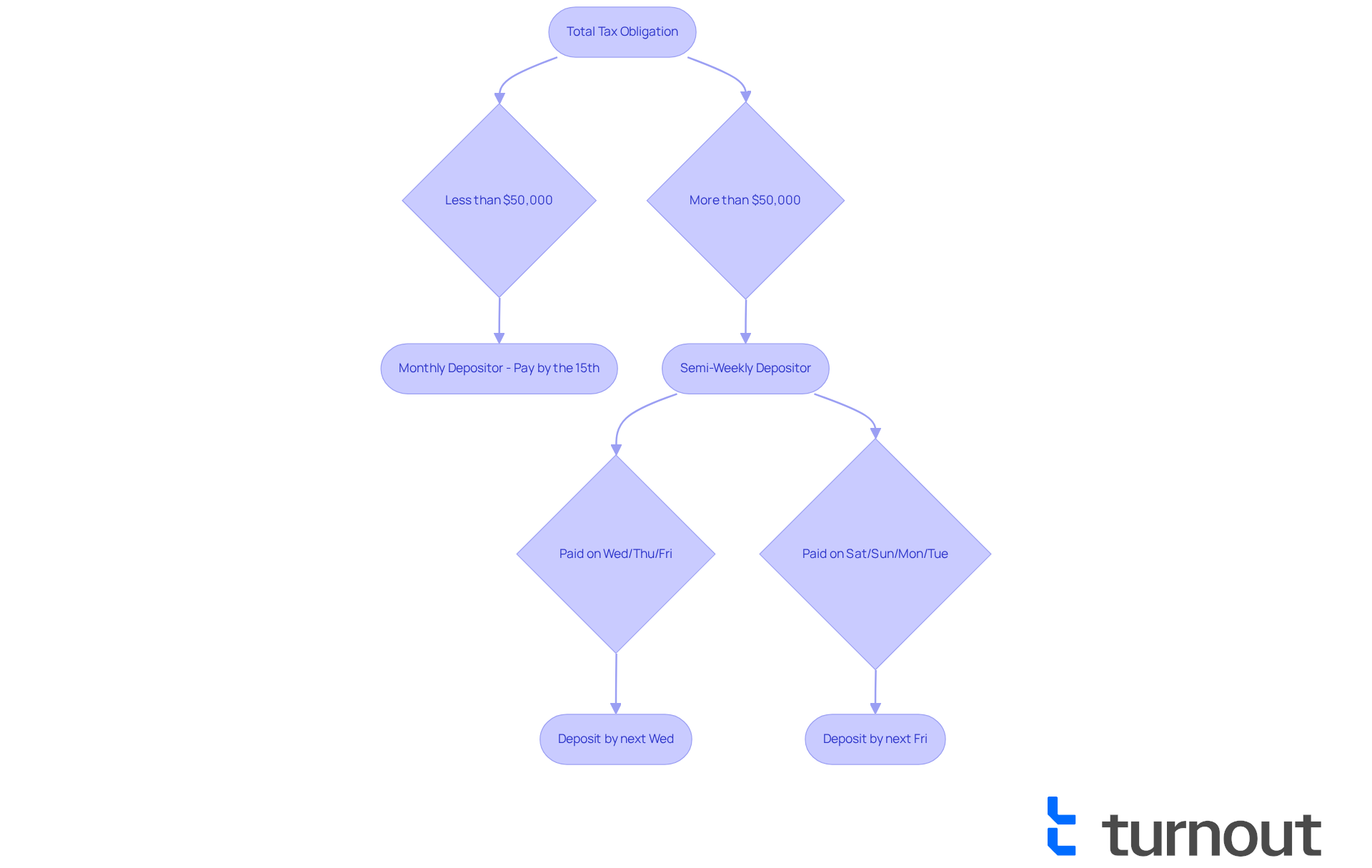
If your total tax liability is $50,000 or less during this period, you are typically classified as a monthly depositor. This means you will need to make payments by the 15th of the following month. However, if your obligations exceed $50,000, you will need to follow a semi-weekly payment schedule, which requires contributions shortly after salary dates. For instance:
- If employees are compensated on a Wednesday, Thursday, or Friday, taxes must be deposited by the next Wednesday.
- Conversely, if payment occurs on a Saturday, Sunday, Monday, or Tuesday, deposits are due by the following Friday.
It's common to feel anxious about the potential for late payments, as these can lead to fines ranging from 2% to 15% depending on the delay. To ease this burden, approximately 800,000 businesses have turned to automated payment systems, like those offered by Paychex. These systems help streamline processes, ensuring timely compliance and reducing administrative challenges.
Moreover, staying updated on changes in compensation regulations at both federal and state levels is crucial to prevent missed deadlines. By understanding these classifications and adhering to the appropriate schedules, organizations can safeguard their financial health and foster trust with their workforce. Remember, you are not alone in this journey—we're here to help you navigate these complexities with confidence.
Explain Implications of Deposit Frequency on Employers
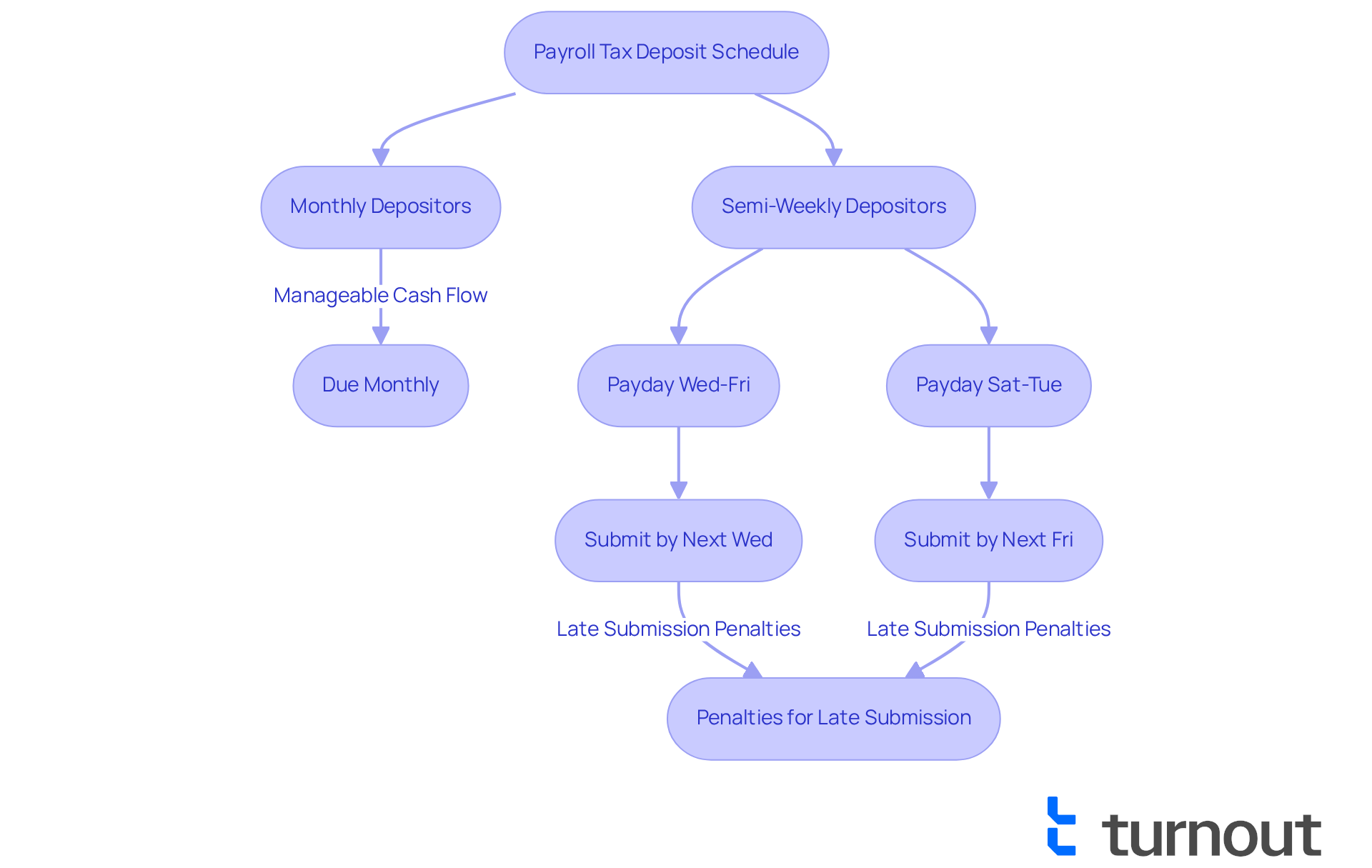
For employers, understanding what determines an employers payroll tax deposit schedule is crucial, as managing tax contributions can significantly impact cash flow in ways that can feel overwhelming. We understand that navigating these responsibilities can be challenging.
For those who deposit monthly, the schedule is more manageable, allowing for easier financial planning with just one payment each month. In contrast, semi-weekly contributors face stricter deadlines, needing to submit payments shortly after payroll. This can create pressure on cash flow and increase administrative tasks. For instance, if payday falls between Wednesday and Friday, taxes need to be submitted by the following Wednesday. If it’s between Saturday and Tuesday, submissions are due by the next Friday.
Missing these deposit deadlines can result in penalties ranging from 2% to 15% of the unpaid tax amount. This underscores the importance of sticking to the designated schedule. In fact, U.S. companies collectively pay over $4.5 billion each year in payroll tax penalties, highlighting the serious financial consequences of non-compliance. Additionally, it’s common to hear from employees—40% report receiving their payments late at least once—which can disrupt their financial planning and erode trust in the organization.
By understanding what determines an employers payroll tax deposit schedule, organizations can take proactive steps to manage their financial obligations more effectively. This not only helps prevent costly mistakes but also fosters a healthier cash flow. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you navigate these complexities with confidence.
Explore the Lookback Period and Its Importance
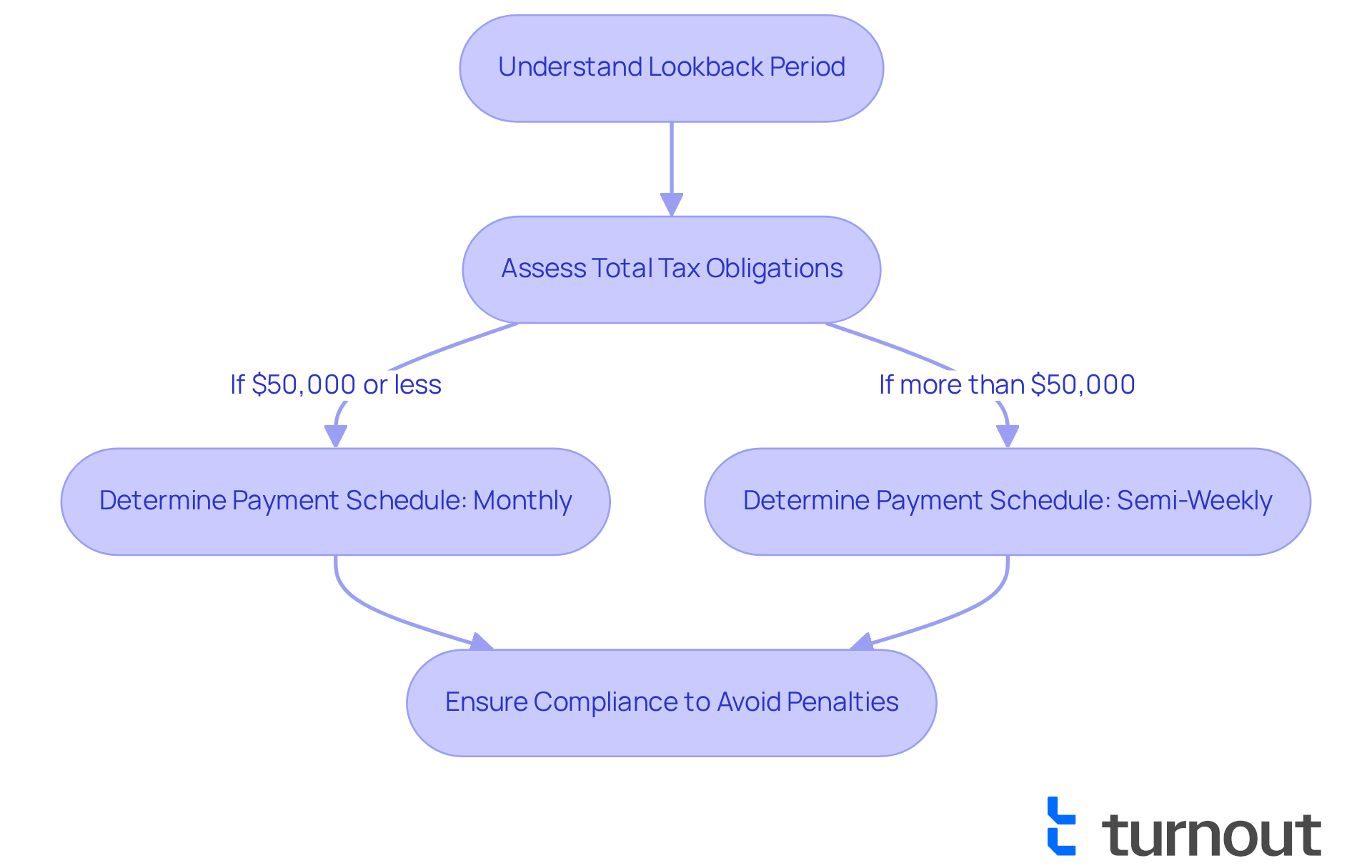
Understanding what determines an employers payroll tax deposit schedule can feel overwhelming, but it’s an essential timeframe that the IRS uses to assess your business's overall tax obligation. This period typically spans 12 months, from July 1 of the previous year to June 30 of the current year. We understand that navigating tax liabilities can be challenging, but it’s crucial for employers to carefully assess their total tax obligations within this timeframe. This assessment will help clarify what determines an employers payroll tax deposit schedule, allowing you to see if you qualify as a monthly or semi-weekly depositor.
It's common to feel anxious about misclassifying payment schedules, as this can lead to substantial penalties. The IRS enforces fines ranging from 2% to 15% of unpaid taxes for tardy payments. Statistics show that many organizations struggle to comply with the lookback period requirements, resulting in costly mistakes. However, by understanding this timeframe, you can maintain compliance with IRS regulations and avoid unexpected penalties.
By correctly categorizing your payment schedules, you can ensure prompt disbursements and protect your business from financial consequences. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you navigate these complexities with confidence.
Discuss Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
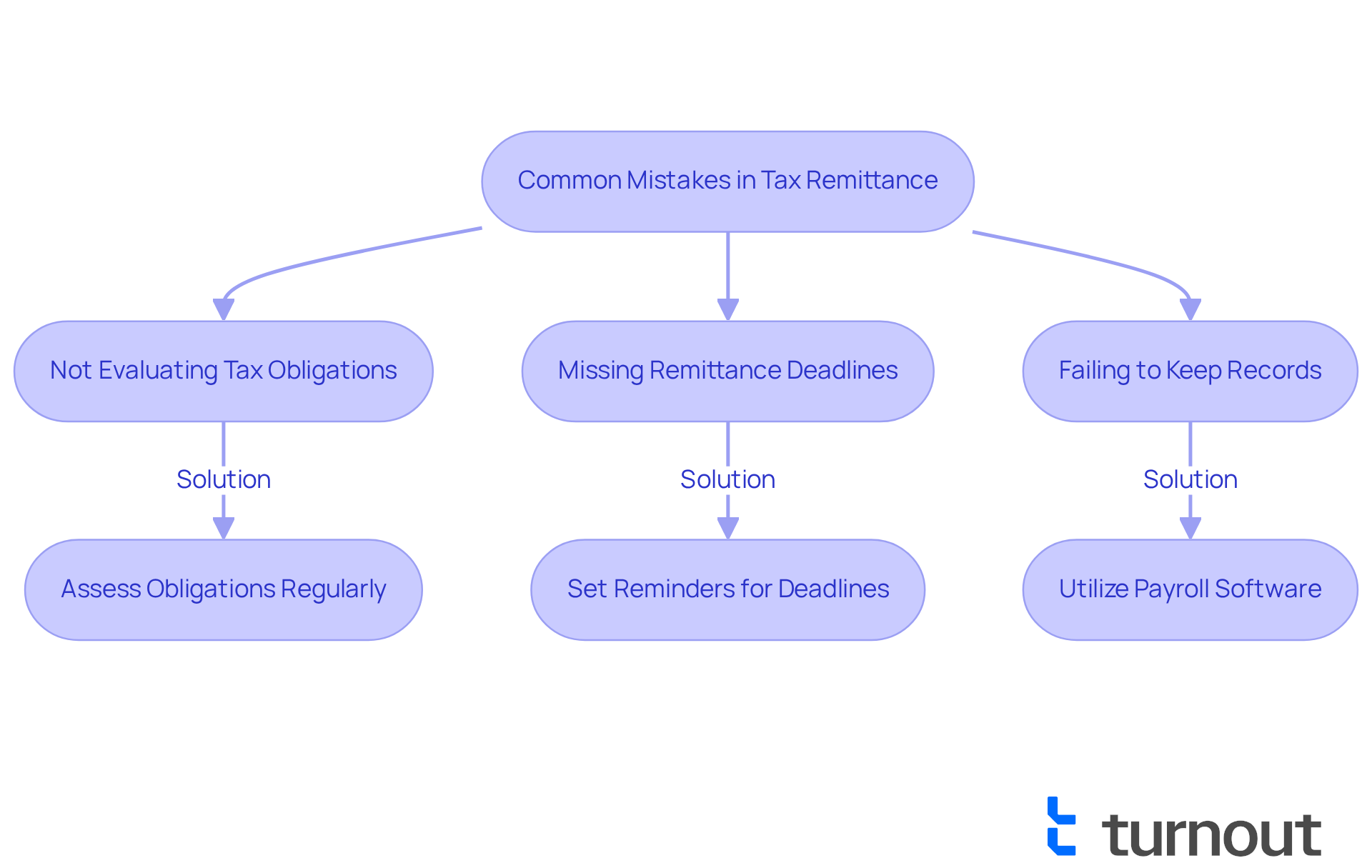
We understand that navigating tax remittance schedules can be daunting. Many organizations face frequent errors, such as:
- Not accurately evaluating their tax obligations during the lookback period
- Missing remittance deadlines
- Failing to keep comprehensive records of taxes withheld
These challenges can lead to stress and confusion.
To help you avoid these pitfalls, it’s essential to consistently assess your tax obligations. Keeping orderly records is crucial, and setting up reminders for payment deadlines can alleviate some of the pressure. Additionally, utilizing payroll software can significantly ease this process. It automates calculations and ensures timely deposits, which can reduce the risk of errors and penalties.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you navigate these complexities with confidence.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of an employer's payroll tax deposit schedule is essential for maintaining compliance and ensuring financial health. We understand that navigating these complexities can feel overwhelming. This schedule, determined by the IRS based on total tax liability during a designated lookback period, categorizes employers as either monthly or semi-weekly depositors. Recognizing these classifications allows businesses to manage their tax obligations effectively and avoid the pitfalls of late payments and penalties.
The article highlights key factors that influence this schedule, including total tax obligations and payment frequency. It's common to feel uncertain about the importance of accurate record-keeping and timely assessments. These practices help avoid common mistakes that could lead to costly penalties. Additionally, leveraging automated payment systems can significantly ease the burden of compliance. This way, organizations can focus on their core operations without the stress of tax deadlines.
Ultimately, staying informed about payroll tax deposit schedules is crucial for all employers. By understanding the implications of deposit frequency on cash flow and the potential consequences of non-compliance, businesses can foster a healthier financial environment and build trust with their employees. Taking proactive steps to navigate these complexities not only safeguards against penalties but also enhances overall operational efficiency. Remember, you are not alone in this journey—we're here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a payroll tax deposit schedule?
A payroll tax deposit schedule is a timetable set by the IRS that helps employers manage federal payroll withholdings from employee earnings, including federal income tax, Social Security tax, and Medicare tax.
How is an employer's payroll tax deposit schedule determined?
An employer's payroll tax deposit schedule is determined based on their total tax liability during a specific lookback period. Employers are categorized as either monthly or semi-weekly contributors depending on whether their tax obligations exceed $50,000 during this timeframe.
What is the lookback period for the 2025 payroll tax contribution schedules?
The lookback period for the 2025 payroll tax contribution schedules runs from July 1, 2023, to June 30, 2024.
What are the deposit requirements for employers with tax obligations exceeding $50,000?
Employers with tax obligations exceeding $50,000 must follow a semi-weekly payment schedule, requiring contributions shortly after salary dates.
What are the deposit requirements for employers with tax obligations of $50,000 or less?
Employers with tax obligations of $50,000 or less are classified as monthly depositors and must make payments by the 15th of the following month.
When are taxes due if employees are paid on a Wednesday, Thursday, or Friday?
If employees are compensated on a Wednesday, Thursday, or Friday, taxes must be deposited by the next Wednesday.
When are taxes due if employees are paid on a Saturday, Sunday, Monday, or Tuesday?
If payment occurs on a Saturday, Sunday, Monday, or Tuesday, deposits are due by the following Friday.
What are the consequences of failing to meet payroll tax deposit deadlines?
Failing to meet payroll tax deposit deadlines can lead to late fees, penalties, and interest from the IRS, which can range from 2% to 15% depending on the delay.
How can employers ensure compliance with payroll tax deposit schedules?
Employers can ensure compliance by utilizing automated payment systems, staying updated on changes in compensation regulations, and understanding their deposit classifications and schedules.
How long must organizations keep tax records after submission?
Organizations are required to keep tax records for four years after submission.




