Introduction
Receiving a Notice of Deficiency from the IRS can stir up a wave of anxiety. It’s a signal that potential tax liabilities may have slipped under the radar. This important document, known as IRS Notice CP2319A, serves as an official warning. The IRS believes additional taxes are owed, often due to discrepancies in reported income.
Understanding what this notice means is crucial. It not only outlines your rights as a taxpayer but also presents a limited window of 90 days to respond and contest the IRS's findings. We understand that this can feel overwhelming. What steps should you take to navigate this complex process and protect your financial future?
You are not alone in this journey. Many people face similar challenges, and there are ways to address them. Let’s explore how you can respond effectively and find peace of mind.
Define the Notice of Deficiency
Receiving a notice of deficiency IRS meaning, which is officially referred to as IRS Notice CP2319A, can be a daunting experience. This document serves as a notice of deficiency IRS meaning, issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to inform you that they believe you owe additional taxes. It often arises when there are discrepancies between what you've reported and the IRS's records.
We understand that this can be concerning. This notice serves as a formal alert that explains the notice of deficiency IRS meaning, indicating that the IRS intends to assess additional tax liabilities, which may include penalties and interest based on their findings. You’re not alone in feeling overwhelmed by this situation.
Fortunately, if you receive this notice, you have a 90-day period to respond, starting from the date it’s mailed to your last known address. During this time, you can challenge the IRS's determination in the U.S. Tax Court without needing to pay the disputed amount upfront. Remember, the IRS cannot assess or collect any tax, penalties, or interest until the 90 days have passed or a Tax Court decision is final.
It’s crucial to respond within this timeframe. Failing to do so may lead to the IRS assessing the tax, penalties, and interest. If you’re feeling uncertain about your next steps, we’re here to help you navigate this process.
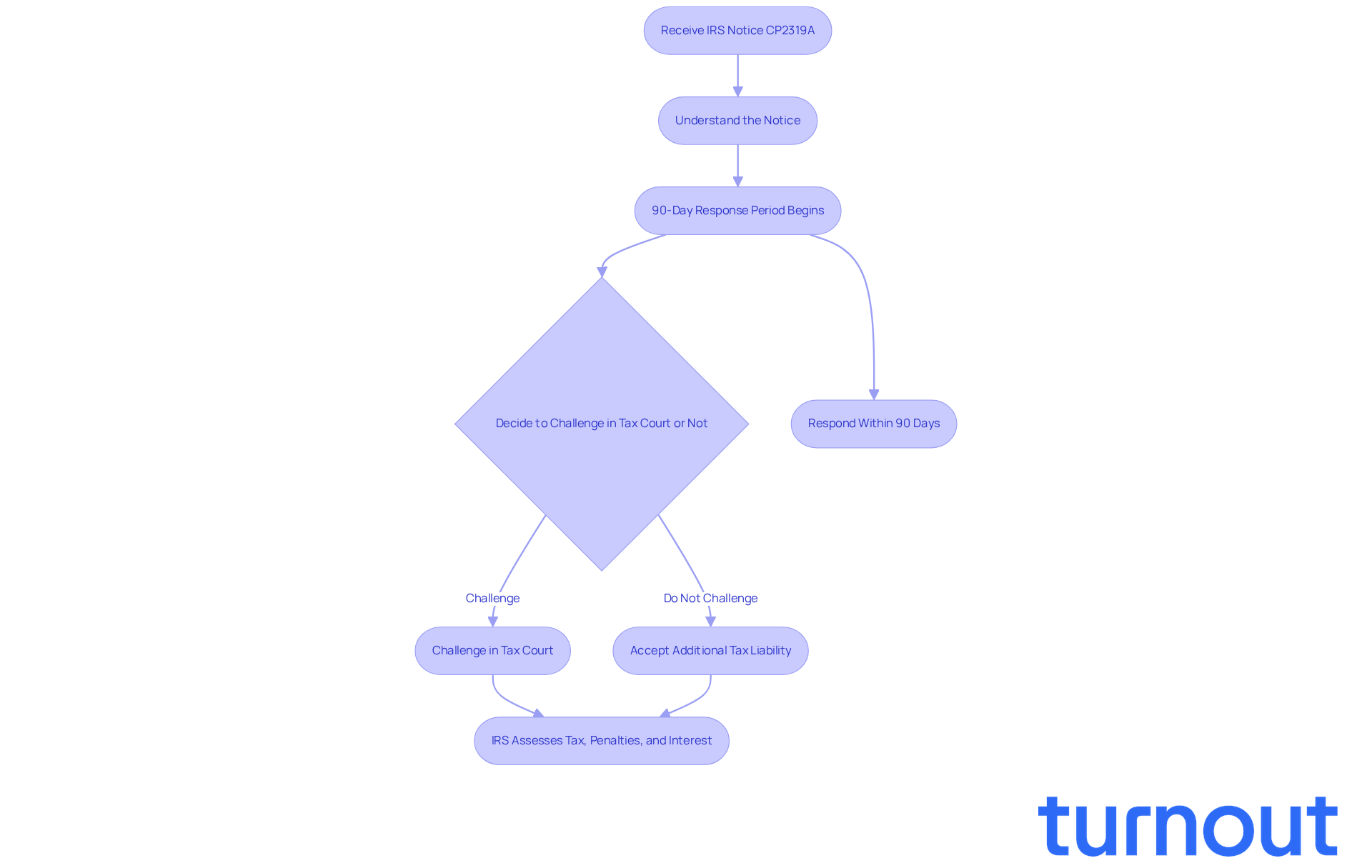
Contextualize the Notice of Deficiency within IRS Procedures
The notice of deficiency IRS meaning is a crucial part of the IRS's process for tax assessments. It typically comes after the IRS has audited or reviewed your return, which relates to the notice of deficiency IRS meaning, pointing out possible discrepancies. This notice is just one of several communications the IRS sends, which may also include initial inquiries or requests for more information.
When you receive a Notice of Shortfall, it means the IRS has made a decision about your tax liability and is ready to take further action if you don’t respond appropriately. It’s important to understand that this notice isn’t just a suggestion; it’s a formal legal document that could lead to more serious legal proceedings if you don’t address it within the specified timeframe.
You have exactly 90 days from the date on the Notice of Shortfall to file a petition in U.S. Tax Court. This is the only way to pause the deadline. If you miss this deadline, your tax liability becomes locked in, allowing the IRS to pursue collection actions like levies and liens.
Recently, there’s been a noticeable increase in Notices of Shortfall issued by the IRS, reflecting a broader trend in tax enforcement. It’s common to feel anxious during this process, as the stakes can be high. Engaging with the IRS early and understanding what the Notice of Shortfall means can lead to better outcomes.
Many taxpayers have found that once their cases reach Tax Court, they are often reviewed by specialized IRS attorneys. This can lead to quicker and more favorable settlements without the need for a full trial. Therefore, taking prompt action upon receiving a Notice of Shortfall is strongly encouraged to protect your rights and explore resolution options effectively.
Additionally, seeking professional support is vital in navigating the complexities of tax law and IRS disputes. It can significantly improve your chances of a favorable resolution. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
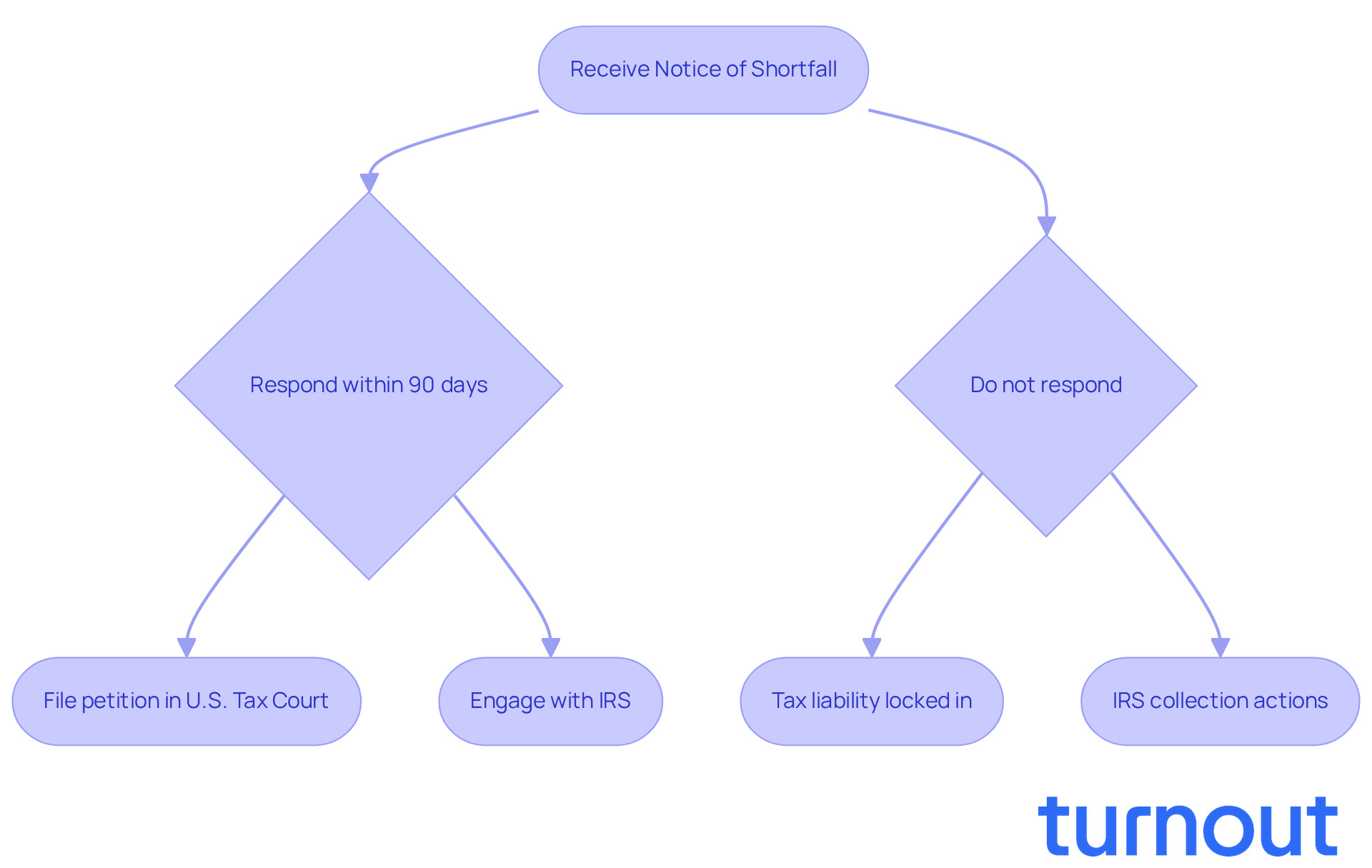
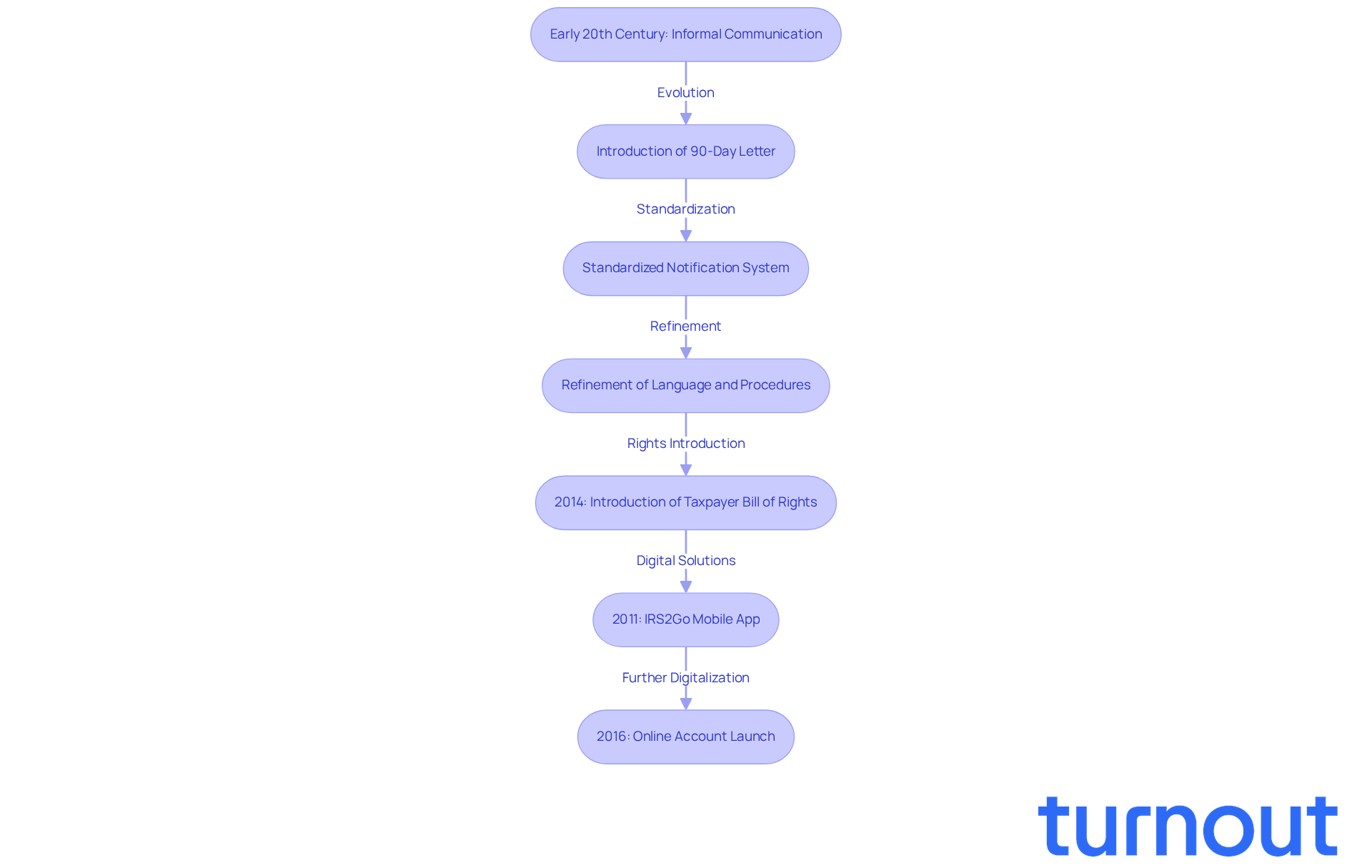
Trace the Origins and Evolution of the Notice of Deficiency
The Notice of Shortfall is more than just a piece of paperwork; it’s a crucial part of the IRS tax assessment process that has evolved significantly since the early 20th century. Back then, the IRS communicated discrepancies informally. But as tax laws became more complex, the need for a standardized notification system became clear. The introduction of the 90-Day Letter was a game changer, giving individuals a specific timeframe to respond to IRS claims. If you receive this letter, remember, you have 90 days to file a petition with the U.S. Tax Court. This timeframe is vital for anyone facing tax issues.
Over the years, the IRS has worked hard to refine the language and procedures surrounding what is known as the notice of deficiency IRS meaning. This effort ensures compliance with legal standards while protecting your rights. It’s important to recognize that this evolution reflects broader trends in tax administration, emphasizing transparency and due process in your interactions with the IRS.
In 2014, the IRS introduced an improved Taxpayer Bill of Rights, consolidating ten essential rights. This move reinforces the agency's commitment to honoring your rights throughout the assessment process. As communication methods have changed, the IRS has embraced digital platforms. For instance, the IRS2Go mobile app, launched in 2011, allows you to check the status of your notices and refunds conveniently.
In November 2016, the IRS launched Online Account, enabling you to view your payment history and the amount you owe for the last two years. This ongoing transformation highlights the IRS's dedication to adapting to your needs while ensuring a fair and accessible tax system.
We understand that dealing with tax issues can lead to significant financial stress, including extra tax evaluations, accumulated interest, and severe penalties. That’s why it’s crucial to comprehend the notice of deficiency IRS meaning and the rights that are granted to you. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you navigate these challenges.
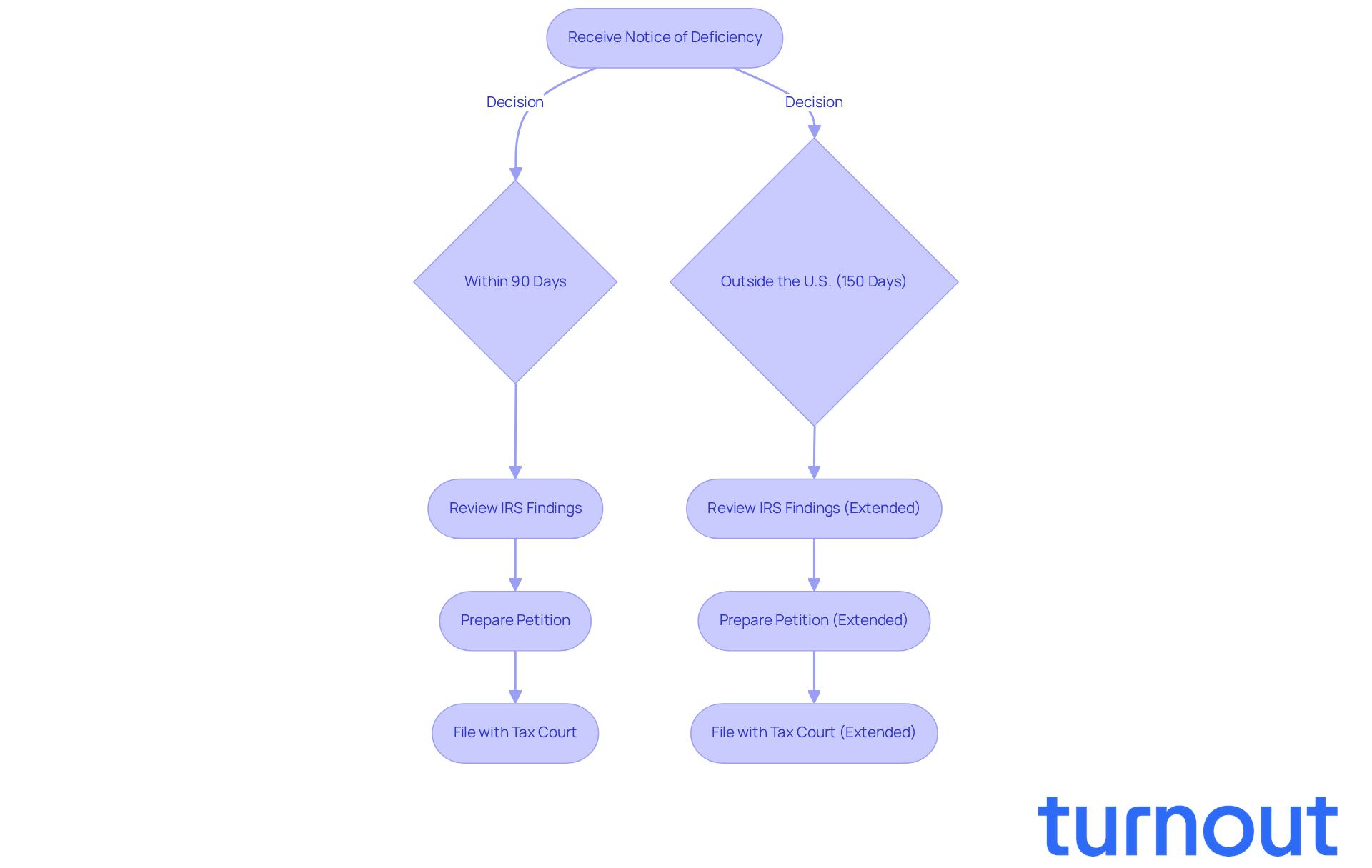
Identify Key Characteristics of the Notice of Deficiency
Understanding the Notice of Shortcoming can feel overwhelming, but you’re not alone in this journey. This formal document has a significant meaning, particularly when considering the notice of deficiency IRS meaning, and it’s essential to grasp its key characteristics. The notice clearly states the IRS's findings, including the amount of additional tax owed and the reasons behind this determination. It’s sent via certified or registered mail, ensuring you receive it directly, which is the standard method for delivering the notice of deficiency IRS meaning.
Inside, you’ll find guidelines on how to respond. Think of it as your 'ticket to the Tax Court.' This allows you to challenge the IRS's claims without needing to prepay the contested taxes. Knowing these traits is crucial for anyone liable for taxes, as it empowers you with knowledge about your rights and the necessary steps to take.
After receiving a properly delivered notice of deficiency IRS meaning (NOD), you have 90 days to file a petition with the Tax Court. If you’re outside the U.S., that deadline extends to 150 days. It’s common to feel anxious about these timelines, but responding promptly is vital. Failing to act within the specified period can lead to automatic tax assessments and collection actions.
Remember, the Taxpayer Advocate Service is here to help you navigate these challenges. Real-world examples show that taxpayers who respond effectively to the notice of deficiency IRS meaning can successfully contest IRS determinations. This highlights just how important it is to understand this document and its implications. You have the power to take action and protect your rights.
Conclusion
Receiving a Notice of Deficiency from the IRS can feel overwhelming. We understand that this formal notification signals potential additional taxes owed, and it’s essential to grasp its significance. This document outlines the steps you can take to challenge the IRS's findings, empowering you to take control of your tax situation.
In this article, we’ve explored key aspects of the Notice of Deficiency, including its:
- Definition
- Context within IRS procedures
- Historical evolution
- Essential characteristics
The emphasis on the 90-day response window highlights the urgency in addressing this notice. Acting promptly can help you avoid automatic tax assessments and further penalties. Many taxpayers have successfully contested their cases in Tax Court by engaging with the IRS quickly and seeking professional assistance.
It’s common to feel anxious when faced with a Notice of Deficiency, but being proactive is vital. Understanding the implications of this document not only protects your rights but also encourages informed decision-making. By taking timely action and leveraging available resources, you can navigate this challenging process more effectively. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you manage your tax liabilities with confidence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a notice of deficiency from the IRS?
A notice of deficiency, officially referred to as IRS Notice CP2319A, is a document issued by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to inform taxpayers that the IRS believes they owe additional taxes due to discrepancies between the taxpayer's reported income and the IRS's records.
What should I do if I receive a notice of deficiency?
If you receive a notice of deficiency, you have a 90-day period to respond, starting from the date it’s mailed to your last known address. During this time, you can challenge the IRS's determination in the U.S. Tax Court without needing to pay the disputed amount upfront.
What happens if I do not respond to the notice of deficiency within 90 days?
Failing to respond within the 90-day timeframe may lead to the IRS assessing the tax, penalties, and interest based on their findings.
Can the IRS collect taxes, penalties, or interest while I am disputing a notice of deficiency?
No, the IRS cannot assess or collect any tax, penalties, or interest until the 90 days have passed or a Tax Court decision is final.
What are the potential consequences of receiving a notice of deficiency?
The notice indicates that the IRS intends to assess additional tax liabilities, which may include penalties and interest based on their findings.




