Introduction
The establishment of Social Security in 1935 was a pivotal moment in American history. It emerged from the shadows of the Great Depression, a time when millions faced dire economic uncertainty. This groundbreaking initiative aimed to provide financial security for the elderly, unemployed, and disabled. More than that, it represented a fundamental shift in the government's role in safeguarding citizens' welfare.
Yet, as the program evolved over the decades, questions arose about its sustainability and effectiveness in addressing modern challenges. We understand that navigating these complexities can feel overwhelming. How has the legacy of the New Deal shaped the Social Security system we rely on today? What practical steps can you take to navigate this essential support network?
You're not alone in this journey. Together, we can explore the answers and find ways to ensure that this vital resource continues to support you and your loved ones.
Explore the Historical Context of Social Security and the New Deal
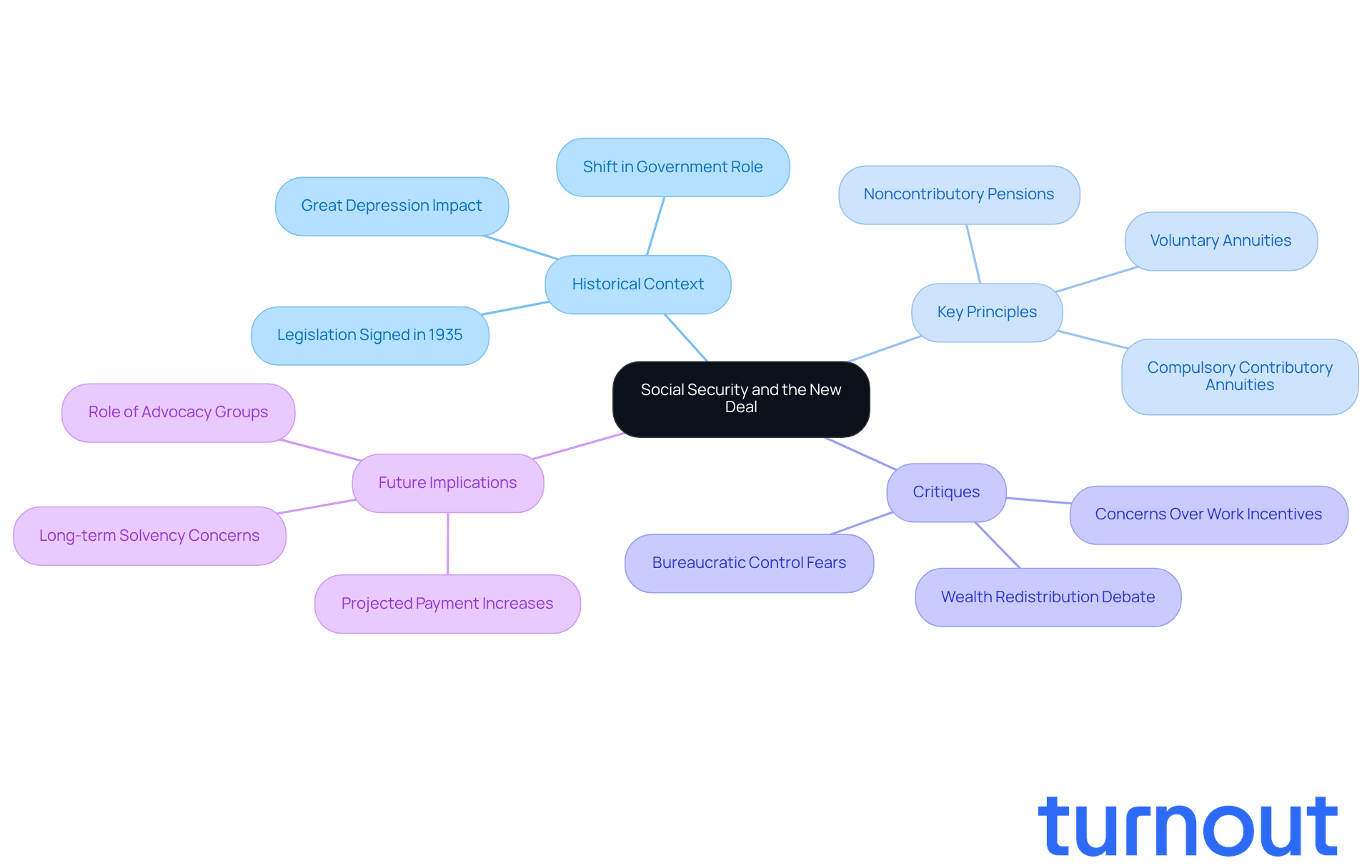
The Social Welfare Act, signed into law by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1935, emerged from the dire financial struggles of the Great Depression. During this challenging time, millions of Americans faced joblessness, poverty, and uncertainty about their futures. As part of social security the new deal, a comprehensive set of programs aimed at economic recovery, it became a vital initiative. It was designed to provide financial assistance to the elderly, unemployed, and disabled, ensuring that everyone could maintain a basic standard of living.
Roosevelt introduced three key principles for old-age security:
- Noncontributory pensions for the elderly
- Compulsory contributory annuities
- Voluntary annuities
This marked a significant shift in the government's role, reflecting a commitment to protect citizens from financial hardships. It wasn't just a safety net; it underscored the belief that financial security is a fundamental right.
However, not everyone was on board. Critics, like Representative James W. Wadsworth, raised concerns that the Act might undermine work incentives and lead to bureaucratic control over finances. Understanding this context is essential, as it highlights the lasting impact of the Support Act and the ongoing importance of social security the new deal during tough financial times-a principle that still resonates today.
Looking ahead, government assistance payments are set to rise by 2.8 percent in 2026, underscoring the program's continued significance in fostering economic stability. In this landscape, Turnout plays a crucial role by simplifying access to government benefits, especially for those navigating SSD claims. With trained nonlawyer advocates, Turnout ensures that individuals can effectively pursue their rights to financial support without the complexities of legal representation. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we're here to help.
Analyze Key New Deal Programs Impacting Social Security Development
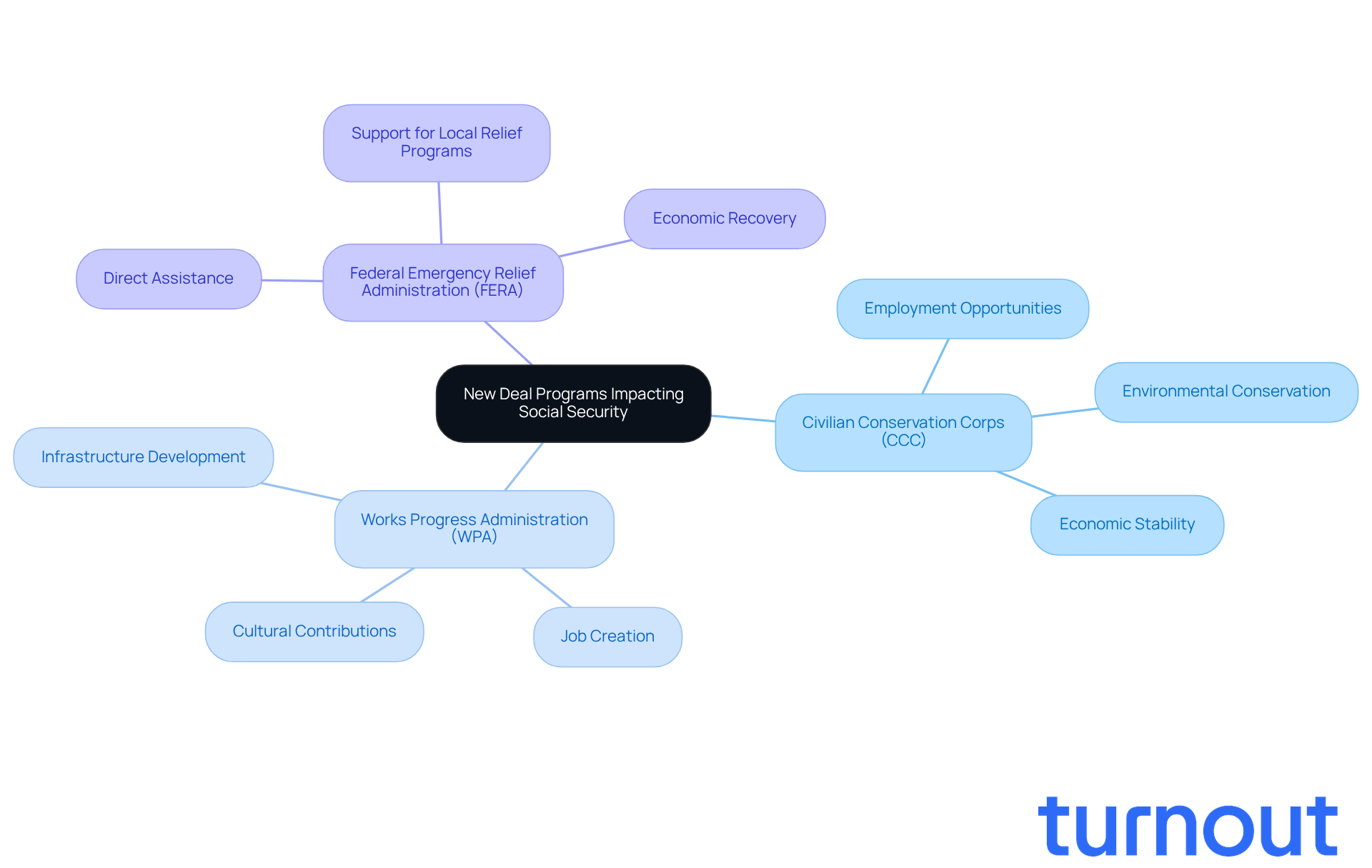
The New Deal introduced several pivotal programs that profoundly influenced the development of social security the new deal. We understand that many faced immense challenges during the Great Depression, and initiatives like the Civilian Conservation Corps (CCC) and the Works Progress Administration (WPA) were crucial in providing immediate employment opportunities. The Federal Emergency Relief Administration (FERA) also stepped in, delivering direct assistance to those in dire need.
These initiatives highlighted the critical need for an organized support system. They ultimately led to the establishment of a social welfare program known as social security the new deal, which we can rely on today. The inclusion of unemployment insurance and retirement pensions in social security the new deal was a direct response to the lessons learned from these programs, ensuring that future generations would benefit from a strong safety net during financial downturns.
The CCC alone employed millions of young men, contributing not just to environmental conservation but also to economic stability. Meanwhile, the WPA became the largest public works program, significantly reducing unemployment and enhancing infrastructure. These programs didn’t just alleviate immediate poverty; they laid the groundwork for social security the new deal, establishing a comprehensive social safety net that continues to serve Americans today.
You are not alone in this journey. We’re here to help, and together, we can build a brighter future.
Examine the Evolution of Social Security: From New Deal to Present Day
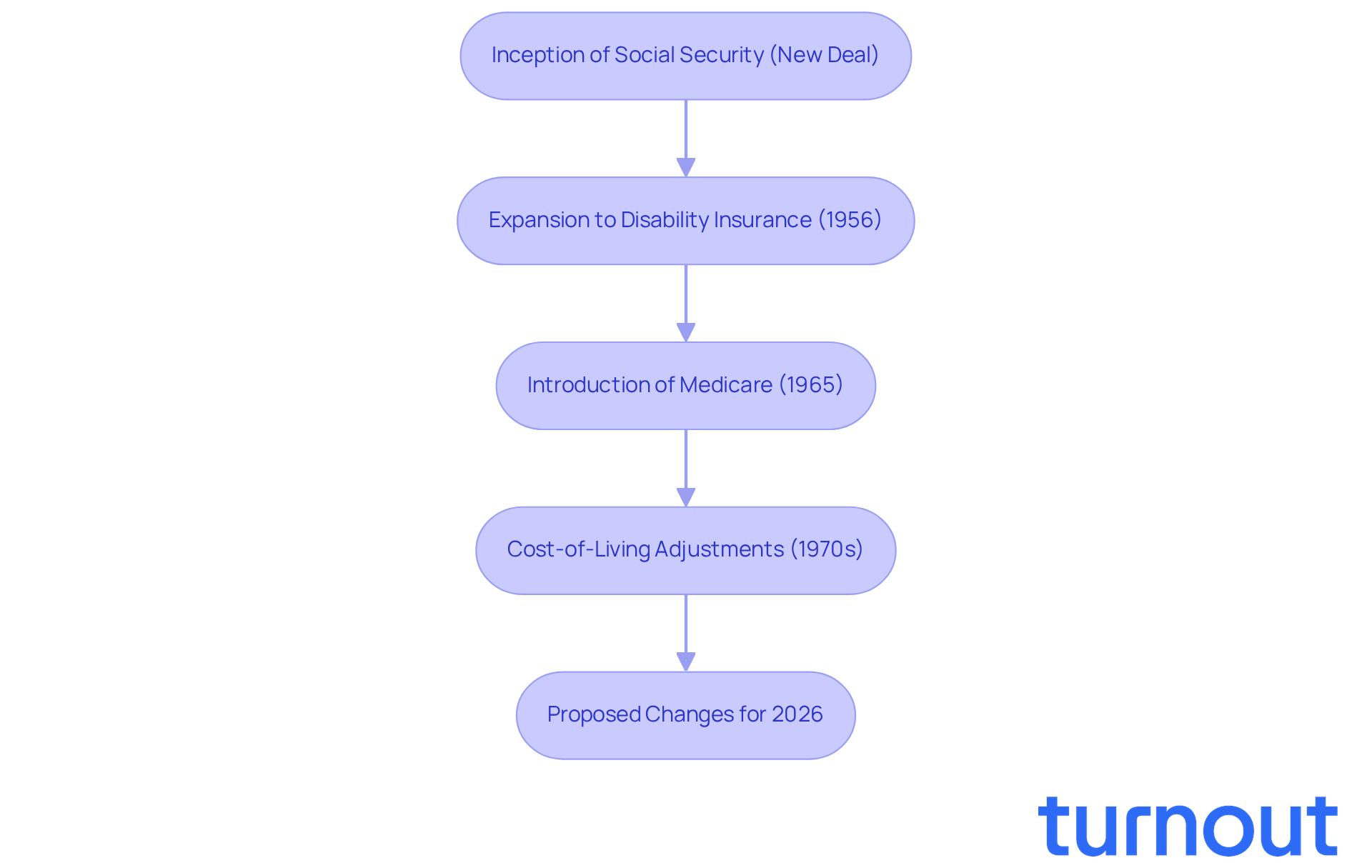
Since its inception, social security the new deal has transformed significantly to address the evolving needs of American society. Initially created to offer retirement assistance, the program expanded in 1956 to include disability insurance. This change reflects a growing recognition of the need for support beyond just retirement. The introduction of Medicare in 1965 further broadened its scope, ensuring healthcare access for seniors. In the 1970s, cost-of-living adjustments (COLA) were introduced to help payments keep pace with inflation, a crucial step in preserving the purchasing power of recipients.
We understand that navigating these systems can be overwhelming. Recent discussions around the Assurance Fairness Act highlight ongoing efforts to address disparities in compensation calculations, particularly for disabled individuals. As of April 2025, about 7.2 million Americans receive disability benefits - a number that has steadily increased since the program began. This evolution showcases the program's adaptability in response to demographic shifts and economic challenges, ensuring it remains a vital resource for millions.
Looking ahead to 2026, proposed changes aim to broaden the program's reach, especially in disability insurance. Experts advocate for a more inclusive approach to support those in need. The history of this program illustrates its critical role in safeguarding against poverty and providing essential support to individuals facing various life challenges, akin to social security the new deal. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Navigate the Social Security System: Practical Steps for Today
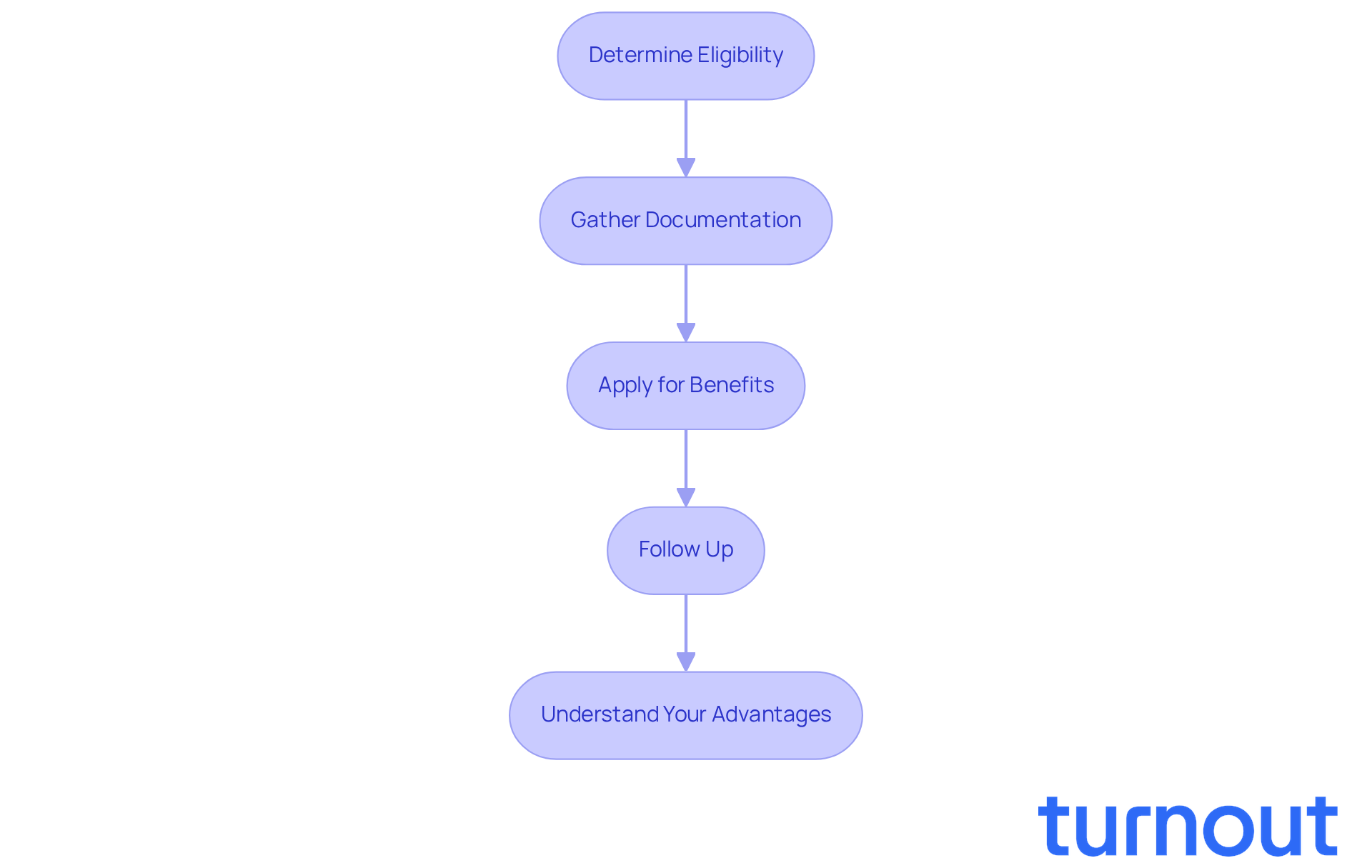
Navigating the social welfare system can feel overwhelming, but you’re not alone in this journey. Here are some practical steps to help you find your way:
-
Determine Eligibility: Start by assessing your qualifications for assistance based on your work history and current circumstances. The Social Security Administration (SSA) offers online tools to check your status. Remember, to qualify for retirement assistance, you need to be a legal, permanent resident of the U.S. for at least five years and have paid payroll taxes through a qualified job for a minimum of 10 years.
-
Gather Documentation: Collect the necessary documents, such as your Social Security number, proof of age, and work history. Having these ready is crucial for a smooth application process.
-
Apply for Benefits: You can apply online through the SSA website, by phone, or in person at your local SSA office. Make sure to complete all required forms accurately. Did you know that 67 percent of first SSDI applications are denied, often due to incomplete information? Turnout can assist you in this process by connecting you with trained nonlawyer advocates who can guide you through the SSD claims process. Just a reminder, Turnout is not a law firm and does not provide legal representation.
-
Follow Up: After applying, keep track of your application status and respond promptly to any requests for additional information. Processing times for SSDI applications typically average six to eight months. However, you might qualify for fast-track processes like Quick Disability Determinations (QDD) or Compassionate Allowances, which can expedite cases for severe health conditions.
-
Understand Your Advantages: Familiarize yourself with the types of benefits available, including retirement, disability, and survivor support. For instance, if you retire at age 62, you’ll receive only 70 percent of your full payout. On the other hand, delaying until age 70 can increase your monthly payment to 124 percent of the total amount.
By following these steps and utilizing Turnout's resources, you can confidently navigate the social security the new deal system and secure the benefits you deserve. Remember, we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Conclusion
The legacy of the New Deal, especially through the Social Security Act, has deeply influenced American social welfare. This initiative arose from the financial despair of the Great Depression, establishing a commitment to economic security that still resonates today. Roosevelt's principles aimed not just to provide immediate relief but also to redefine the government's role in protecting the financial well-being of its citizens.
We understand that navigating social welfare can feel overwhelming. Key arguments throughout this article illustrate how various New Deal programs, like the Civilian Conservation Corps and the Works Progress Administration, laid the foundation for the social safety net we depend on today. The evolution of Social Security - from its original focus on retirement to its expansion to include disability and healthcare - reflects our ongoing adaptation to societal needs. Continuous updates to the program, including proposed changes for 2026, highlight its vital role in addressing the challenges faced by millions of Americans.
As we look to the future, it’s crucial to understand and navigate the Social Security system. Empowering individuals with the knowledge and resources to access their benefits ensures that the foundational principles of the New Deal endure. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Embracing this legacy not only honors the past but also reinforces our commitment to a more secure and equitable future for all. We're here to help you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What was the Social Welfare Act and when was it enacted?
The Social Welfare Act, signed into law by President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1935, was a response to the financial struggles of the Great Depression, aimed at providing financial assistance to the elderly, unemployed, and disabled.
What were the key principles introduced by Roosevelt for old-age security?
Roosevelt introduced three key principles for old-age security: noncontributory pensions for the elderly, compulsory contributory annuities, and voluntary annuities.
What was the significance of the Social Welfare Act?
The Act marked a significant shift in the government's role, reflecting a commitment to protect citizens from financial hardships and underscoring the belief that financial security is a fundamental right.
Were there any criticisms of the Social Welfare Act?
Yes, critics, including Representative James W. Wadsworth, raised concerns that the Act might undermine work incentives and lead to bureaucratic control over finances.
How does the historical context of the Social Welfare Act relate to today's social security system?
Understanding the context of the Social Welfare Act highlights its lasting impact and the ongoing importance of social security during tough financial times, a principle that still resonates today.
What is the expected change in government assistance payments in 2026?
Government assistance payments are set to rise by 2.8 percent in 2026, indicating the program's continued significance in fostering economic stability.
How does Turnout assist individuals in accessing government benefits?
Turnout simplifies access to government benefits, especially for those navigating SSD claims, by providing trained nonlawyer advocates to help individuals pursue their rights to financial support without the complexities of legal representation.




