Introduction
Scoliosis affects millions, yet many may not realize the profound impact it can have on daily life and overall well-being. We understand that navigating the complexities of this spinal curvature can be overwhelming. That's why it's essential to grasp the types, health implications, and available support to manage your journey effectively.
Securing disability benefits for scoliosis can feel daunting. What are the key criteria? How can you effectively advocate for your needs? You're not alone in this. This article delves into the intricacies of scoliosis disability, offering valuable insights and guidance to empower you as you face this challenge. Remember, we're here to help.
Define Scoliosis: Types and Characteristics
Scoliosis is more than just a medical term; it’s a condition that affects many lives. Defined as an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine, it typically exceeds 10 degrees and influences around 2% to 3% of the population in the United States. That means an estimated 6 to 9 million individuals are grappling with idiopathic spinal curvature alone. Understanding the different types of scoliosis can help you navigate this journey with compassion and care.
Idiopathic Curvature of the Spine is the most common type, often identified in teenagers without a clear cause. We understand that early detection can significantly reduce the need for surgery, allowing for effective bracing treatment in many cases. Orthopedic specialists emphasize that tailored treatment approaches are crucial for managing this type effectively. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
Congenital Curvature of the Spine arises from spinal malformations during fetal development. Management often involves careful monitoring and may require surgery depending on the severity. A case study of a young patient showed that a combination of observation and timely surgical intervention can lead to successful outcomes. It’s common to feel anxious about the future, but there are paths to hope.
Neuromuscular Curvature is associated with conditions like cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy, affecting muscle control and leading to significant spinal deformities. Treatment typically focuses on addressing the underlying condition while managing scoliosis itself. Experts recommend a multidisciplinary approach to optimize outcomes for these patients. We’re here to help you find the right support.
Degenerative Scoliosis develops in adults due to age-related degeneration of the spine. This type often results from wear and tear, leading to chronic pain and impairment. Studies indicate that patients may benefit from both surgical and non-surgical management strategies. If you’re experiencing these challenges, know that there are options available.
Each type of spinal curvature presents unique challenges that can influence symptoms and may contribute to scoliosis disability. For instance, a study of over 100 patients who underwent surgery for adolescent idiopathic spinal curvature found that most reported a good quality of life two decades later. Incorporating insights from orthopedic specialists can guide effective management strategies tailored to your specific needs. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and support is available.
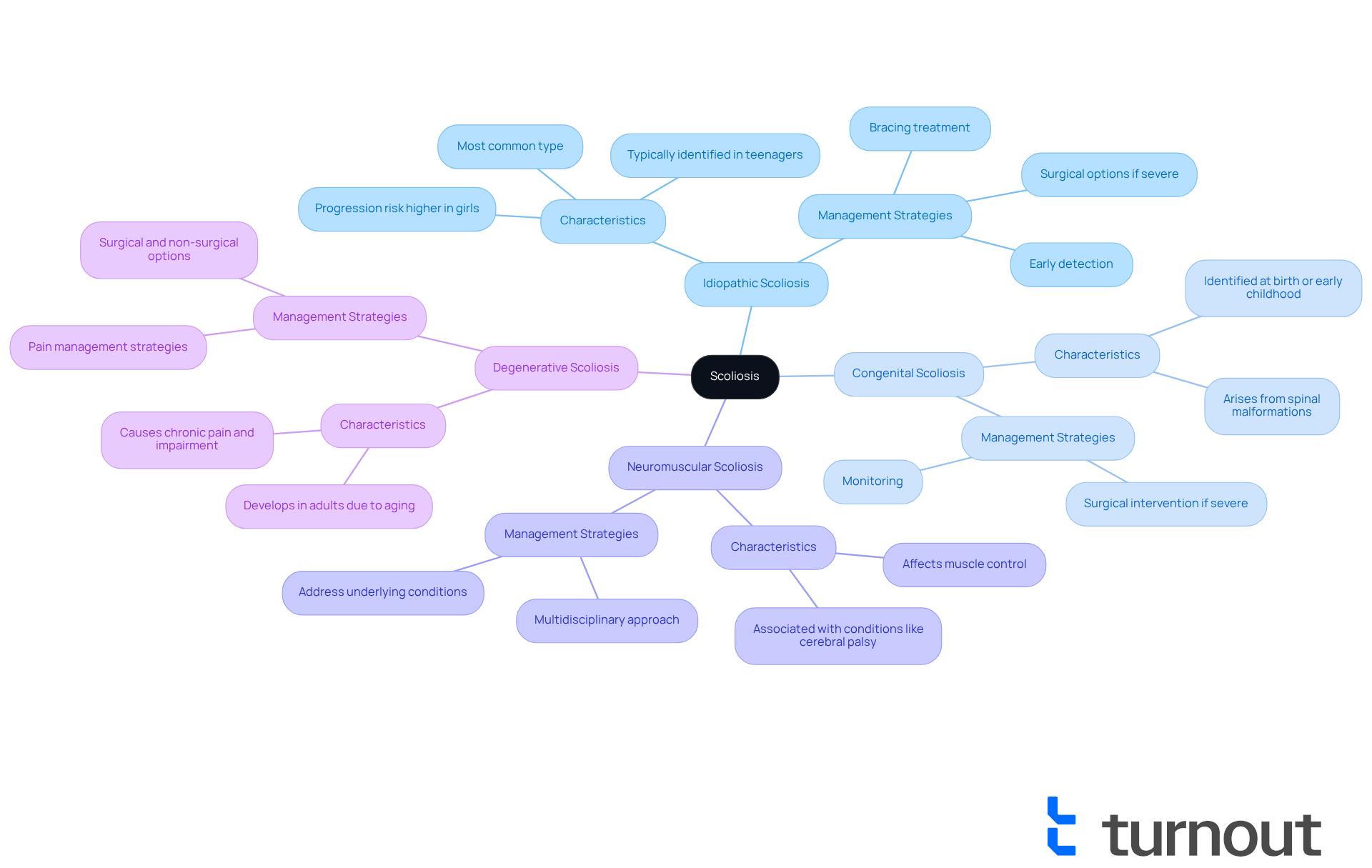
Evaluate Disability Criteria for Scoliosis
If you're facing challenges due to a spinal curvature, we understand how overwhelming it can feel. To qualify for disability benefits, it's essential to clearly demonstrate how your condition significantly impacts your ability to perform essential work activities. The Social Security Administration (SSA) evaluates scoliosis claims based on several key factors that can help you navigate this process:
-
Medical Documentation: Comprehensive medical records are crucial. This includes imaging studies like X-rays and MRIs that illustrate the severity of your spinal curvature. It's important that these documents detail any nerve compression or related complications you may be experiencing due to scoliosis disability.
-
Functional Limitations: You’ll need to provide evidence of how your scoliosis disability affects your daily activities. This includes documentation of mobility issues, pain levels, and your ability to perform job-related tasks, highlighting any specific restrictions you face.
-
Residual Functional Capacity (RFC): The SSA will evaluate your RFC to assess your ability to engage in any significant gainful activity despite your spinal condition. This assessment considers the severity of your symptoms and their impact on your work capabilities.
Successfully meeting these criteria is vital for a favorable outcome in your claim for scoliosis disability assistance. Remember, thorough and precise documentation can significantly enhance your chances of approval. You're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you every step of the way.
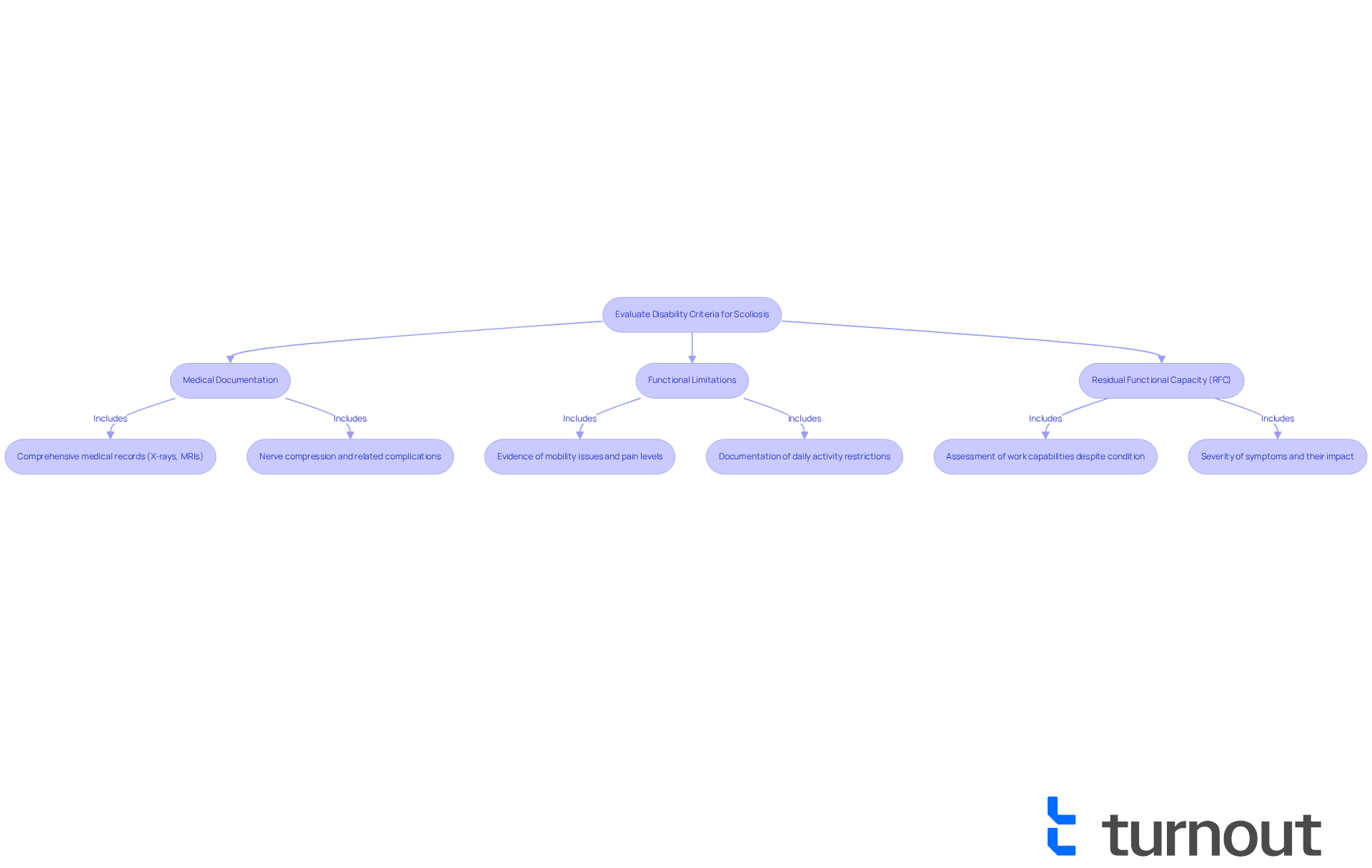
Navigate the Application Process for Disability Benefits
Navigating the application process for scoliosis disability benefits can feel overwhelming, but you’re not alone. We’re here to help you through each step with care and understanding.
-
Gather Necessary Documentation: Start by collecting your medical records. This includes treatment history and imaging studies like X-rays and MRIs that clearly show the severity of your condition. Remember, the SSA needs objective evidence to support your claim, so this documentation is crucial.
-
Complete the Application: When filling out the SSA's application form, take your time to ensure every section is completed accurately. You can apply online or visit your local SSA office. Attention to detail is vital here; incomplete applications can lead to delays or denials, and we want to avoid that for you.
-
Submit Your Claim: Once your application is ready, submit it along with all supporting documents. Don’t forget to keep copies for your records. This will help you track your submission and respond quickly to any requests from the SSA.
-
Follow Up: After you submit your application, it’s important to actively monitor its status. If the SSA requests additional information, be prepared to provide it promptly. Timely responses can really help speed up the review process.
-
Consider Representation: If your application is denied, don’t lose hope. Seeking assistance from a disability advocate or lawyer who specializes in cases involving scoliosis disability can significantly improve your chances of success. Professional representation can guide you through the complexities of the appeals process and ensure your case is presented effectively.
We understand that this journey can be challenging, but remember, you are not alone. Each step you take brings you closer to the support you deserve.
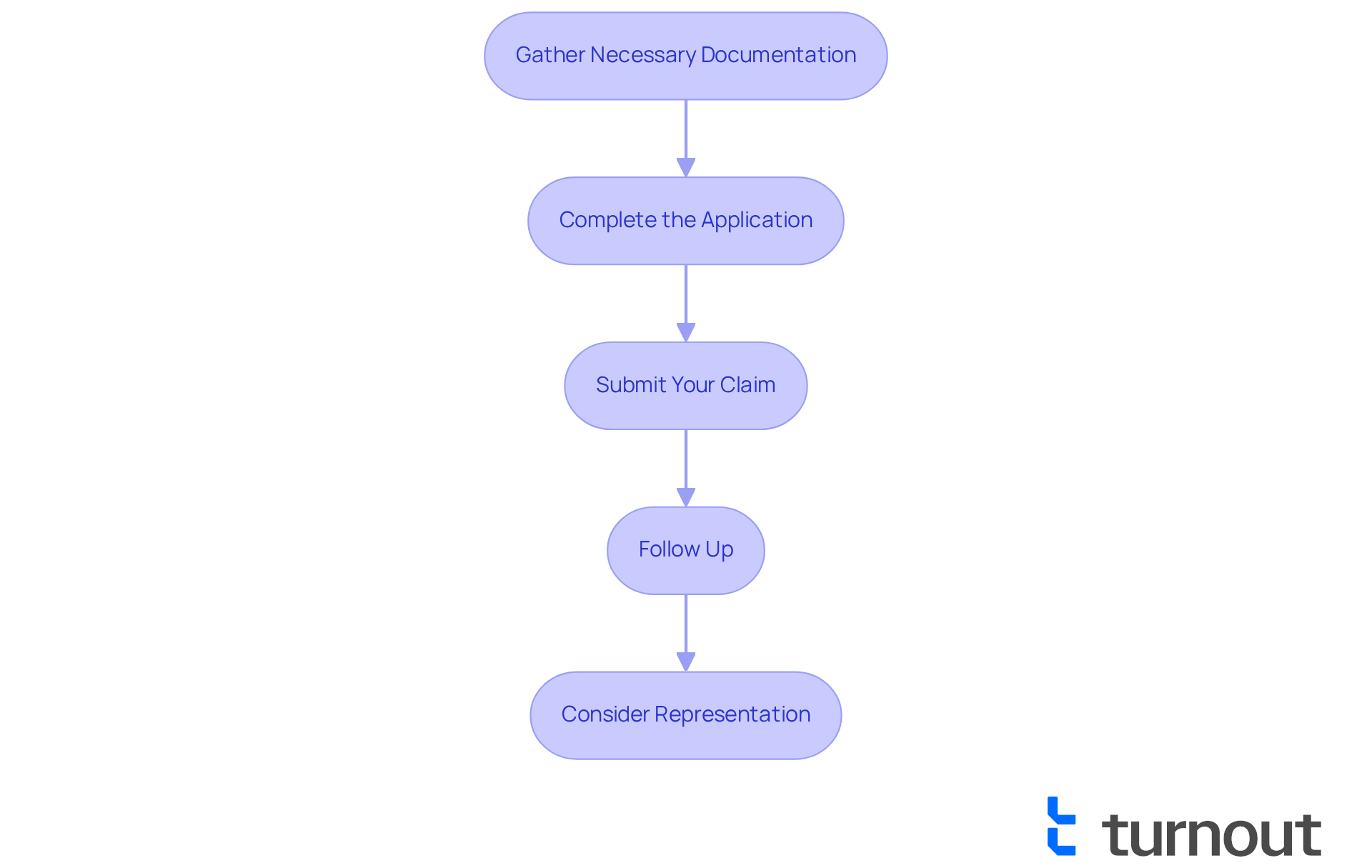
Understand Health Implications and Daily Life Impact
Scoliosis can deeply affect many aspects of daily life, and it’s important to recognize these challenges:
-
Physical Limitations: Severe curvature often leads to chronic pain and reduced mobility. Everyday tasks can become daunting, impacting both work and personal activities.
-
Emotional and Psychological Effects: The emotional toll can be significant. Many individuals experience anxiety, depression, or low self-esteem, especially when their spinal curvature affects their appearance or social interactions. It’s common to feel that the emotional impact can be just as debilitating as the physical symptoms, influencing overall quality of life.
-
Impact on Employment: Struggling to maintain stable employment is a reality for many with spinal curvature. Persistent pain and functional limitations can create financial strain. The inability to perform consistently may lead to job loss or reduced hours, which only adds to stress and anxiety.
-
Long-term Health Risks: If left untreated, scoliosis can lead to serious health complications, including respiratory issues and cardiovascular problems. These risks not only affect physical well-being but can also diminish overall quality of life.
Understanding these implications is crucial for those seeking benefits related to scoliosis disability. It highlights the need for support and resources tailored to your unique challenges. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help.
Conclusion
Scoliosis is more than just a medical condition; it profoundly affects the lives of millions. We understand that navigating this journey can be overwhelming. By recognizing the different types of scoliosis - idiopathic, congenital, neuromuscular, and degenerative - you can better explore your treatment options and find the support you need. Each type brings its own challenges, highlighting the importance of personalized management strategies. Remember, help is always available.
When it comes to securing disability benefits for scoliosis, understanding the criteria set by the Social Security Administration is crucial. Key factors like medical documentation, functional limitations, and residual functional capacity are essential in the evaluation process. By carefully gathering evidence and following the application steps, you can significantly improve your chances of receiving the support you deserve.
It's vital to acknowledge the deep health implications and daily life impacts of scoliosis. From physical limitations to emotional hurdles, this condition can touch many aspects of your life, including your job and overall well-being. Seeking assistance and understanding your rights to disability benefits can lead to a more manageable future. Embracing this journey with the right resources and support can truly enhance your quality of life. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is scoliosis?
Scoliosis is defined as an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine that typically exceeds 10 degrees, affecting around 2% to 3% of the population in the United States, which translates to an estimated 6 to 9 million individuals with idiopathic spinal curvature.
What are the main types of scoliosis?
The main types of scoliosis include idiopathic scoliosis, congenital scoliosis, neuromuscular scoliosis, and degenerative scoliosis.
What is idiopathic scoliosis?
Idiopathic scoliosis is the most common type, often identified in teenagers without a clear cause. Early detection can significantly reduce the need for surgery, allowing for effective bracing treatment.
How is congenital scoliosis managed?
Congenital scoliosis arises from spinal malformations during fetal development and is managed through careful monitoring. Depending on the severity, it may require surgical intervention.
What is neuromuscular scoliosis?
Neuromuscular scoliosis is associated with conditions like cerebral palsy or muscular dystrophy, affecting muscle control and leading to significant spinal deformities. Treatment focuses on addressing the underlying condition while managing scoliosis.
What causes degenerative scoliosis?
Degenerative scoliosis develops in adults due to age-related degeneration of the spine, often resulting from wear and tear, which can lead to chronic pain and impairment.
What are the treatment options for scoliosis?
Treatment options vary by type of scoliosis and may include bracing, surgical intervention, and non-surgical management strategies. A multidisciplinary approach is often recommended to optimize outcomes.
How can scoliosis impact quality of life?
Each type of scoliosis presents unique challenges that can influence symptoms and contribute to scoliosis-related disability. However, studies indicate that many patients report a good quality of life even years after surgical intervention.




