Introduction
Tax penalties can feel overwhelming, creating a sense of dread and confusion as you navigate the complexities of compliance. We understand that these financial burdens can weigh heavily on your mind. It's crucial to grasp the implications of failing to pay taxes, as the consequences can escalate quickly, affecting both your finances and legal standing.
With the IRS increasing enforcement and rolling out new regulations, you might wonder: how can you effectively shield yourself from these penalties? How can you maintain control over your financial obligations? This article is here to help. We’ll delve into the intricacies of tax penalties, offering insights and strategies designed to help you avoid unnecessary stress and navigate your tax responsibilities with confidence. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
Define Tax Penalties and Their Importance
Tax fines can feel overwhelming, can't they? These financial charges, imposed by the IRS or state tax authorities, may include a penalty for not paying taxes when taxpayers struggle to comply with tax laws. Whether it’s failing to file a tax return, underreporting income, or missing a payment deadline, these fines can add significant pressure to your finances.
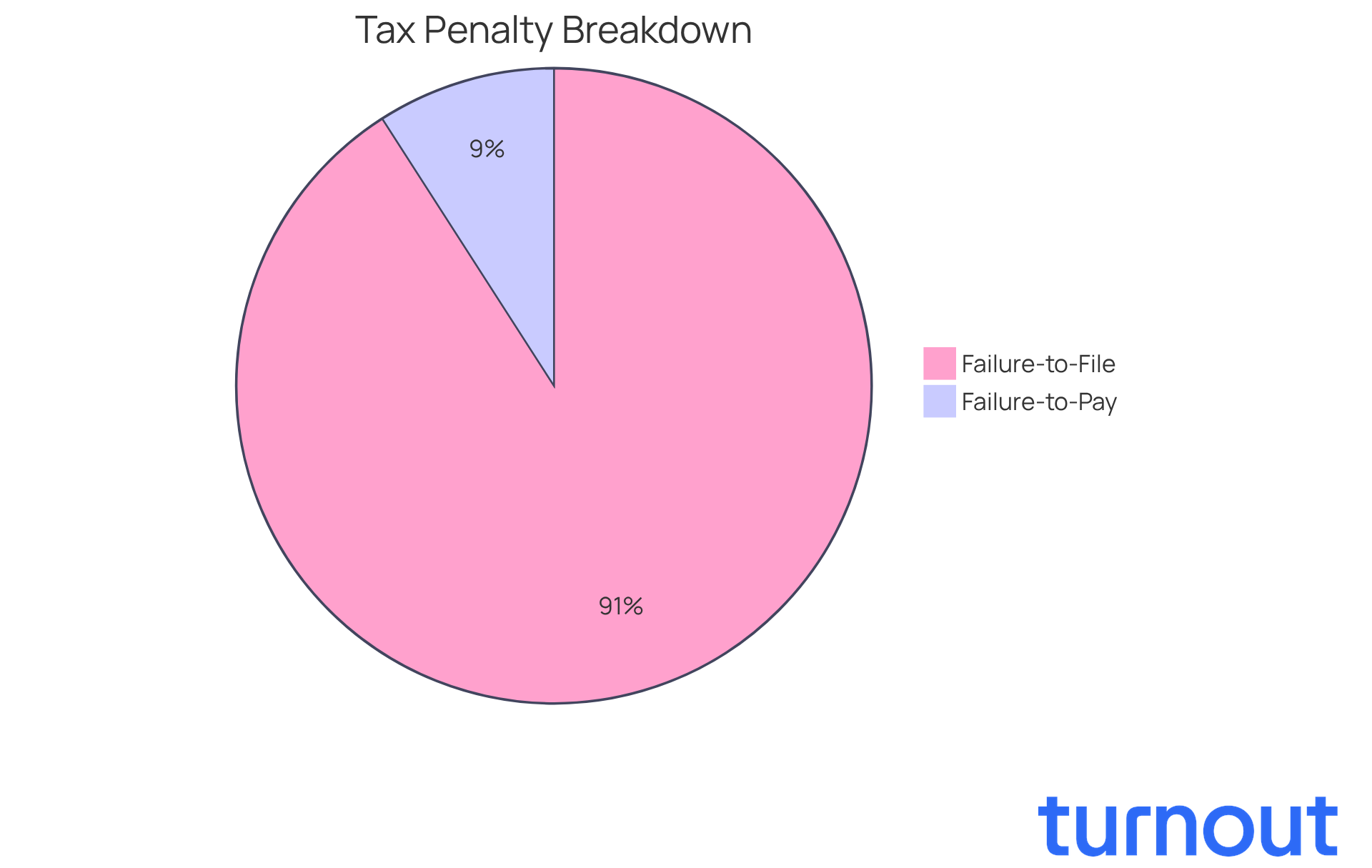
For example, did you know that the failure-to-file fee is typically 5% of the unpaid tax for each month your return is late? Meanwhile, the failure-to-pay charge is 0.5% of the unpaid tax per month, capped at 25%. It’s common to feel anxious about these penalties, especially with the IRS acknowledging in 2025 that many individuals may not have the systems in place to meet new reporting requirements. This highlights just how important it is to stay informed about your tax obligations to avoid unnecessary financial burdens.
Real-world examples show the repercussions of non-compliance. Individuals who don’t file their taxes often face a penalty for not paying taxes, which can worsen their financial challenges. Fortunately, under the One Big Beautiful Bill Act, the IRS is offering relief from fines for employers, reflecting the situations many individuals face.
Experts emphasize that understanding tax repercussions not only aids in compliance but also empowers you to make informed financial choices. This knowledge can promote a more stable economic environment for everyone. With marginal tax rates for the tax year 2026 likely to impact many taxpayers, being aware of these consequences is more vital than ever. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you navigate these challenges.
Explore Types of Tax Penalties: Civil vs. Criminal
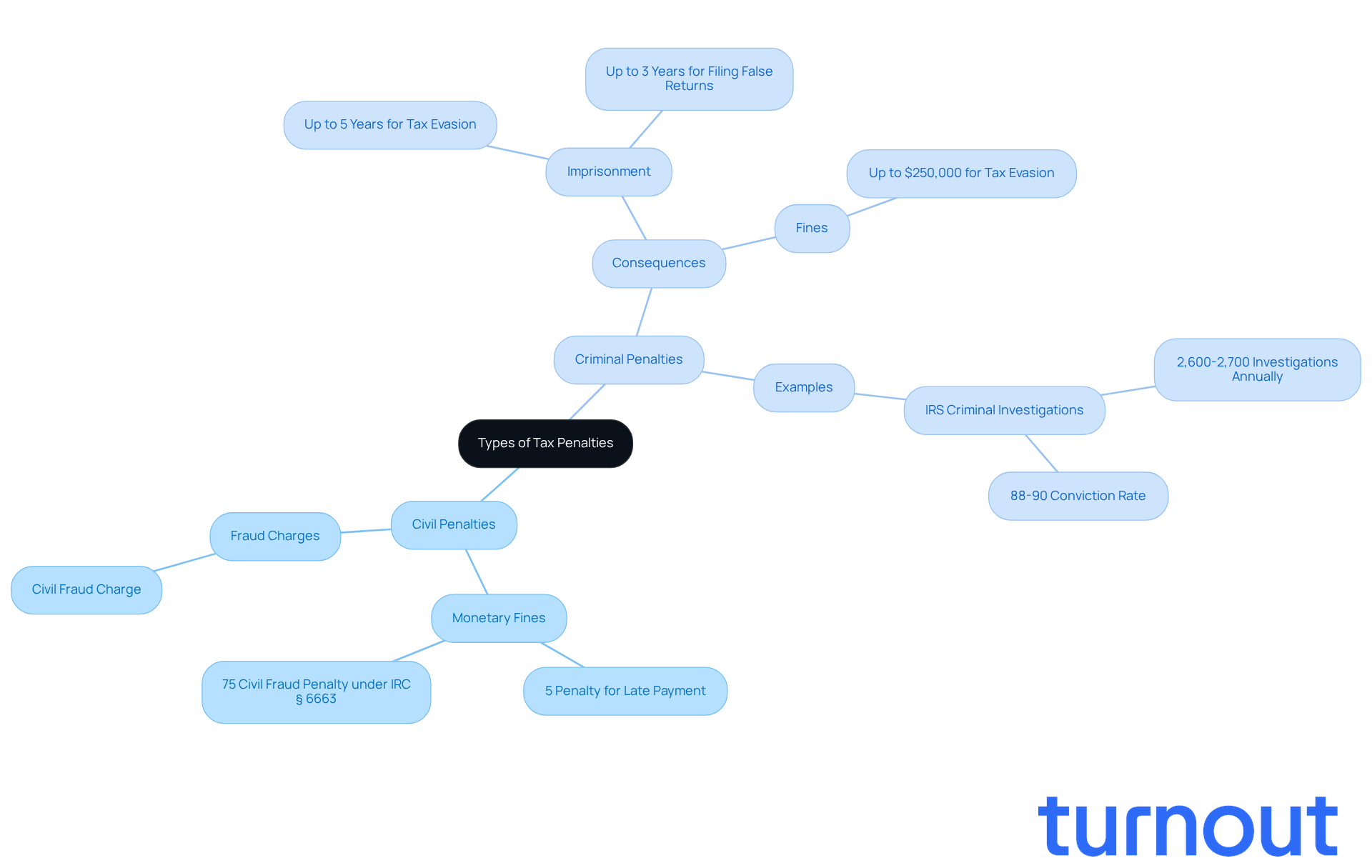
Tax fines can feel overwhelming, and understanding them is crucial for every taxpayer. They fall into two main categories: civil and criminal. Civil sanctions usually involve monetary fines, such as a penalty for not paying taxes on time. For example, the IRS might impose a civil charge of 5% of the unpaid tax for each month a return is delayed. Additionally, if fraud is involved, the civil fraud charge under IRC § 6663 can reach a staggering 75% of the underpayment, which can significantly increase the financial burden on individuals.
On the flip side, criminal sanctions carry much heavier consequences, including the possibility of imprisonment for tax fraud or evasion. These charges require proof of willful intent to defraud the government, which can lead to hefty fines and jail time. For instance, tax evasion under 26 U.S.C. § 7201 can result in up to five years in prison and fines as high as $250,000. It's important to note that the IRS Criminal Investigation division initiates around 2,600-2,700 criminal investigations each year, showing how rare criminal prosecutions are compared to the total number of tax returns filed. Moreover, the conviction rate for criminal tax prosecutions is about 88-90%, illustrating the challenges individuals face in these situations.
We understand that navigating these categories of fines can be daunting. Civil fines often allow for resolution through payment, enabling individuals to correct their tax situations and avoid the penalty for not paying taxes without long-term repercussions. However, the implications of criminal charges can be life-altering, affecting not just freedom but future opportunities as well. As the IRS wisely states, "If you come forward to the IRS before they start investigating you, you may be able to resolve your tax problems civilly rather than criminally."
Engaging a tax attorney early in the process can be a vital step. They can provide the guidance you need to navigate these complexities and help mitigate potential risks. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we're here to help.
Understand Consequences of Tax Penalties: Financial and Legal Impacts
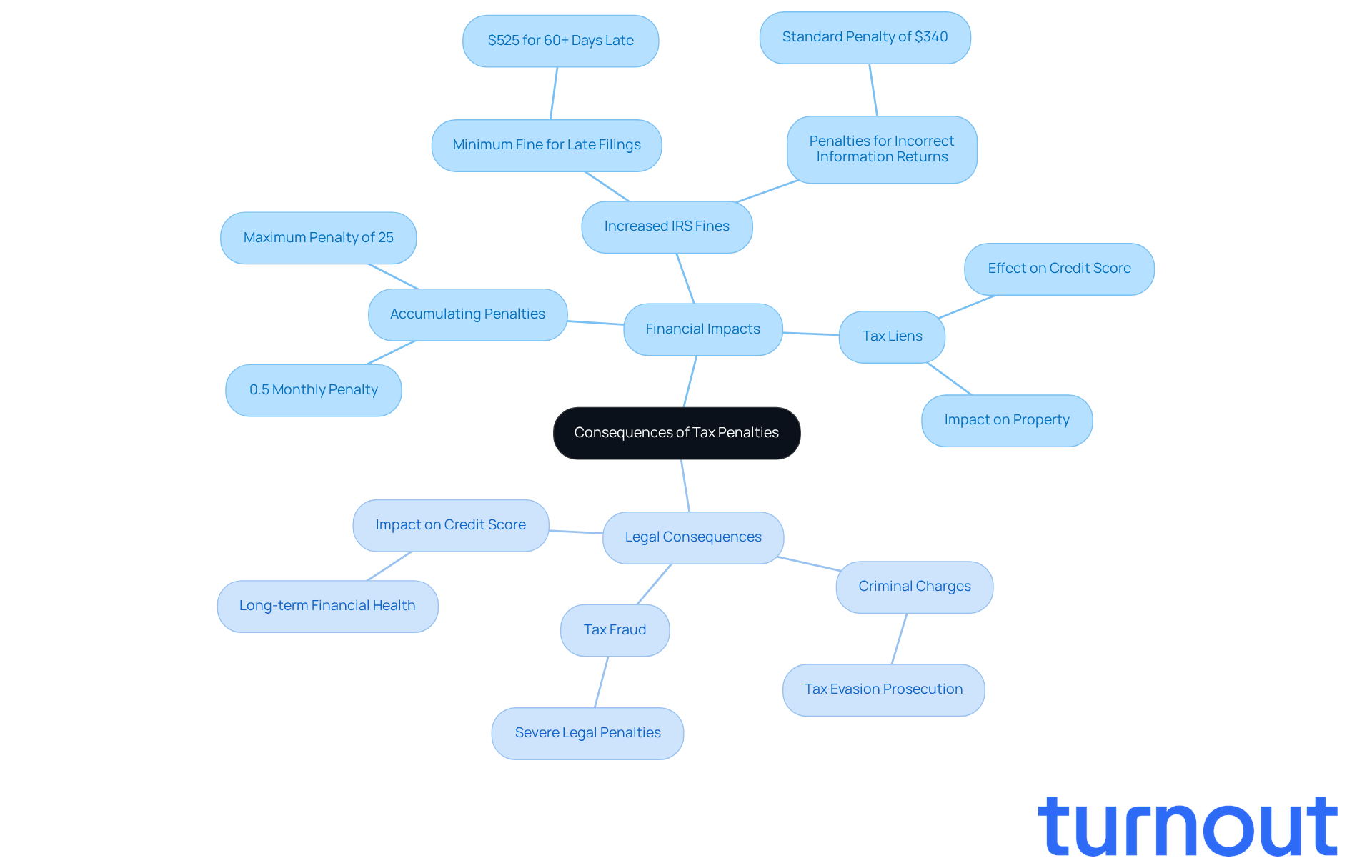
The penalty for not paying taxes can lead to serious financial and legal challenges, and we understand how overwhelming that can feel. Financially, the penalty for not paying taxes can accumulate quickly, making the total amount owed much larger than expected. For example, if you owe $1,000 in taxes and miss the payment deadline, you might be subjected to a penalty for not paying taxes of 0.5% on the unpaid tax each month. This can result in a penalty for not paying taxes that adds up to a maximum of 25% of what you owe. In 2025, the IRS has increased the minimum fine for individual filers who submit returns over 60 days late to $525, up from $510 in 2024. This change highlights the importance of staying on top of your tax obligations.
Legally, not complying with tax laws can lead to severe consequences, including a penalty for not paying taxes and criminal charges for tax fraud. Such violations can lead to severe consequences, including a penalty for not paying taxes and even imprisonment. Additionally, if you incur a penalty for not paying taxes, tax liens may be placed on your property, which can hurt your credit score and overall financial health. With recent IRS enforcement actions ramping up due to increased federal funding, more individuals are facing audits, liens, wage garnishments, and the penalty for not paying taxes. Understanding these potential consequences is crucial, especially the penalty for not paying taxes.
Timely action can help reduce these risks. Sharon Goldstein-Shapiro, a spokesperson for Legal Tax Defense, emphasizes the importance of seeking help before things escalate. She notes, "People often wait until the IRS freezes their bank account or withholds their wages before asking for help." Understanding these possible outcomes is vital for recognizing the importance of compliance and taking proactive steps to avoid the penalty for not paying taxes.
If you find yourself in a tough spot, remember: you’re not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you navigate these challenges and find the best solutions.
Implement Strategies to Avoid Tax Penalties
To avoid the penalty for not paying taxes, we recognize that taxpayers often feel overwhelmed. But there are several effective strategies you can implement to ease your worries:
-
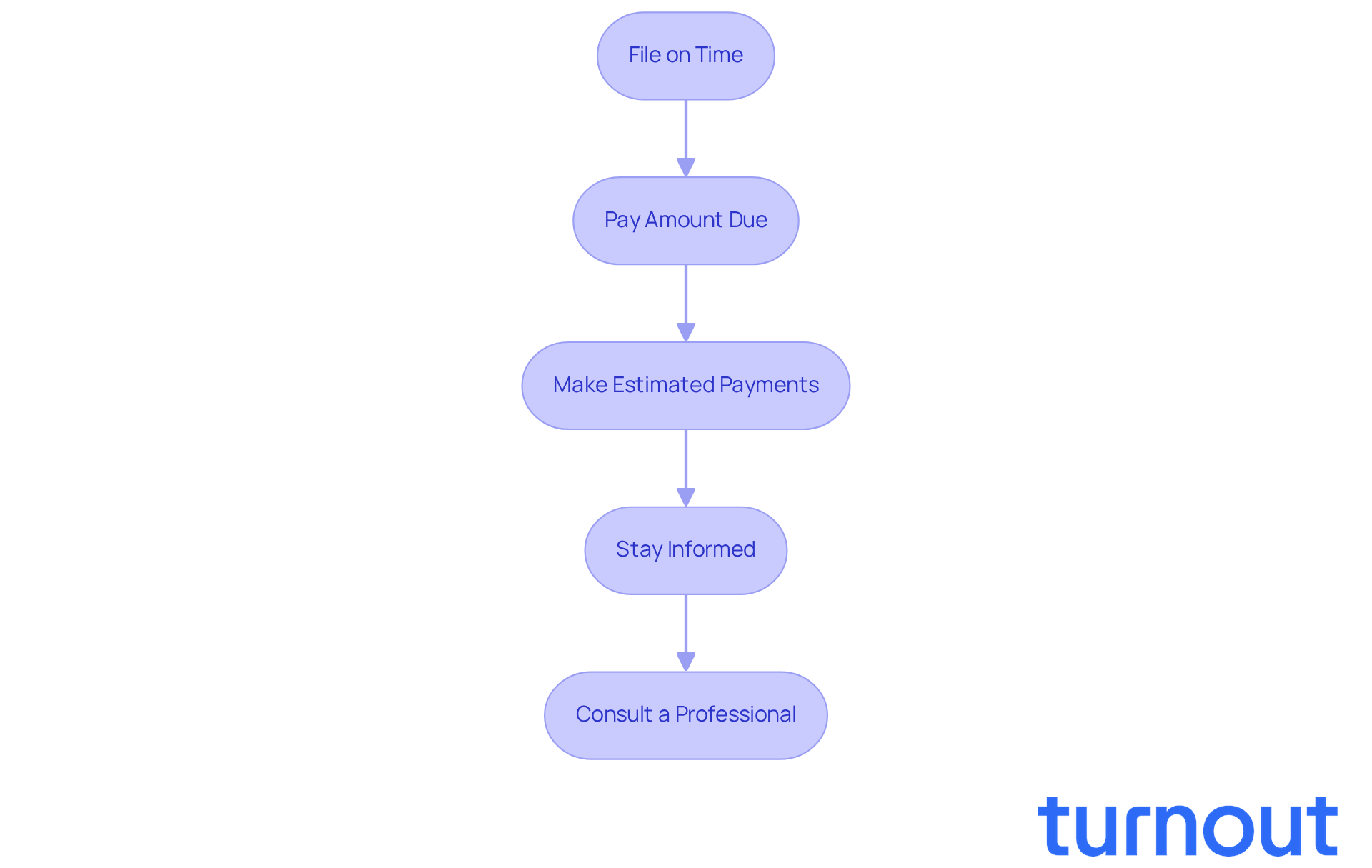
File on Time: Always submit your tax returns by the due date, even if you can’t pay the full amount owed. Missing the deadline can lead to a failure-to-file charge of 5% of the unpaid tax per month, up to a maximum of 25%. It’s common to feel anxious about deadlines, but staying on top of them can save you from unnecessary stress.
-
Pay Amount Due: If possible, settle your dues in full by the due date. This helps you avoid the failure-to-pay charge, which is 0.5% of unpaid amounts each month. If the IRS issues a notice of intent to levy, this charge rises to 1%. We know that financial burdens can be heavy, but addressing them promptly can lighten your load.
-
Make Estimated Payments: If you expect to owe taxes, consider making estimated payments throughout the year. Failing to do so can result in a 7% non-deductible penalty for each underpaid installment. Remember, planning ahead can help you avoid surprises down the road.
-
Stay Informed: Keeping up with tax law changes and deadlines is crucial for compliance. The IRS has revamped various notifications to enhance clarity and accessibility, which can assist you in staying informed. We’re here to help you navigate these changes.
-
Consult a Professional: If you’re unsure about your tax situation, consulting a tax professional can provide clarity and help you navigate complex tax laws. More than half of individuals seek assistance from tax professionals to avoid potential pitfalls. You are not alone in this journey; seeking help is a wise step.
By following these strategies, you can significantly reduce your risk of incurring a penalty for not paying taxes and maintain better control over your financial obligations. Remember, we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Understanding the penalties associated with not paying taxes is crucial for your financial well-being and compliance with tax laws. We know that tax penalties can weigh heavily on individuals, whether it’s through civil fines for late filings or more serious criminal charges for tax evasion. By grasping these concepts, you can navigate your obligations more effectively and avoid unnecessary financial strain.
Throughout this article, we’ve shared key insights about the types of tax penalties - civil and criminal - and the consequences of failing to meet your tax obligations. Civil penalties often come in the form of monetary fines, while criminal penalties can lead to severe legal ramifications, including imprisonment. It’s essential to file on time, make estimated payments, and seek professional guidance. These strategies can help you steer clear of penalties.
Ultimately, understanding tax penalties is vital. By staying informed and proactive, you can protect yourself from financial and legal repercussions while fostering a more stable economic environment. Engaging with tax professionals and implementing effective practices can make a significant difference in navigating the complexities of tax compliance. Remember, taking these steps today can lead to a more secure financial future tomorrow. You are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are tax penalties?
Tax penalties are financial charges imposed by the IRS or state tax authorities for failing to comply with tax laws, which can include not filing a tax return, underreporting income, or missing a payment deadline.
What are the common types of tax penalties?
Common types of tax penalties include the failure-to-file fee, which is typically 5% of the unpaid tax for each month the return is late, and the failure-to-pay charge, which is 0.5% of the unpaid tax per month, capped at 25%.
Why is it important to understand tax penalties?
Understanding tax penalties is important because it helps individuals comply with tax laws and avoid unnecessary financial burdens, promoting informed financial choices and a more stable economic environment.
What relief is available for tax penalties under the One Big Beautiful Bill Act?
Under the One Big Beautiful Bill Act, the IRS is offering relief from fines for employers, acknowledging the financial challenges many individuals face.
How can tax penalties impact individuals financially?
Tax penalties can significantly pressure individuals' finances, especially for those who do not file their taxes, as the penalties can worsen their financial challenges.
What should taxpayers be aware of regarding future tax obligations?
Taxpayers should be aware of their obligations, especially with changes like the marginal tax rates for the tax year 2026, which may impact many taxpayers. Staying informed can help avoid penalties.




