Overview
This article addresses the important requirements and steps for reporting income received through Zelle, particularly focusing on the use of Form 1099-K. While Zelle does not issue this form, it’s essential to understand that any earnings over $600 must still be reported. We recognize that navigating these regulations can feel overwhelming, but we’re here to guide you through the necessary documentation and accurate reporting practices.
In addition to providing clarity, the article highlights common mistakes to avoid, ensuring that you can remain compliant with IRS regulations. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; many individuals face similar challenges. By following our guidance, you can approach your reporting with confidence and peace of mind.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of tax reporting can often feel daunting, especially regarding digital payment platforms like Zelle. We understand that as more individuals and businesses turn to these services for quick and convenient transactions, the tax implications can be overwhelming. This guide delves into the essential steps for accurately reporting Zelle income on Form 1099-K. It highlights the importance of meticulous record-keeping and compliance with IRS regulations.
With the looming changes in reporting requirements set for 2025, it's common to feel uncertain. Are you prepared to meet these new standards, or do you worry about the risks of facing penalties for underreporting your earnings? You're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you navigate these challenges with confidence.
Understand Zelle and Its Tax Reporting Requirements
This digital payment service offers a convenient way for you to transfer and receive funds quickly through your bank's application. However, we understand that navigating the world of taxes can be daunting. It's important to recognize that any funds received through this service may require tax reporting, including reporting on Zelle 1099 K. According to IRS guidelines, if you receive over $600 in a calendar year through a digital payment service, such as Zelle, you are required to report this income with a Zelle 1099 K.
While this service does not issue Form 1099-K, typically provided by payment processors, it also does not send details or tax forms to the IRS. This means that the responsibility for accurate reporting rests entirely on you. Keeping thorough records of all your transactions throughout the year is crucial for preparing your tax return. Remember, failing to report qualifying business revenue can lead to penalties, including a 20% negligence charge from the IRS.
Looking ahead, it's important to note that as of 2025, the IRS will require peer-to-peer payment apps to issue Zelle 1099-K statements for self-employed workers receiving more than $5,000 in payments. This change further emphasizes the need for diligent recordkeeping. Understanding these requirements is vital for ensuring compliance and avoiding potential penalties. You are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you navigate these challenges.
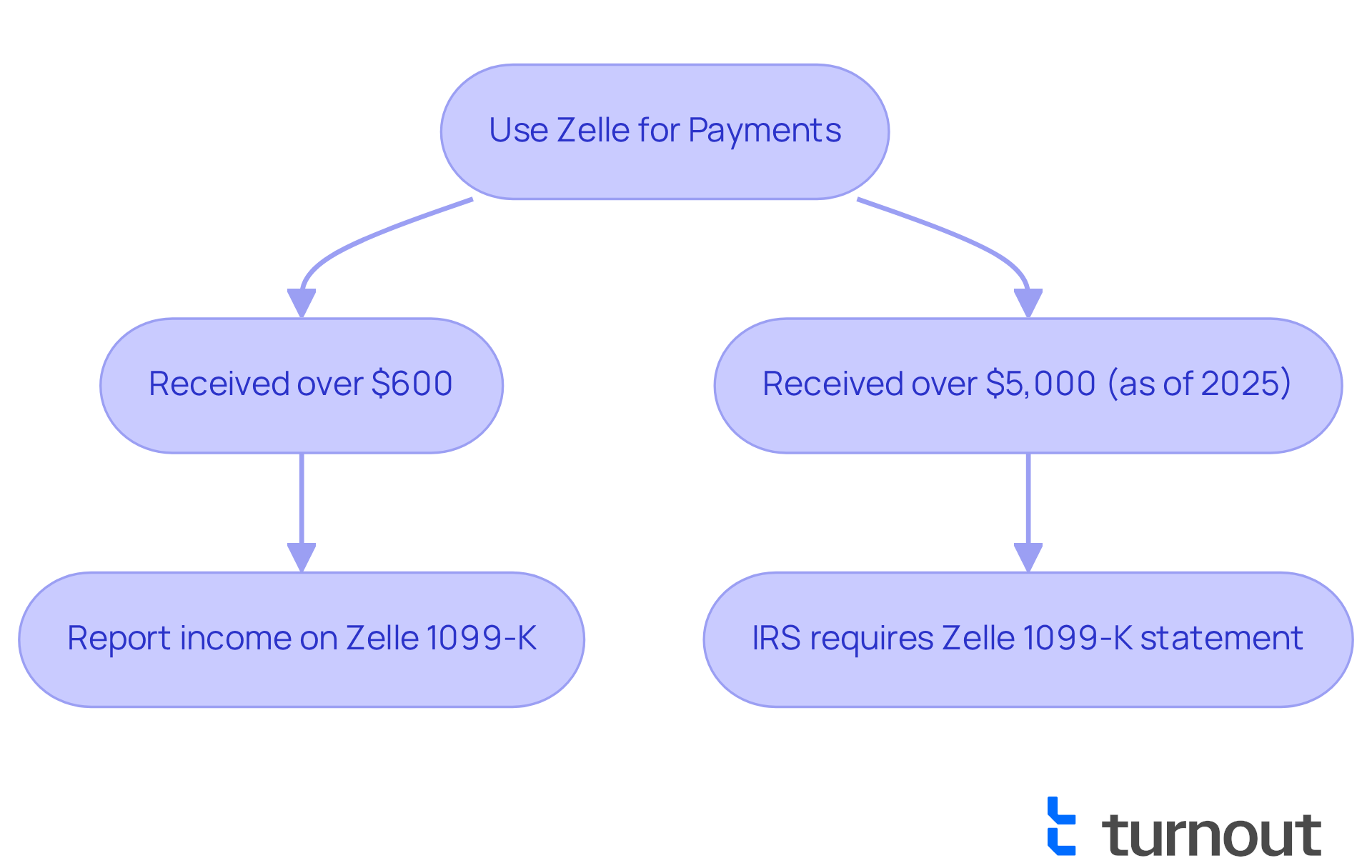
Gather Necessary Documentation for Reporting Zelle Income
To report your Zelle income accurately, especially for the Zelle 1099 K, it's important to gather the right documentation. We understand that navigating this process can feel overwhelming, but we’re here to help you every step of the way. Here are some key documents to consider:
- Payment Records: Keeping a comprehensive log of all payments made through Zelle, including dates, amounts, and purposes, will help you monitor your earnings efficiently.
- Bank Statements: Make sure to acquire bank statements that show electronic transfer transactions. These will serve as verification of your earnings and can be referenced during tax preparation.
- Invoices or Receipts: If applicable, gather any invoices or receipts related to the services or products for which you received payment through Zelle. This documentation is essential for validating your earnings.
- Form 1099-K: While Zelle does not provide tax documents, if you meet the reporting threshold, ensure you receive Form 1099-K from your bank or payment processor. This form summarizes your earnings from the service for the year.
It's common to feel uncertain about what needs to be reported. Remember, personal transactions conducted via Zelle do not require reporting as earnings, but all business revenue must be recorded. Organizing these documents will streamline the reporting process and provide necessary evidence if questioned by tax authorities.
Neglecting to declare earnings from digital payments can lead to significant legal repercussions. For instance, if you received $21,000 from one client via a 1099-K and $1,000 from another client, you would report a total of $22,000 on your tax return, including the Zelle 1099 K. Additionally, be aware that the 1099-K reporting threshold is changing, which may affect your responsibilities soon. Keeping separate accounts for personal and business transactions can further simplify your record-keeping efforts.
You are not alone in this journey; we’re here to support you.
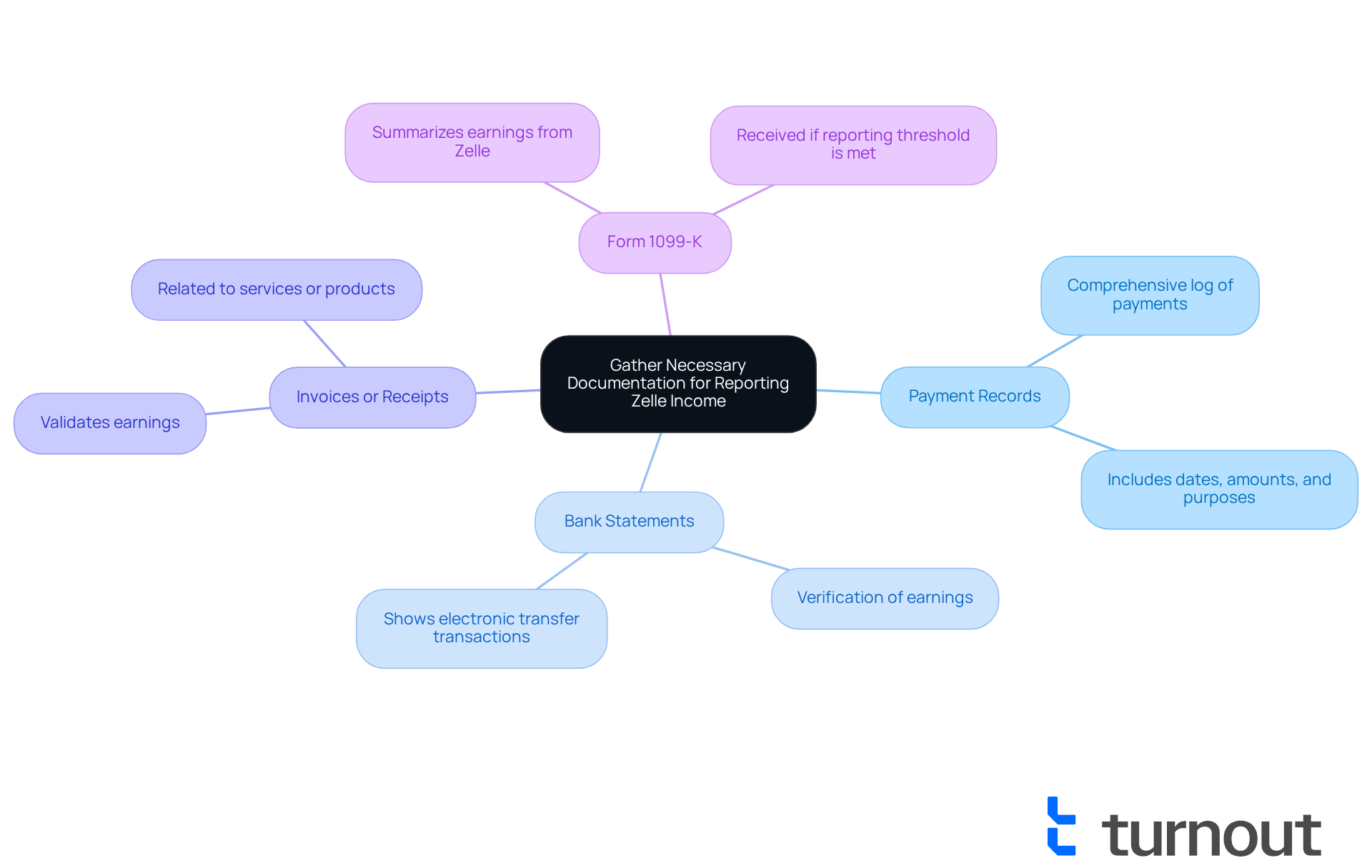
Report Your Zelle Income on Form 1099-K and Other Tax Forms
To accurately report your Zelle income, we understand that it can feel overwhelming. Here are some essential steps to help you navigate this process with confidence:
-
Understand Reporting Requirements: It's important to know that Zelle 1099 K is not issued, as Zelle is not classified as a payment settlement entity. If you earn more than $600 from additional sources, you need to declare this revenue on your tax return. Remember, all earnings obtained through this payment service for goods or services are taxable, even without a Zelle 1099 K form. Think of transactions with this service as cash; all earnings from goods or services received through this platform are taxable.
-
Complete Your Tax Return: If you are self-employed, report your payments received via Zelle on Schedule C. If not, include it on your personal tax return (Form 1040). Ensure that you consider all revenue sources to provide a comprehensive overview of your earnings. This thorough approach helps you feel more secure about your reporting.
-
Document Additional Earnings: If you have other revenue sources, report them alongside your Zelle earnings. This comprehensive method can help prevent inconsistencies that might lead to an audit. The IRS can detect unreported earnings through bank inspections or lifestyle indicators, so it’s best to be thorough.
-
Maintain Accurate Records: Keeping copies of all relevant forms and documentation, including transaction logs and bank statements, is crucial. This practice not only aids in future reference but also protects you in the event of an audit. You are taking proactive steps to safeguard your financial health.
-
Consult a Tax Expert: Given the complexities of reporting digital payments, consider seeking advice from a tax expert. They can guide you on how to report earnings from digital transactions accurately, helping you navigate the nuances of tax regulations and ensuring compliance.
By following these steps, you can confidently declare your earnings and maintain compliance with IRS regulations. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you reduce the risk of penalties related to underreporting.
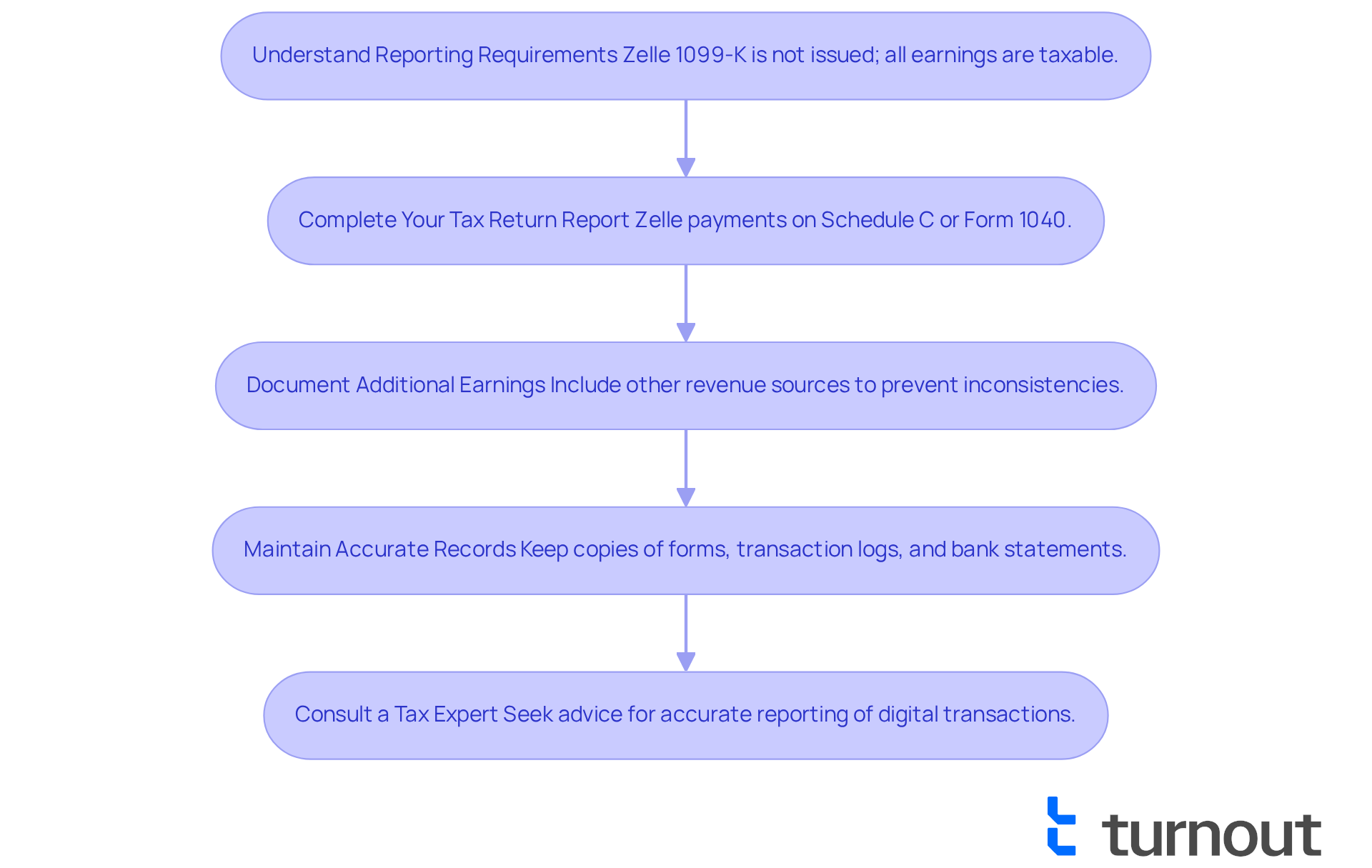
Avoid Common Mistakes When Reporting Zelle Income
To help you avoid common mistakes when reporting your Zelle income, we want to share some supportive tips:
-
Don’t Overlook Small Deals: Even if a deal seems minor, remember that if it contributes to your total income exceeding $600, it must be reported. It’s common to feel uncertain about what counts, but statistics show many taxpayers overlook minor financial activities, leading to issues with the IRS.
-
Ensure Accuracy: We understand how overwhelming tax forms can be. Double-checking all figures is essential to avoid discrepancies that could trigger an audit. Good bookkeeping practices are your allies in achieving precise tax reporting related to digital payments.
-
Keep Personal and Business Activities Distinct: If you use Zelle for both personal and business purposes, maintaining clear records is crucial. This distinction will help you avoid confusion and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
-
File on Time: It’s important to file your tax return by the deadline to avoid penalties for late filing. We’re here to help you stay on track!
By being aware of these common mistakes, you can navigate the reporting process more smoothly and confidently. Remember, the responsibility for accurate reporting lies with you. If you’re uncertain which payments qualify as taxable income or need assistance organizing your digital transfers, consider consulting a CPA or enrolled agent. Proactive management of your Zelle 1099 k transactions is crucial to avoid potential back taxes, interest, and penalties. You are not alone in this journey!
Conclusion
Understanding the tax implications of using Zelle is crucial for anyone engaging in digital transactions. We understand that the responsibility of reporting income received through this platform can feel overwhelming. Especially with the IRS updating its guidelines regarding reporting thresholds, it's common to feel uncertain about what to do next. With the impending changes in 2025, where peer-to-peer payment apps will be required to issue Zelle 1099-K statements for payments exceeding $5,000, being proactive about recordkeeping and compliance is more important than ever.
Throughout this guide, we’ve outlined essential aspects of Zelle income reporting, including the necessity of maintaining accurate documentation and understanding the reporting requirements. Avoiding common pitfalls is key. We emphasize strategies such as:
- Distinguishing between personal and business transactions
- Ensuring thorough recordkeeping
- Consulting tax professionals
By being diligent and informed, you can confidently meet your tax obligations and minimize the risk of penalties.
Ultimately, the significance of mastering Zelle 1099-K reporting cannot be overstated. As digital payments become increasingly prevalent, understanding the associated tax responsibilities is vital for your financial health and compliance. Taking the necessary steps now to prepare for future requirements will not only simplify the reporting process but also empower you to manage your finances effectively. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; embrace the steps to mastering your Zelle transactions and ensure that you are well-equipped to meet the challenges ahead.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Zelle and how does it work?
Zelle is a digital payment service that allows users to transfer and receive funds quickly through their bank's application.
Do I need to report income received through Zelle?
Yes, if you receive over $600 in a calendar year through Zelle, you are required to report this income using a Zelle 1099-K.
Does Zelle issue Form 1099-K?
No, Zelle does not issue Form 1099-K, which is typically provided by payment processors.
Who is responsible for reporting income received via Zelle?
The responsibility for accurate reporting rests entirely on you, as Zelle does not send details or tax forms to the IRS.
What are the consequences of failing to report qualifying business revenue from Zelle?
Failing to report qualifying business revenue can lead to penalties, including a 20% negligence charge from the IRS.
What changes are coming regarding tax reporting for Zelle in 2025?
Starting in 2025, the IRS will require peer-to-peer payment apps to issue Zelle 1099-K statements for self-employed workers receiving more than $5,000 in payments.
Why is recordkeeping important for Zelle transactions?
Keeping thorough records of all your transactions throughout the year is crucial for preparing your tax return and ensuring compliance with tax reporting requirements.




