Introduction
Navigating the complexities of tax debt can feel overwhelming, especially when you’re facing the prospect of IRS back taxes. We understand that this can be a challenging time, and knowing the various payment plans available is crucial for anyone looking to regain control over their financial obligations. This guide offers a step-by-step approach to mastering IRS payment plans, empowering you to choose the best option tailored to your unique circumstances.
With so many choices and eligibility requirements, it’s common to feel uncertain. How can you ensure you’re making the right decision to avoid penalties and pave the way to financial stability? Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. We're here to help you navigate these waters with confidence.
Understand IRS Payment Plans for Back Taxes
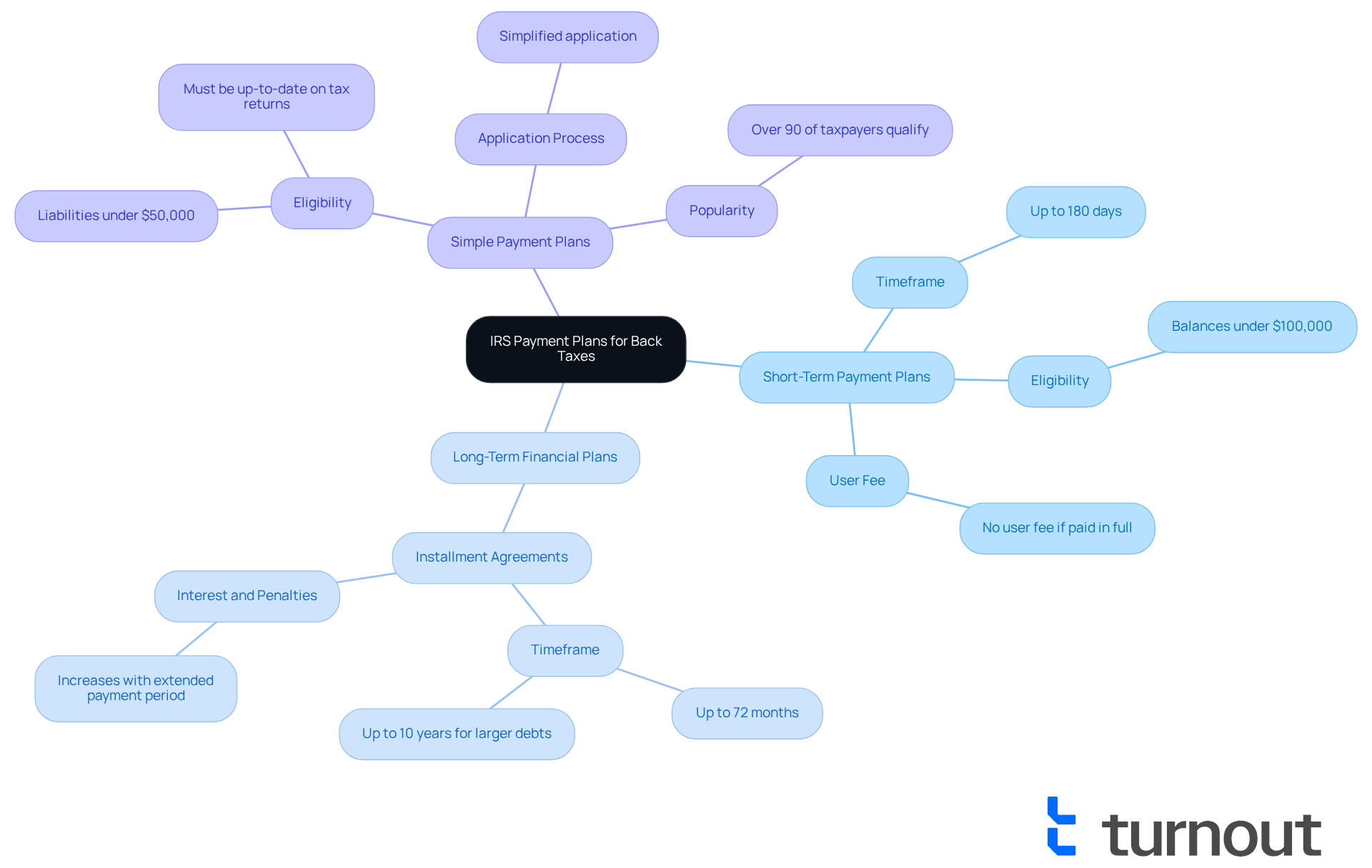
The IRS provides an IRS back taxes payment plan along with various financial arrangements to help you manage your overdue taxes effectively. We understand that dealing with tax debt can be overwhelming, and familiarizing yourself with these options is crucial for finding a resolution. Here are the primary types:
-
Short-Term Payment Plans: These plans allow you to settle your tax debt within 180 days. They’re perfect if you can quickly gather the necessary funds but need a little extra time.
-
Long-Term Financial Plans (Installment Agreements) can be structured as an IRS back taxes payment plan, allowing you to make payments over a longer period, usually up to 72 months, if you need more time. This option is especially helpful for those facing larger debts who can’t pay in full right away. Most taxpayers have up to 10 years to settle their balance, but extending the timeframe can increase the interest and penalties owed.
-
Simple Payment Plans: Tailored for taxpayers with liabilities under $50,000, these streamlined options simplify the application process and reduce paperwork, making it easier to get started.
One of the most convenient ways to settle your bills is by setting up automatic monthly transfers from your bank account. This method not only provides a lower user fee but also eliminates the need for checks, envelopes, or trips to the post office.
In 2025, over 90% of individual taxpayers with outstanding balances qualified for a Simple Arrangement. This reflects a growing trend in utilizing these financial plans. Understanding these strategies will empower you to choose the best option for an IRS back taxes payment plan based on your financial situation and repayment abilities. Remember, as the IRS states, "It's always in your best interest to pay in full as soon as you can to minimize the additional charges." We're here to help you navigate this journey.
Determine Your Eligibility for a Payment Plan
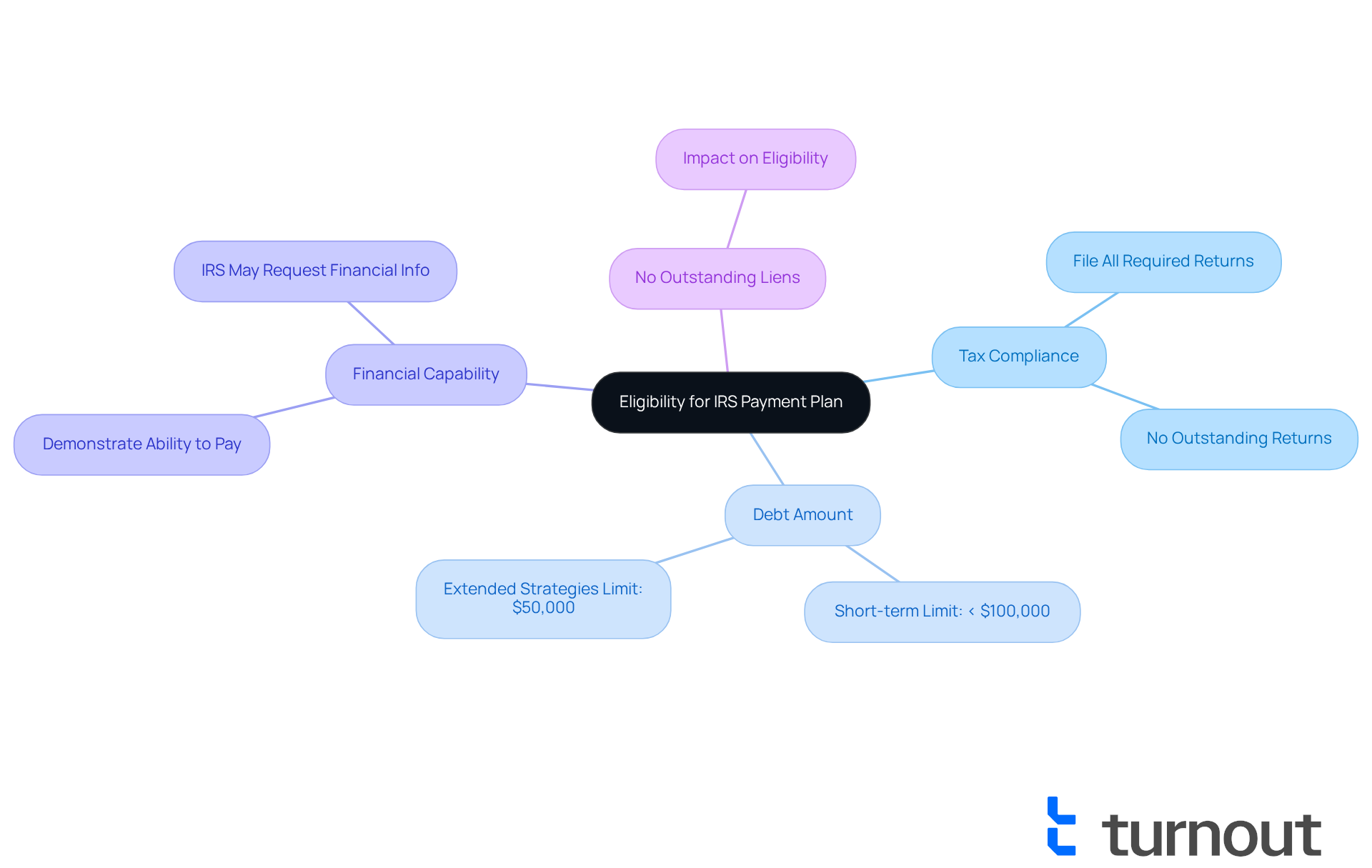
Navigating the process of qualifying for an IRS payment plan can feel overwhelming, but we're here to help you through it. To ensure you’re on the right path, let’s take a look at the key criteria you need to meet:
- Tax Compliance: It’s essential to have filed all required tax returns. The IRS won’t authorize a payment arrangement if there are outstanding returns, so make sure you’re up to date.
- Debt Amount: For short-term arrangements, your total tax debt should be less than $100,000. If you’re considering extended strategies, the limit is typically $50,000.
- Financial Capability: You’ll need to demonstrate that you can manage the necessary monthly payments. The IRS may request financial information to assess your ability to pay, but don’t worry - this is a common step in the process.
- No Outstanding Liens: If the IRS has placed a lien on your property, it could affect your eligibility for certain options.
We understand that this can be a lot to take in, but reviewing these criteria will help you determine if you can move forward with the application process. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and taking these steps can lead you toward a more manageable financial future.
Apply for Your IRS Payment Plan
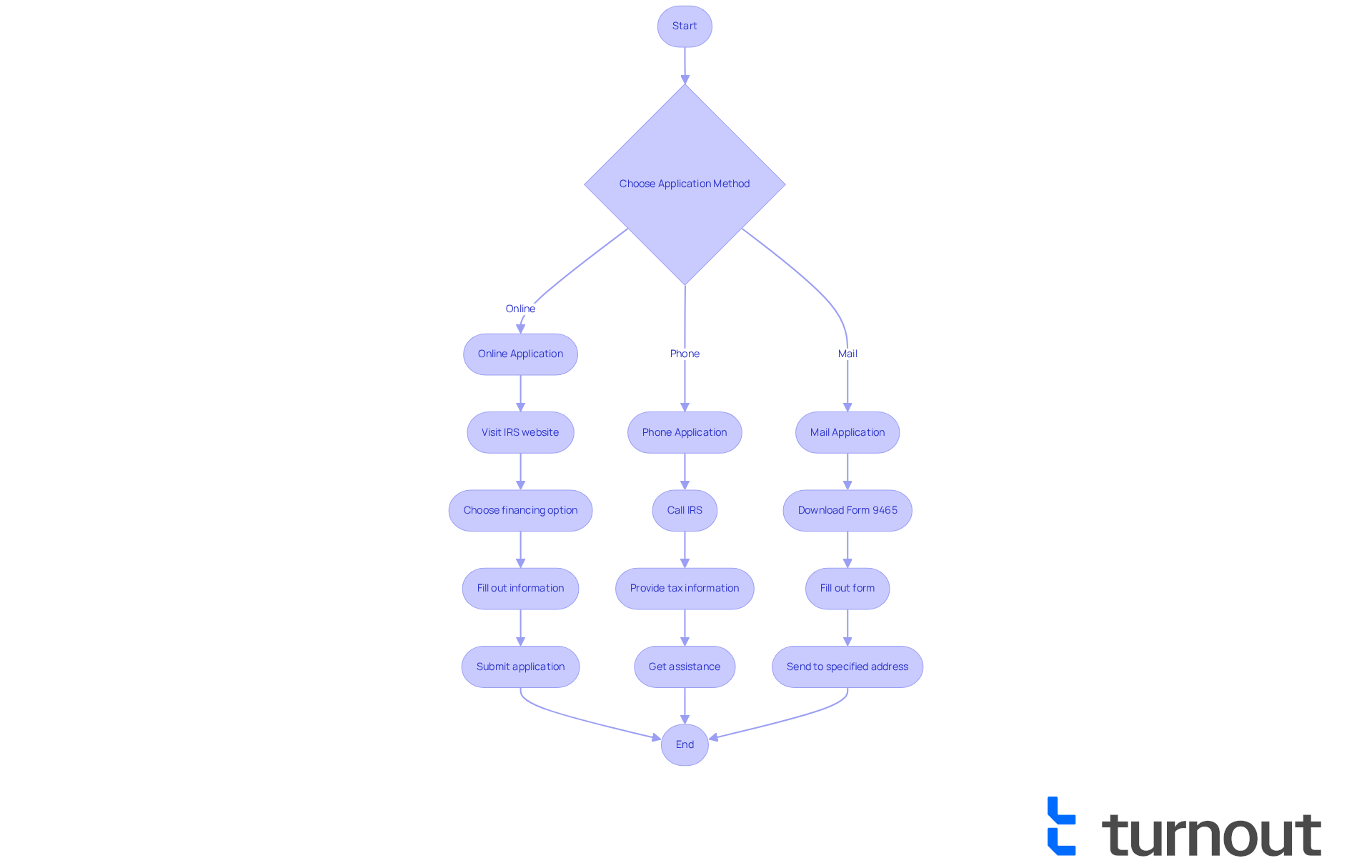
Requesting an IRS back taxes payment plan can feel overwhelming, but we're here to assist you. You can complete the process online, via phone, or through mail. Here’s how:
Online Application: The easiest way is through the IRS Online Payment Agreement tool. If you don’t have an IRS Online Account, you’ll need to create one. Just follow these simple steps:
- Visit the IRS website and navigate to the Online Payment Agreement page.
- Choose the type of financing option, including the IRS back taxes payment plan, you wish to apply for.
- Fill out the required information, including your tax details and preferred options for the IRS back taxes payment plan.
- Submit your application to join the IRS back taxes payment plan.
Phone Application: If you prefer speaking to someone, you can call the IRS at 1-800-829-1040. Be prepared to provide your tax information and financial details. It’s common to feel anxious about this, but the representatives are there to assist you.
Mail Application: For those who like to handle things the traditional way, download Form 9465 (Installment Agreement Request) from the IRS website. Fill it out and send it to the address specified in the form instructions.
Make sure you have all necessary documentation ready to expedite the process. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and taking these steps can lead you to a more manageable financial situation.
Manage Your Payment Plan Effectively
Once you've set up your financial plan, effective management becomes crucial to avoid penalties and ensure compliance. We understand that navigating this process can feel overwhelming, but there are key strategies that can help you stay on track:
-
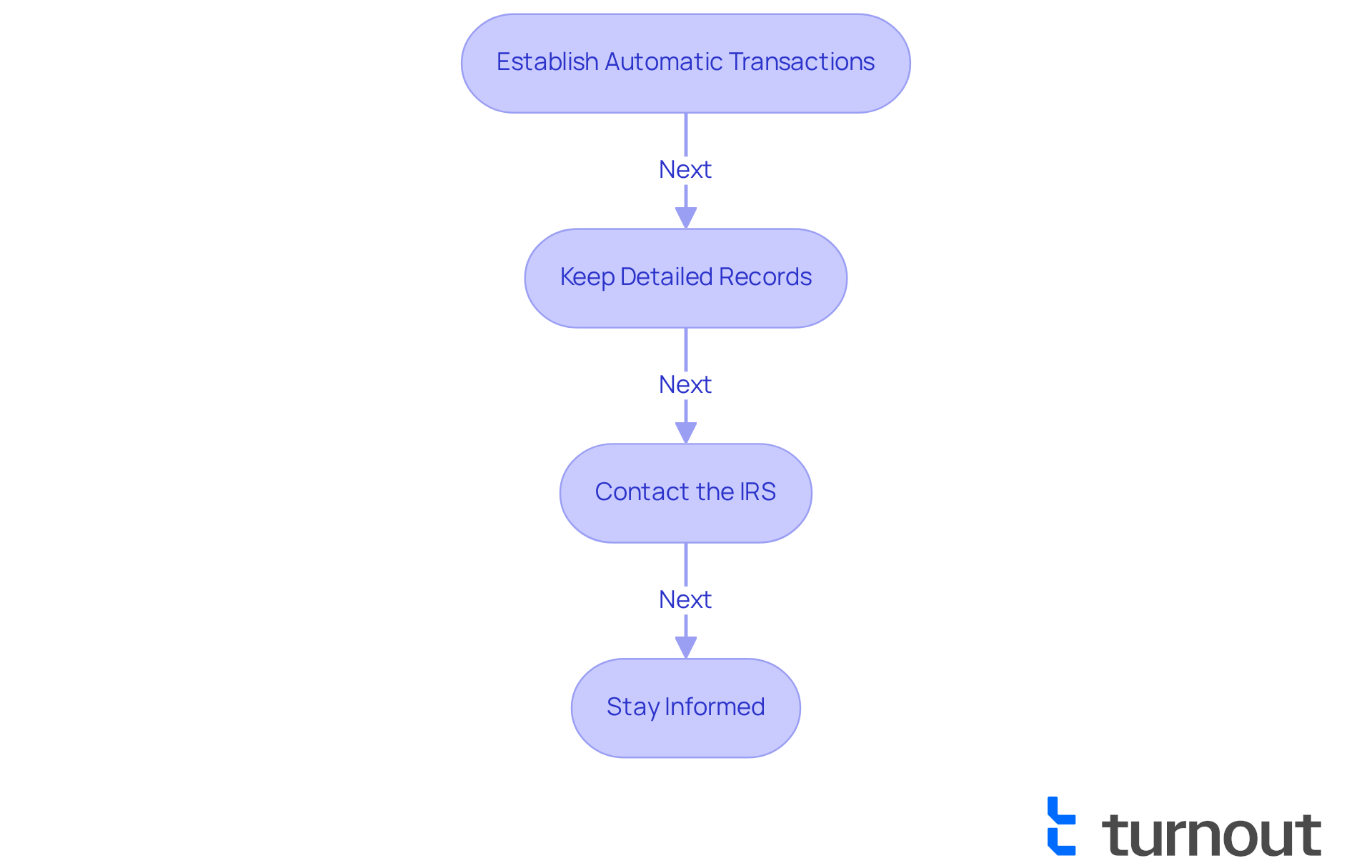
Establish Automatic Transactions: Signing up for automatic transactions is a proactive way to ensure you never miss a due date. This simple step can significantly reduce the risk of late fees and penalties, which can add up quickly. Did you know that nearly 88% of individual taxpayers owe less than $25,000? This makes automatic transfers a popular choice for those managing smaller debts. In fact, streamlined installment agreements (SLIAs) account for about 70% of all IRS plans, highlighting the effectiveness of this approach.
-
Keep Detailed Records: It's essential to maintain thorough documentation of all your transactions, including dates and amounts. This practice not only helps you monitor your progress but also assists in addressing any discrepancies with the IRS, ensuring your contributions are accurately reflected in your account.
-
Contact the IRS: If you foresee any challenges in making a contribution, don’t hesitate to reach out to the IRS as soon as possible. They may offer options to adjust your financial plan or provide temporary relief, which can be vital for maintaining your financial stability. Remember, if the IRS determines that you're unable to pay, they may delay collection until your situation improves.
-
Stay Informed: Regularly checking your IRS account online is a great way to keep an eye on your balance and confirm that your contributions are being applied correctly. This vigilance can help you catch any issues early and avoid potential penalties. Keep in mind that the late fee penalty is typically 0.5 percent per month on any outstanding balance, underscoring the importance of timely payments.
By implementing these management strategies, you can effectively maintain your payment plan and work towards resolving your tax debt. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and taking these steps can lead you to a more secure financial future.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of IRS back taxes payment plans can feel overwhelming. We understand that taking this step is essential for regaining your financial stability. This guide has shed light on the various types of payment plans available, including short-term and long-term arrangements, as well as simpler options for those with smaller debts. By familiarizing yourself with these plans, you can choose the most suitable strategy to ease your tax burden.
Key insights discussed include:
- The importance of tax compliance
- Eligibility criteria
- The application process - whether online, by phone, or through mail
Managing your chosen payment plan effectively is crucial. Consider:
- Setting up automatic transactions
- Keeping detailed records to avoid penalties and ensure compliance
Each step you take brings you closer to resolving your tax debts and achieving peace of mind.
Ultimately, mastering the IRS back taxes payment plan is about more than just making payments; it’s about taking control of your financial future. By following the outlined steps and staying informed, you can navigate this process with confidence. Embracing these strategies can lead to a more secure financial situation and a brighter outlook for the years ahead. Remember, you are not alone in this journey - we're here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What types of IRS payment plans are available for back taxes?
The IRS offers several payment plans for back taxes, including Short-Term Payment Plans, Long-Term Financial Plans (Installment Agreements), and Simple Payment Plans.
What is a Short-Term Payment Plan?
A Short-Term Payment Plan allows you to settle your tax debt within 180 days. It is suitable for those who can quickly gather the necessary funds but need a little extra time.
How does a Long-Term Financial Plan work?
A Long-Term Financial Plan, also known as an Installment Agreement, allows you to make payments over a longer period, usually up to 72 months, which is helpful for those facing larger debts who cannot pay in full immediately.
Who qualifies for a Simple Payment Plan?
Simple Payment Plans are tailored for taxpayers with liabilities under $50,000. They simplify the application process and reduce paperwork, making it easier to get started.
What is the benefit of setting up automatic monthly transfers for payments?
Setting up automatic monthly transfers from your bank account provides a lower user fee and eliminates the need for checks, envelopes, or trips to the post office.
What percentage of taxpayers qualified for a Simple Arrangement in 2025?
In 2025, over 90% of individual taxpayers with outstanding balances qualified for a Simple Arrangement, indicating a growing trend in utilizing these financial plans.
What does the IRS recommend regarding paying tax debts?
The IRS recommends that it is always in your best interest to pay your tax debt in full as soon as possible to minimize additional charges.




