Introduction
Navigating the complexities of tax obligations can feel overwhelming, especially when the thought of owing money to the IRS looms large. We understand that this can be a stressful time, but there’s hope. The federal payment plan offers a lifeline, allowing you to manage your debts through structured installment agreements instead of facing daunting lump sums all at once.
This guide explores various options available to you. From short-term solutions that provide quick relief to long-term plans designed for those who need a bit more time, there’s a path forward. However, it’s also important to consider what happens if a taxpayer defaults on these arrangements. Understanding the potential consequences is crucial for anyone looking to take control of their financial future. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help.
Explore Federal Payment Plans: Key Concepts and Options
The federal payment plan IRS, often referred to as installment agreements, allows you to settle your tax obligations gradually rather than all at once. We understand that managing taxes can be overwhelming, but the IRS offers several options to help you navigate this process:
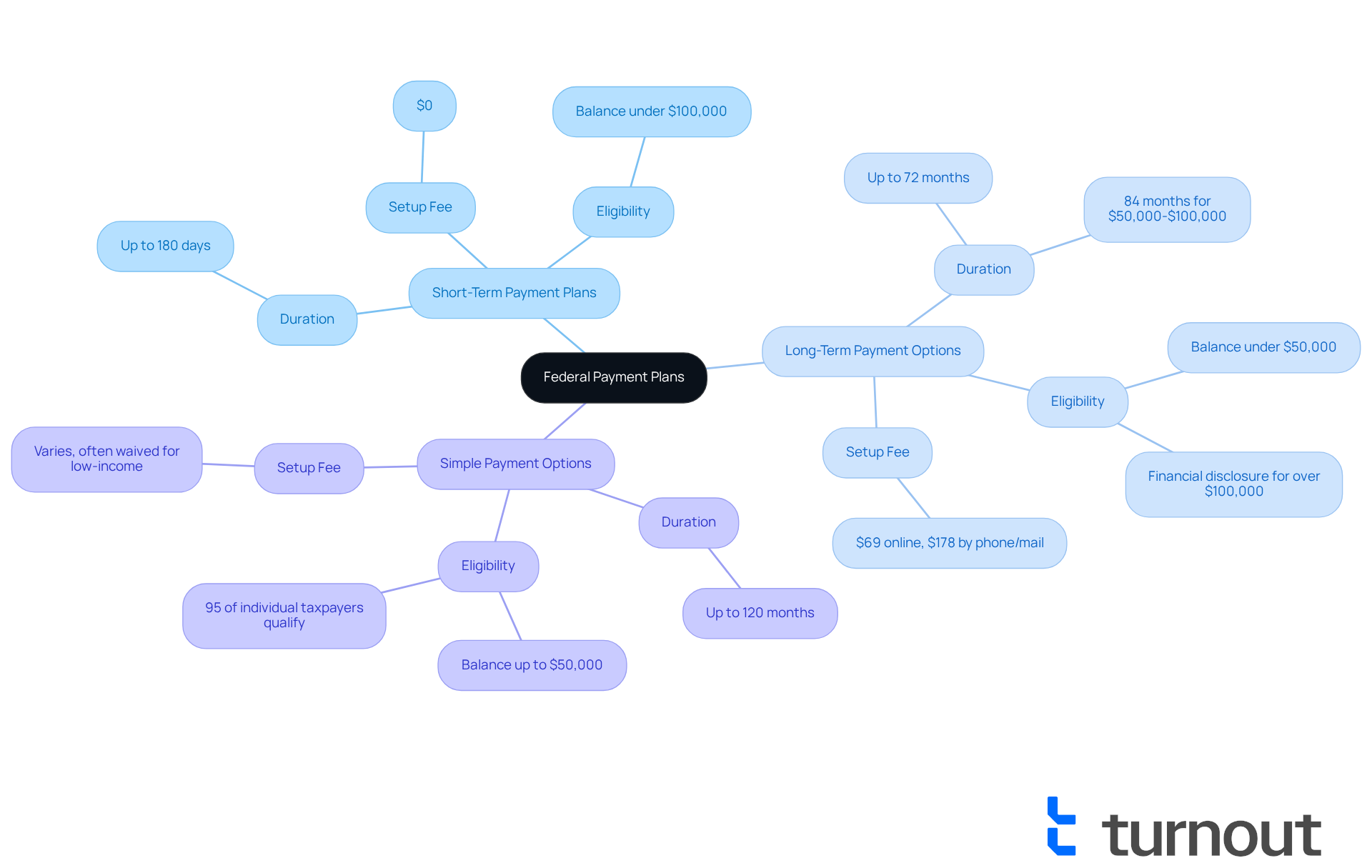
- Short-Term Payment Plans: If your balance is under $100,000, you can take up to 180 days to pay off your debt without incurring extra fees. This gives you some breathing room.
- Long-Term Payment Options: For those with debts under $50,000, a federal payment plan IRS can extend these arrangements up to 72 months. This can be a manageable way to settle your obligations through a federal payment plan IRS while easing financial pressure.
- Simple Payment Options: Introduced in 2025, these options simplify the process, making it easier for you to understand eligibility and application requirements.
Understanding these options is the first step in effectively managing your tax liabilities and avoiding penalties. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you find the best solution for your situation.
Differentiate Between Short-Term and Long-Term Payment Plans
When evaluating federal payment plans, we understand that navigating your options can feel overwhelming. It's essential to grasp the differences between short-term and long-term plans to find the best fit for your situation, especially when considering a federal payment plan IRS.
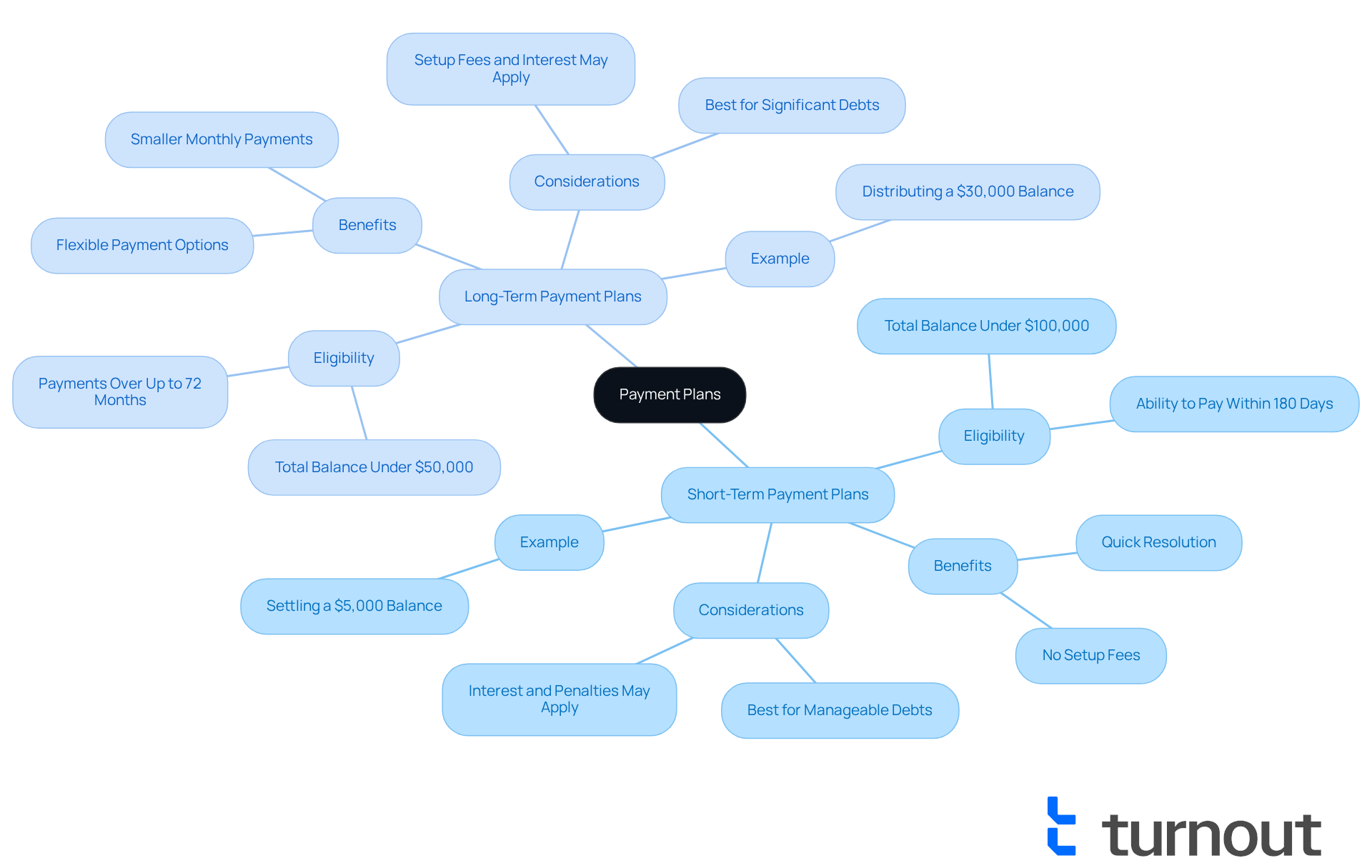
Short-Term Payment Plans: If you can settle your balance within 180 days, this option might be just what you need. Designed for taxpayers with a total balance under $100,000, these plans come with no setup fees. However, keep in mind that if you do not utilize the federal payment plan IRS, interest and penalties may still apply if your balance isn't paid by the deadline. This choice is particularly beneficial for those with manageable debts, allowing for a quick resolution without long-term financial strain. For instance, if you have a $5,000 balance, this strategy can help you settle your debt swiftly, avoiding extra costs associated with extended repayment periods. It's worth noting that 88% of individual taxpayers owe less than $25,000, making this a popular and practical choice.
Extended Repayment Options: On the other hand, if you need more time to settle your tax obligations, extended repayment options might be the way to go. These plans allow contributions over a span of up to 72 months for amounts under $50,000. While they offer flexibility, be aware that they may involve setup fees and interest, which can increase the total amount owed. Financial advisors often recommend this choice for individuals facing significant debts or inconsistent income, as it allows for smaller, more manageable monthly payments. For example, if you have a $30,000 balance, a long-term strategy can help you distribute costs over several years, ensuring you can meet your responsibilities without straining your budget.
Ultimately, the choice between short-term and long-term financial arrangements hinges on your personal economic situation, including income stability, total tax liabilities, and considerations related to the federal payment plan IRS. We encourage you to carefully assess your ability to meet monthly obligations and consider how interest and fees might impact your overall financial health. Remember, you're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you find the best path forward.
Navigate the Application Process for IRS Payment Plans
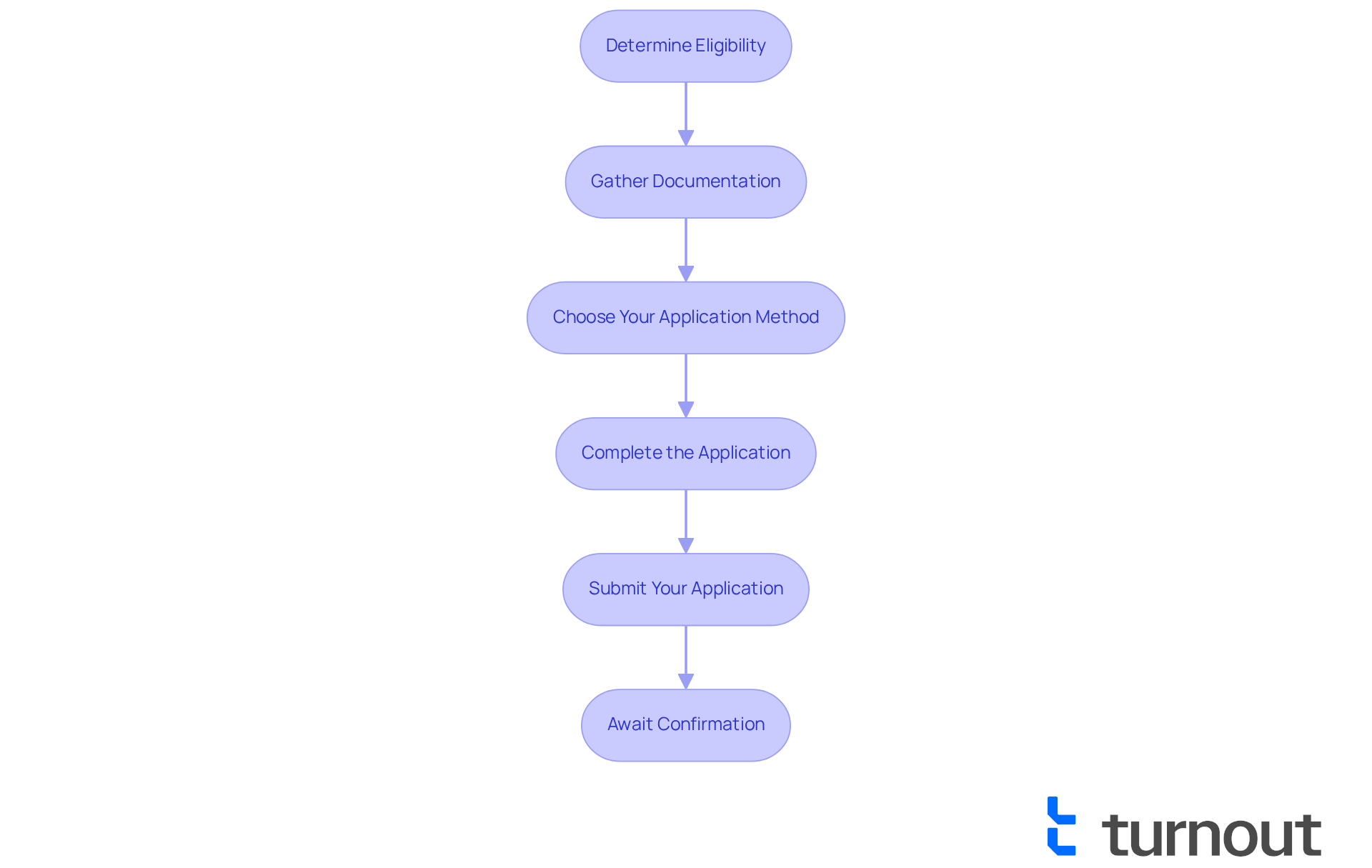
Applying for a federal payment plan IRS can seem overwhelming, but we're here to help you navigate this process with ease. Follow these steps to find a solution that works for you:
-
Determine Eligibility: First, check if you owe less than $50,000 for long-term options or less than $100,000 for short-term options. Most individual taxpayers qualify for a federal payment plan IRS, which makes this a viable choice. If you owe $50,000 or less, you might even be eligible for a federal payment plan IRS, such as a streamlined installment agreement (SLIA), which simplifies the application process.
-
Gather Documentation: Next, collect the necessary documents, such as your tax return and any notices from the IRS. This may include Form 9465 and relevant financial statements, depending on your situation. Having everything ready can ease your mind.
-
Choose Your Application Method: You have options for applying: online through the IRS Online Payment Agreement tool, by phone, or by mailing Form 9465. The online method is often the quickest, with many applicants receiving immediate approval for streamlined options under $50,000.
-
Complete the Application: When filling out the required forms, be sure to provide all requested information accurately. Jim Buttonow, a tax professional, emphasizes that being thorough here is crucial to avoid any processing delays.
-
Submit Your Application: If you’re applying online, just follow the prompts to submit. If you’re mailing it, double-check that you send it to the correct address to prevent unnecessary delays.
-
Await Confirmation: After submission, the IRS will notify you about your application status. If approved, you’ll receive details about your financial arrangement. Typically, online applications are processed almost instantly, while phone or mail requests may take 30-45 days. Remember, interest continues to accumulate during this time, so stay aware of your responsibilities.
By following these steps carefully, you can simplify the process and secure a manageable financial arrangement with a federal payment plan IRS. You’re not alone in this journey, and taking these steps can help you handle your tax responsibilities with confidence.
Understand the Consequences of Defaulting on Payment Plans
Defaulting on an IRS payment plan can lead to significant repercussions, and we understand how overwhelming this can feel:
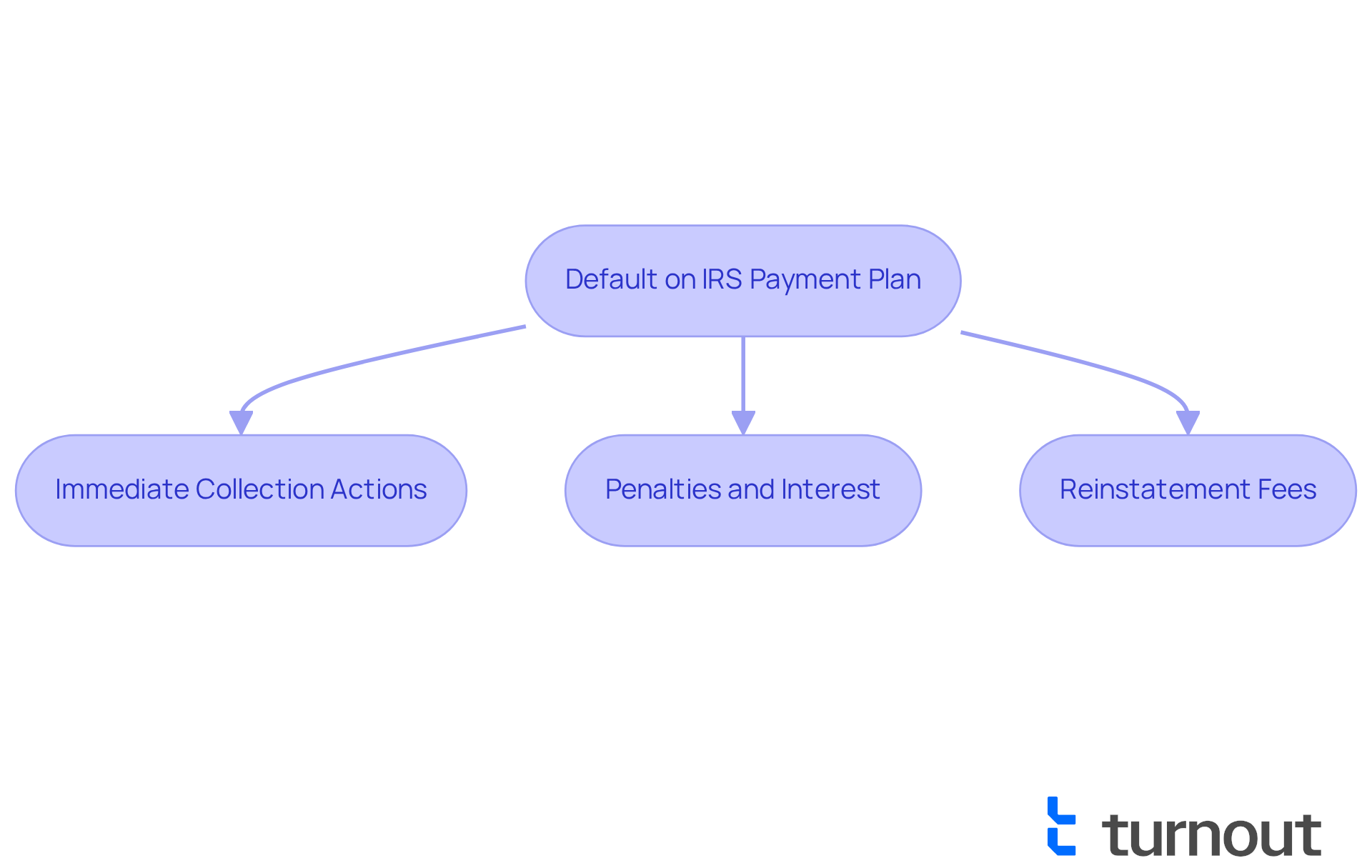
- Immediate Collection Actions: Missing a payment can result in the IRS terminating your agreement and resuming aggressive collection efforts, including wage garnishments and bank levies. With IRS enforcement actions at record highs in 2025 due to expanded funding under the Inflation Reduction Act, the urgency for compliance has never been greater.
- Penalties and Interest: Defaulting not only adds to your financial burden through additional penalties and interest on the unpaid balance but can also escalate your overall debt significantly. It's concerning to note that, according to the IRS Data Book (2024), more than 59% of taxpayers default on their federal payment plan IRS agreements within three years, often leading to severe financial strain.
- Reinstatement Fees: If your financial arrangement is terminated, reinstatement may incur fees, complicating your recovery. Many taxpayers accept terms they cannot maintain, which can lead to defaults and additional penalties. However, reinstatement is more likely if no new tax liabilities have been incurred and the reason for default is quickly corrected.
To prevent default, it’s crucial to assess your ability to meet payment obligations before entering a federal payment plan IRS. If you receive Notice CP523, remember that you have only 30 days to respond before enforcement actions resume. If you foresee challenges, please reach out to a tax resolution professional promptly. They may provide flexibility or alternative arrangements to help you maintain compliance. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we're here to help.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of federal payment plans with the IRS can feel overwhelming. We understand that managing tax obligations is no small feat, and knowing your options is crucial for easing that burden. The federal payment plan IRS offers both short-term and long-term arrangements, allowing you to settle your debts gradually and alleviate financial stress. By familiarizing yourself with these options, you can take meaningful steps toward compliance and financial stability.
Throughout this article, we’ve shared key insights about the differences between short-term and long-term payment plans, the application process, and the potential consequences of defaulting on these agreements.
- Short-term plans are designed for those who can pay off their balance within 180 days.
- Long-term options extend up to 72 months for larger debts.
Understanding the application steps and being aware of the repercussions of defaulting can empower you to make informed decisions that align with your financial situation.
Ultimately, mastering the federal payment plan IRS isn’t just about settling debts; it’s about taking control of your financial future. By utilizing the resources and options available, you can navigate your tax responsibilities with confidence and avoid the pitfalls of default. Remember, engaging with a tax professional for tailored advice can further enhance your journey, ensuring that you find the best path forward in managing your obligations effectively. You are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a federal payment plan IRS?
A federal payment plan IRS, often referred to as installment agreements, allows you to settle your tax obligations gradually instead of paying the full amount at once.
What are the short-term payment plans available?
Short-term payment plans are available for balances under $100,000, allowing you to pay off your debt within 180 days without incurring extra fees.
What are the long-term payment options for tax debts?
Long-term payment options are available for those with debts under $50,000, allowing arrangements to extend up to 72 months to help manage payments more comfortably.
What are the simple payment options introduced in 2025?
Simple payment options simplify the process of understanding eligibility and application requirements for federal payment plans, making it easier for taxpayers to navigate their options.
Why is it important to understand these payment options?
Understanding these options is crucial for effectively managing tax liabilities and avoiding penalties, providing taxpayers with a clearer path to settle their obligations.




