Introduction
Navigating the complexities of IRS regulations for pensions and annuities can feel overwhelming. We understand that many individuals struggle with the nuances of taxable versus non-taxable income, eligibility criteria, and the necessary documentation for submission. It’s essential to grasp these details if you want to secure your financial future.
As the stakes rise, you might wonder: how can you ensure compliance while maximizing your benefits? This guide is here to help. We offer a step-by-step approach to mastering IRS general rules, empowering you to tackle your pension and annuity concerns with confidence and clarity. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to support you every step of the way.
Understand IRS General Rules for Pensions and Annuities
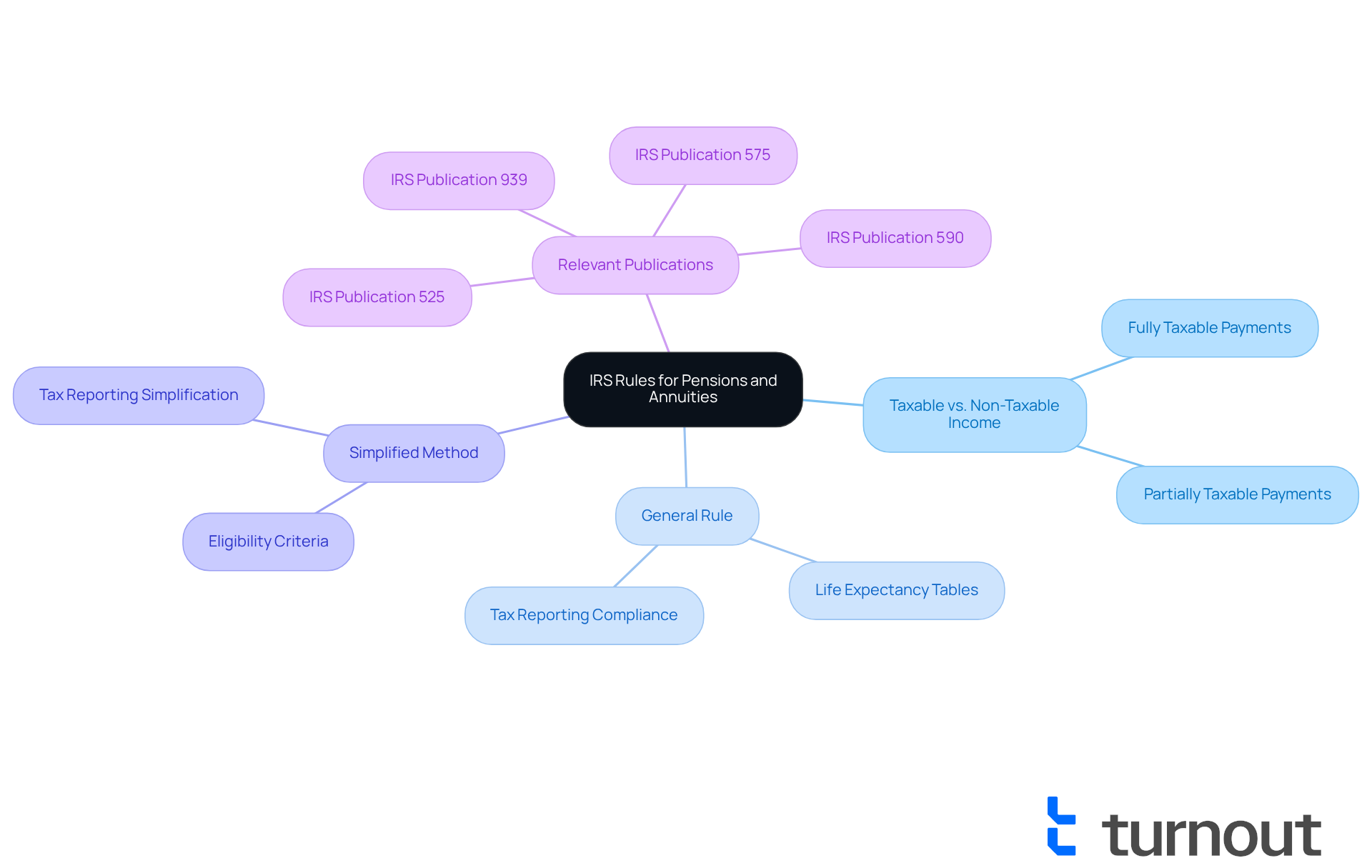
Navigating the IRS general rule for pensions and annuities can feel overwhelming, but you’re not alone in this journey. To start, take a look at IRS Publication 939. It provides essential details on how pension and retirement earnings are taxed. Here are some key points to consider:
- Taxable vs. Non-Taxable Income: Understanding whether your pension and annuity payments are fully or partially taxable is crucial. If you haven’t invested in the contract, the entire payment may be subject to taxes.
- IRS General Rule for Pensions and Annuities: You will need to use the life expectancy tables from the IRS to determine the taxable and tax-free portions of your pension payments. This method helps ensure you report accurately and comply with tax regulations.
- Simplified Method: For certain retirement plans, there’s a simplified approach to help you figure out the taxable portion, making tax reporting easier for beneficiaries.
It’s important to note that in 2013, the IRS started treating payments from nonqualified plans as net investment income, adding complexity to tax reporting. Also, IRS Publication 939 doesn’t cover income from life insurance or IRAs, so it’s wise to consult other IRS publications, like Publication 575, for a fuller understanding.
Recognizing these distinctions can significantly impact your tax obligations. For example, if you accurately identify the taxable portion of your retirement fund, you could save a lot on your tax bill. On the other hand, misclassifying your income might lead to unexpected liabilities.
We understand that this can be a lot to digest, but reviewing the relevant IRS publications and guidelines will help you feel more confident in navigating your financial landscape. Remember, you’re not alone in this process; we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Identify Eligibility Criteria for Pensions and Annuities
Navigating the world of pensions and annuities can feel overwhelming, but understanding your eligibility in relation to the IRS general rule for pensions and annuities is a crucial first step. Let’s explore some important criteria together:
-
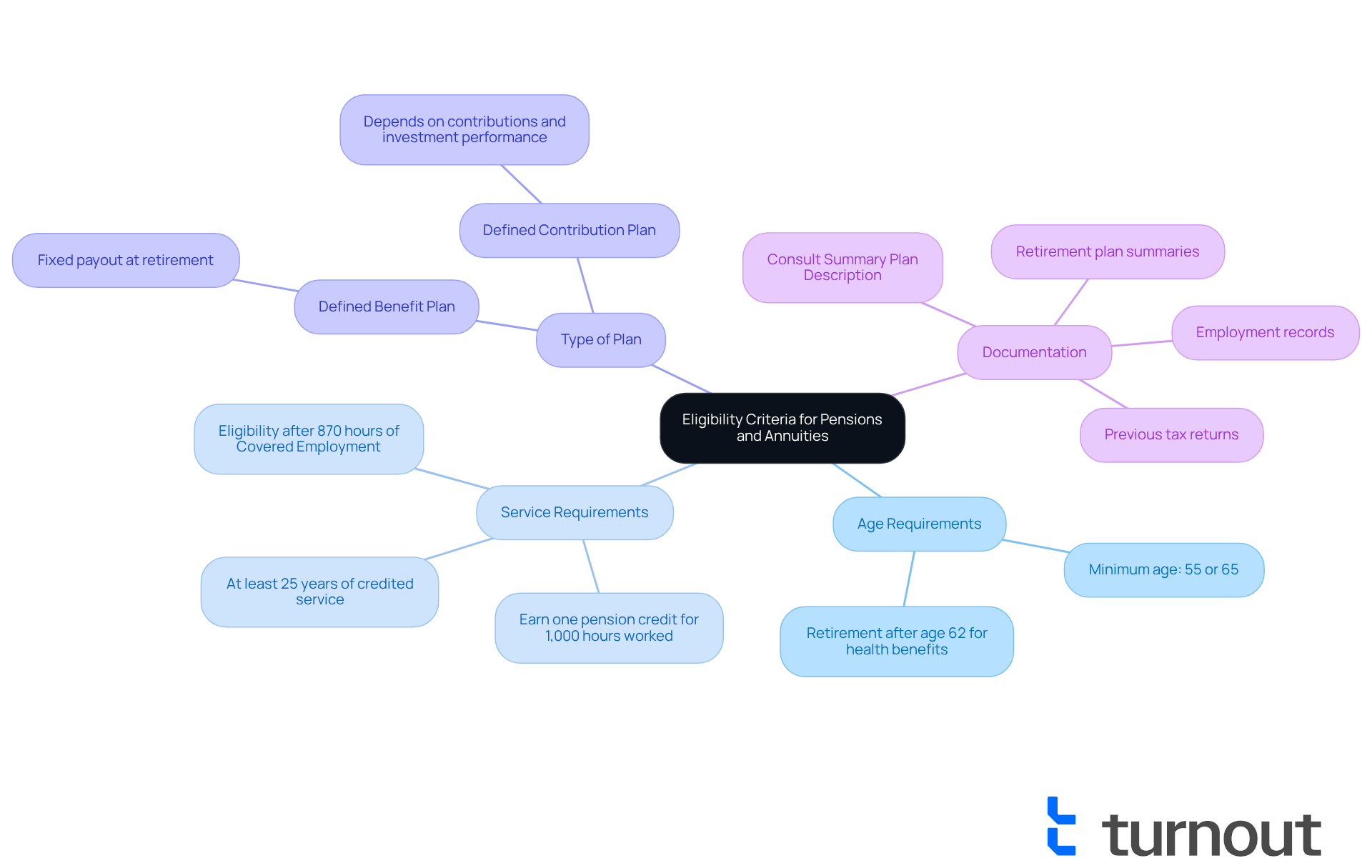
Age Requirements: Many pension plans require you to be at least 55 or 65 years old to start receiving benefits. For example, if you’re a member of the 1199SEIU Greater New York Retirement Fund, you’ll need to retire after age 62 or qualify for a disability benefit to access retiree health benefits. This typically requires at least 25 years of credited or vesting service.
-
Service Requirements: It’s common for employers to set a minimum number of years of service before you can tap into your retirement benefits. Generally, you’ll need at least 25 years of credited or vesting service to qualify for retiree health benefits. Remember, you earn one retirement credit for every 1,000 hours worked in a calendar year, which is essential for meeting these service requirements.
-
Type of Plan: Understanding whether you’re dealing with a defined benefit plan or a defined contribution plan is key, as the eligibility criteria can vary widely. Defined benefit plans usually offer a fixed payout at retirement, while defined contribution plans rely on your contributions and investment performance.
-
Documentation: It’s important to gather any necessary paperwork that confirms your eligibility, such as employment records, retirement plan summaries, or previous tax returns. We recommend consulting the Summary Plan Description or reaching out to the provided contact number if you have questions about your eligibility. This information is vital when reviewing specific plan documents or the IRS general rule for pensions and annuities to confirm your status.
By grasping these standards, you can navigate the complexities of retirement fund and income eligibility with greater ease. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Gather Required Documentation for IRS Submission
Preparing for your IRS submission can feel overwhelming, but gathering the right documentation can make a world of difference. Here’s what you need to collect:
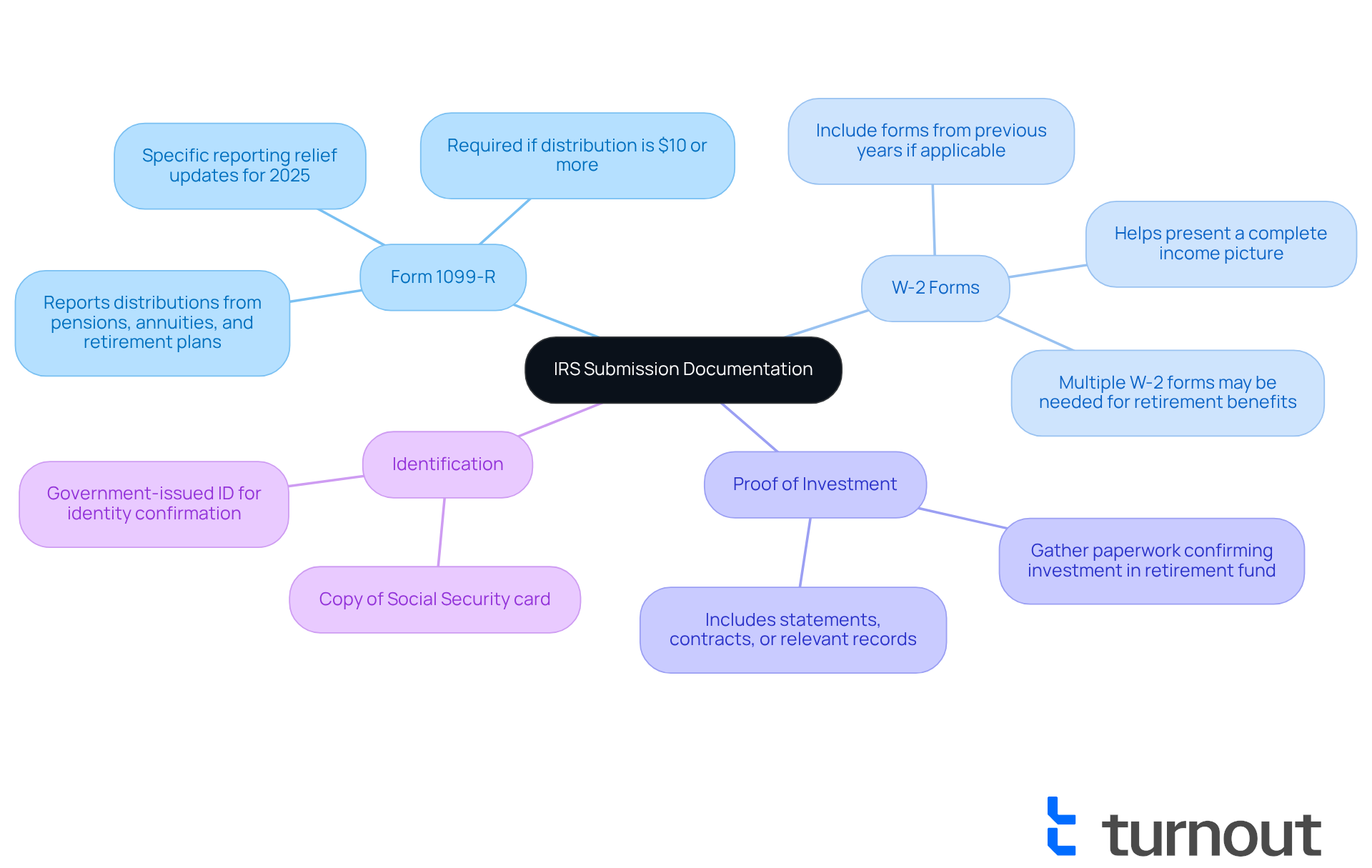
- Form 1099-R: This important form reports distributions from pensions, annuities, and retirement plans. Make sure you have the correct year’s form. For 2025, there are specific reporting relief updates for issuers completing box 8. If you received a distribution of $10 or more from your retirement plan, you should receive a Form 1099-R.
- W-2 Forms: Don’t forget to include your W-2 forms from previous years, if applicable. This helps present a complete picture of your income. Many individuals submit several W-2 forms when claiming retirement benefits, highlighting the importance of thorough documentation.
- Proof of Investment: Gather any paperwork that confirms your investment in the retirement fund or insurance product. This could be statements, contracts, or other relevant records that show your financial contributions.
- Identification: Have a copy of your Social Security card and a government-issued ID ready. This will help confirm your identity during the submission process.
Organizing these documents in a dedicated folder can really streamline your submission, reducing the chances of delays or complications. We understand that navigating this process can be tricky. The significance of Form 1099-R cannot be overstated; tax specialists emphasize its role in accurately reporting retirement distributions to the IRS in line with the IRS general rule for pensions and annuities, ensuring compliance and maximizing potential benefits. In fact, C. Adam Bee noted that about two-thirds of respondents who received 1099-R forms didn’t report the distributions in surveys, which highlights common challenges many face during the IRS submission process.
After gathering your documentation, take a moment to review everything for accuracy. This simple step can facilitate a smoother process. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Complete IRS Forms Accurately and Efficiently
Completing IRS forms can feel overwhelming, but we're here to help you through it. Follow these steps to make the process smoother:
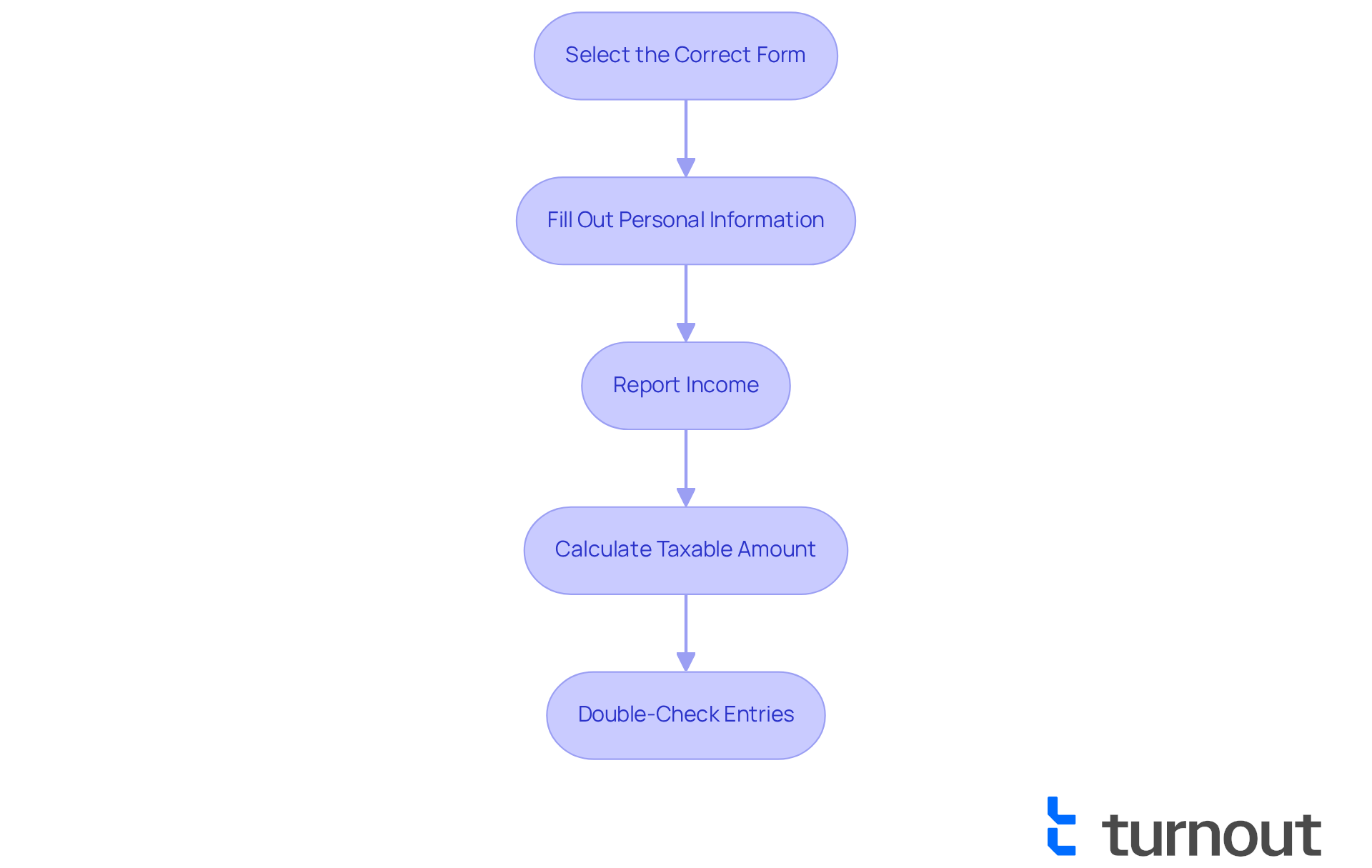
- Select the Correct Form: Based on the IRS general rule for pensions and annuities, you’ll typically use Form 104. The IRS general rule for pensions and annuities outlines the taxation process for retirement income and Form 1099-R. It’s important to choose the right forms to avoid any confusion.
- Fill Out Personal Information: Make sure your name, address, and Social Security number are accurate. This helps prevent any issues down the line.
- Report Income: Enter the total pension or annuity payments received as reported on your Form 1099-R. This is a crucial step in ensuring your income is reported correctly.
- Calculate Taxable Amount: Use the guidelines from IRS Publication 939 to determine the taxable portion of your income as outlined by the IRS general rule for pensions and annuities. It’s common to feel unsure about this, but taking it step by step can help.
- Double-Check Entries: Review all entries for accuracy before submission to avoid mistakes. A little extra care here can save you from future headaches.
If you’re feeling uncertain about any part of the process, consider using tax software or consulting a tax professional. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and seeking help is a smart choice.
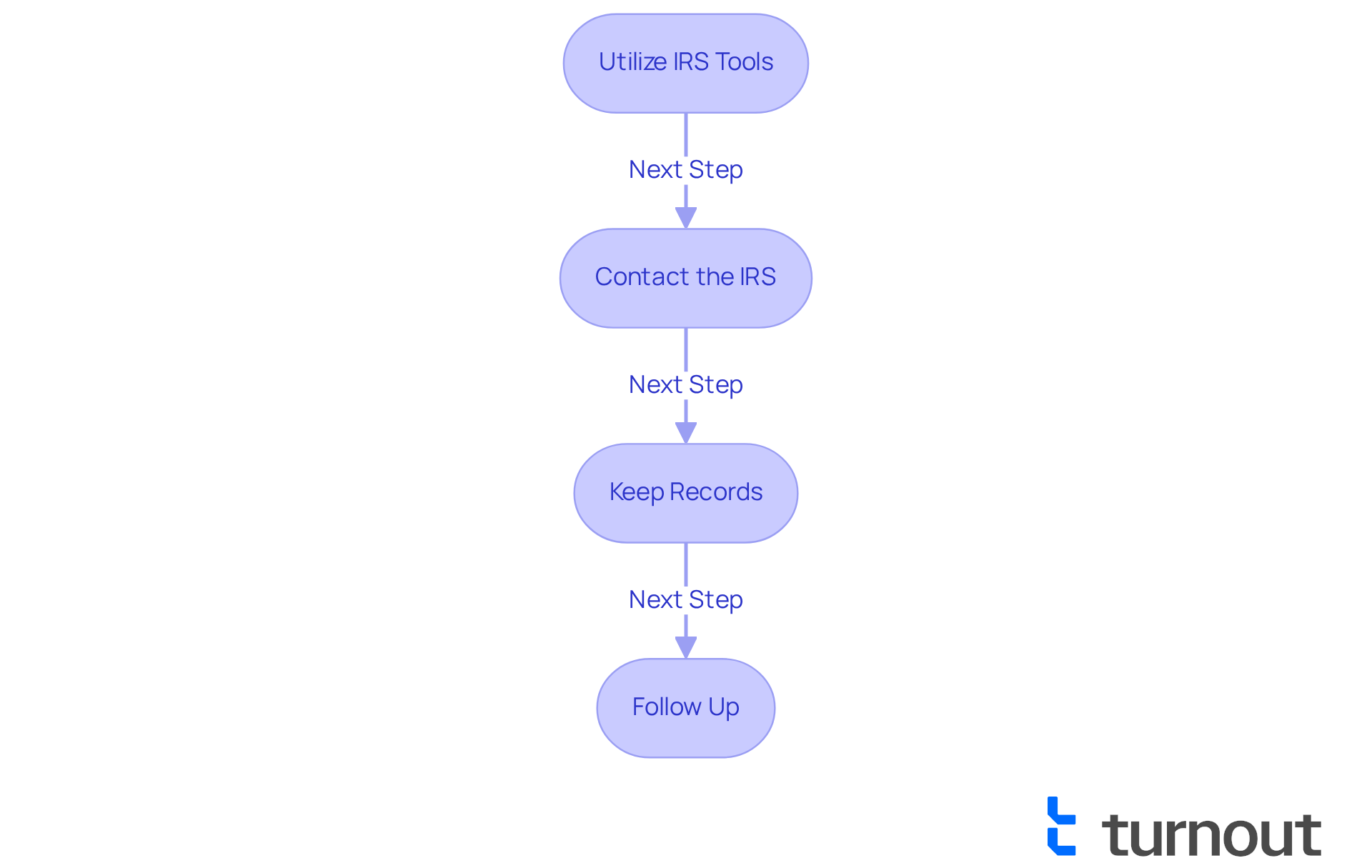
Track Application Status and Address Potential Issues
To effectively track your application status and address any potential issues, consider these supportive steps:
-
Utilize IRS Tools: We understand that waiting can be stressful. That’s why leveraging the IRS 'Where's My Refund?' tool or the IRS2Go app can be so helpful. These resources provide real-time updates, keeping you informed about your case. Remember, having the right tools at your disposal is crucial. As the IRS states, "An EFIN is used to identify firms that have completed the IRS e-file application to become an authorized IRS e-file provider."
-
Contact the IRS: If you experience delays or encounter issues, don’t hesitate to reach out to the IRS directly at their customer service number. Engaging with a representative can clarify uncertainties and expedite the resolution process. It’s common to feel overwhelmed, but remember, passing a suitability check is essential for those involved in electronic filing, as noted in IRS guidelines.
-
Keep Records: Maintaining copies of all submitted forms and correspondence with the IRS is vital. This documentation serves as a reference point and can be invaluable if discrepancies arise. One applicant shared that having detailed records helped resolve a misunderstanding regarding their application status. You are not alone in this journey; keeping track can make a difference.
-
Follow Up: Should you not receive a response within the expected timeframe, proactively following up with the IRS is key. Regular check-ins can ensure your application is being processed and highlight any potential issues early on. We’re here to help you navigate this process.
Being proactive in these areas can significantly enhance your ability to resolve issues quickly and efficiently. Remember, you’re taking important steps towards clarity and resolution.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of IRS rules for pensions and annuities can feel overwhelming. We understand that grasping these regulations is crucial for your financial planning. This article offers a step-by-step guide designed to empower you, helping you confidently address your tax obligations, eligibility criteria, and documentation needs.
Key points discussed include:
- The importance of distinguishing between taxable and non-taxable income
- The eligibility criteria based on age and service requirements
- The necessary documentation for IRS submissions
It’s common to feel uncertain about accurately completing IRS forms and tracking application status. However, doing so can alleviate potential issues and enhance your overall experience in managing pensions and annuities.
Ultimately, understanding IRS regulations on pensions and annuities goes beyond mere compliance; it’s about securing your financial future. By taking proactive steps—like consulting relevant IRS publications, gathering necessary documents, and utilizing available tools—you can navigate this landscape with confidence. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Embracing these strategies will simplify the process and pave the way for a more secure and informed retirement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the IRS general rules for pensions and annuities?
The IRS general rules for pensions and annuities involve understanding how pension and retirement earnings are taxed, determining whether payments are fully or partially taxable, and using IRS life expectancy tables to report taxable and tax-free portions accurately.
How can I determine if my pension or annuity payments are taxable?
To determine if your pension or annuity payments are taxable, you need to assess whether you have invested in the contract. If you haven't, the entire payment may be subject to taxes. Additionally, you can use the life expectancy tables from the IRS for accurate reporting.
What is the simplified method for reporting pensions and annuities?
The simplified method is an approach available for certain retirement plans that helps beneficiaries figure out the taxable portion of their pension or annuity payments, making tax reporting easier.
What changes did the IRS make regarding nonqualified plans in 2013?
In 2013, the IRS began treating payments from nonqualified plans as net investment income, which added complexity to tax reporting for these payments.
Does IRS Publication 939 cover income from life insurance or IRAs?
No, IRS Publication 939 does not cover income from life insurance or IRAs. It is advisable to consult other IRS publications, such as Publication 575, for a more comprehensive understanding.
What are the age requirements for receiving pension benefits?
Many pension plans require individuals to be at least 55 or 65 years old to start receiving benefits. For example, members of the 1199SEIU Greater New York Retirement Fund must retire after age 62 or qualify for a disability benefit.
What service requirements must be met to qualify for retirement benefits?
Generally, you need at least 25 years of credited or vesting service to qualify for retiree health benefits. You earn one retirement credit for every 1,000 hours worked in a calendar year.
How do I know if I'm dealing with a defined benefit or defined contribution plan?
Understanding whether you are dealing with a defined benefit plan or a defined contribution plan is key, as eligibility criteria vary. Defined benefit plans offer a fixed payout at retirement, while defined contribution plans depend on your contributions and investment performance.
What documentation is needed to confirm my eligibility for pensions and annuities?
You need to gather necessary paperwork such as employment records, retirement plan summaries, or previous tax returns. Consulting the Summary Plan Description or contacting the provided number for your plan can also help confirm your eligibility.




