Introduction
Understanding employment tax liabilities can feel overwhelming for any employer. We know that the complexities surrounding these responsibilities often lead to confusion and missteps. These liabilities include various taxes, such as:
- federal income tax
- Social Security
- Medicare
Each with its own set of obligations and potential consequences.
As you navigate these challenges, you might wonder: how can you ensure compliance while avoiding the pitfalls that could lead to significant penalties? You're not alone in this journey. Many employers share these concerns, and it's completely normal to feel this way.
This guide is here to help demystify employment tax liabilities. We aim to offer valuable insights and practical strategies to support you in managing your responsibilities effectively. Together, we can tackle these challenges and find a path forward.
Define Employment Tax Liabilities and Their Importance
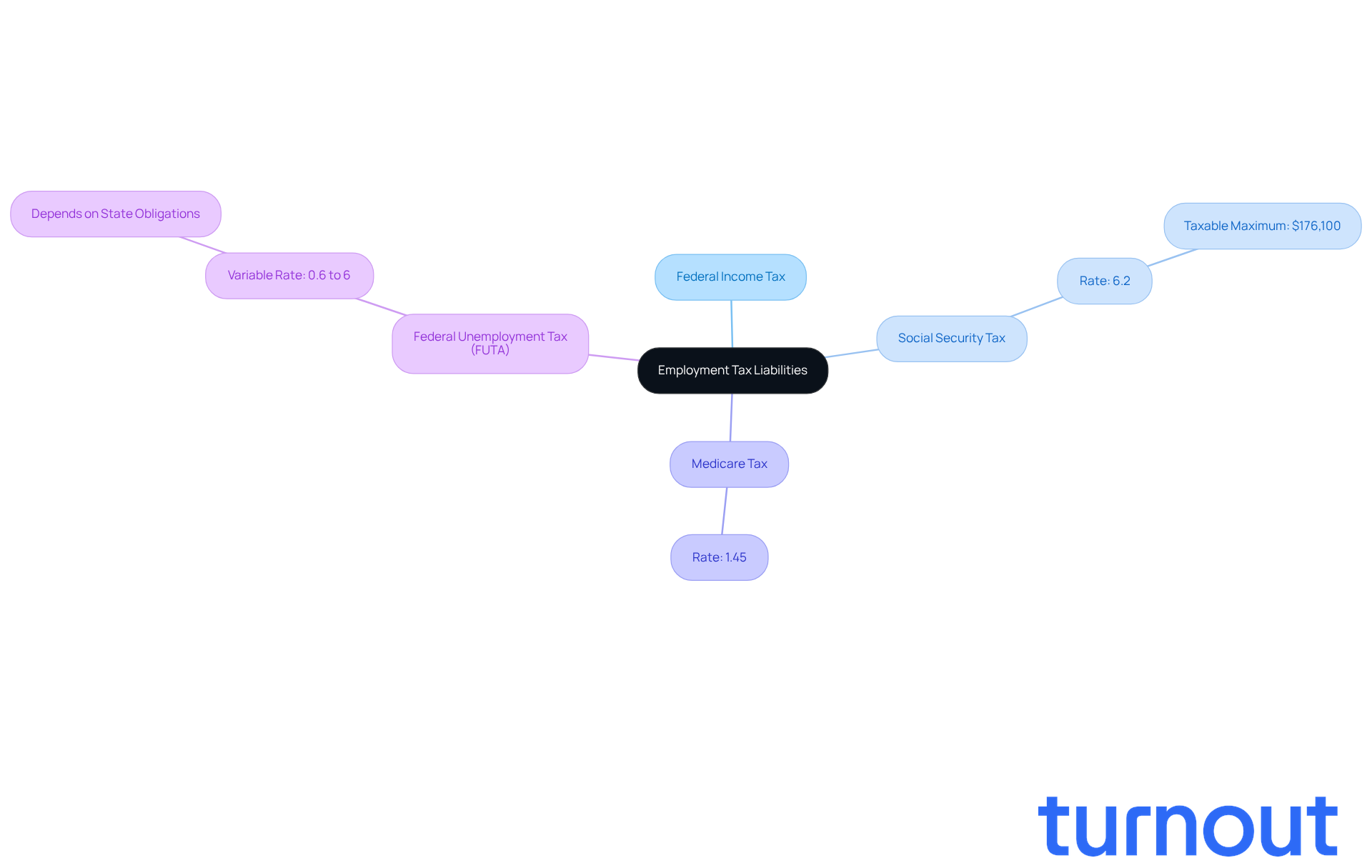
Understanding employment tax liabilities can feel overwhelming, but you’re not alone in this journey. Employers are responsible for deducting certain taxes, known as employment tax liabilities, from their workers' wages and contributing on their behalf. This includes:
- Federal income tax
- Social Security tax
- Medicare tax
- Federal unemployment tax (FUTA)
For the tax year 2026, Social Security tax is set at 6.2% on wages up to a taxable maximum of $176,100, while Medicare tax is 1.45% of gross wages.
It’s common to feel uncertain about these responsibilities. Employers must also contribute to FUTA, which varies between 0.6% to 6% depending on state obligations. Understanding employment tax liabilities is essential for adhering to tax regulations and avoiding penalties. Misclassification of workers can lead to significant consequences, including fines and back wages.
To help you navigate this, the IRS suggests a 'Paycheck Checkup' to ensure accurate withholding amounts for your workers. By accurately calculating and remitting your employment tax liabilities on time, you not only fulfill your legal obligations but also maintain financial stability. This ensures your business can operate smoothly and avoid costly disruptions. Remember, we’re here to help you through this process.
Explore Types of Employment Tax Liabilities
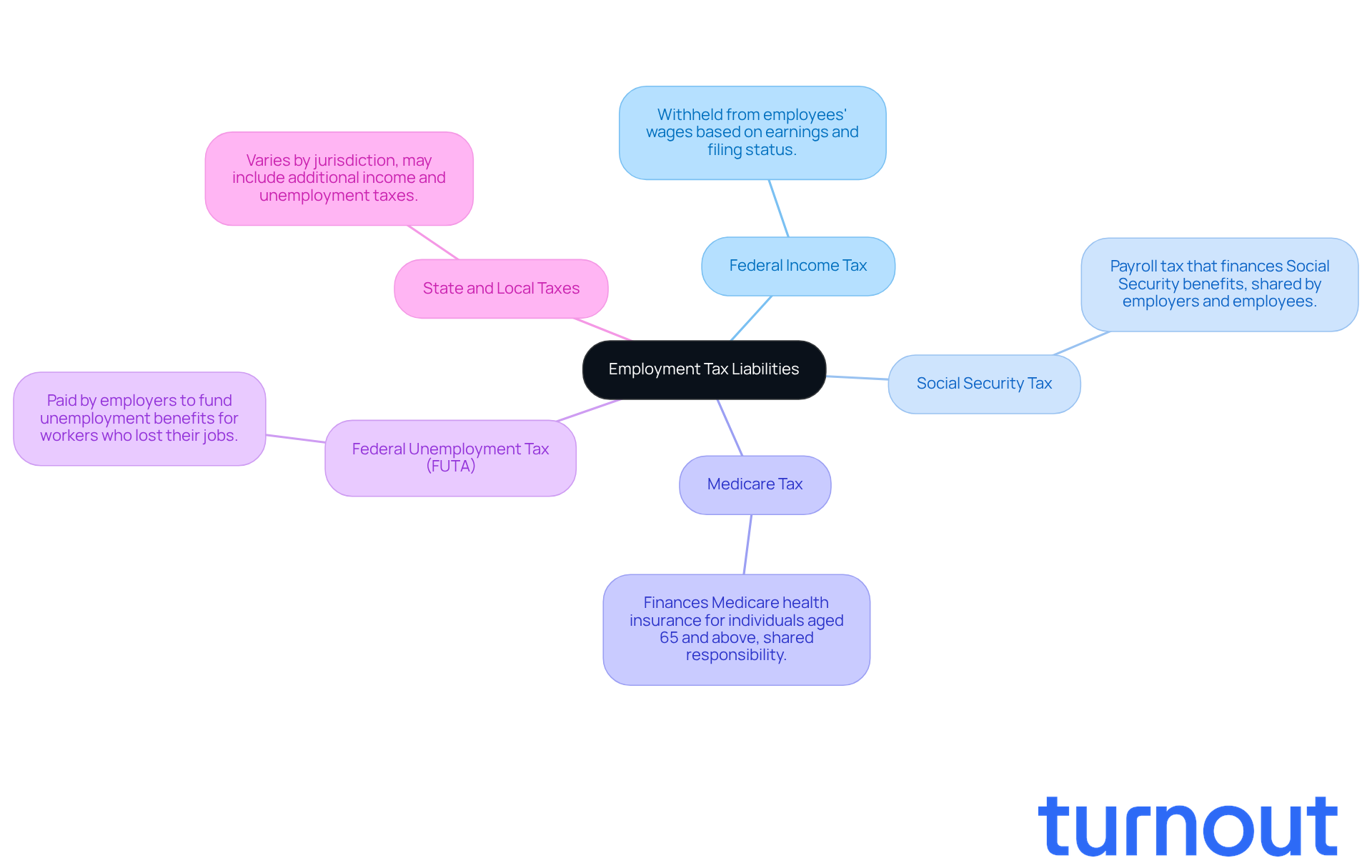
Navigating employment tax liabilities can feel overwhelming; however, understanding employment tax liabilities is crucial for every employer. Here’s a breakdown of the key types you should be aware of:
- Federal Income Tax: This is withheld from your employees' wages based on their earnings and filing status. It’s important to ensure accurate withholding to support your team.
- Social Security Tax: This payroll tax helps finance Social Security benefits. Both employers and workers contribute, making it a shared responsibility.
- Medicare Tax: This tax finances Medicare health insurance for individuals aged 65 and above. Like Social Security, it’s also shared between employers and employees.
- Federal Unemployment Tax (FUTA): This tax is paid by employers to fund unemployment benefits for workers who have lost their jobs. It’s a safety net that supports your team during tough times.
- State and Local Taxes: These can vary by jurisdiction and may include additional income taxes and unemployment taxes. Staying informed about employment tax liabilities can help you navigate your obligations more effectively.
We understand that keeping track of these taxes can be daunting, but you’re not alone in this journey. We're here to help you every step of the way.
Calculate and Track Employment Tax Liabilities Effectively
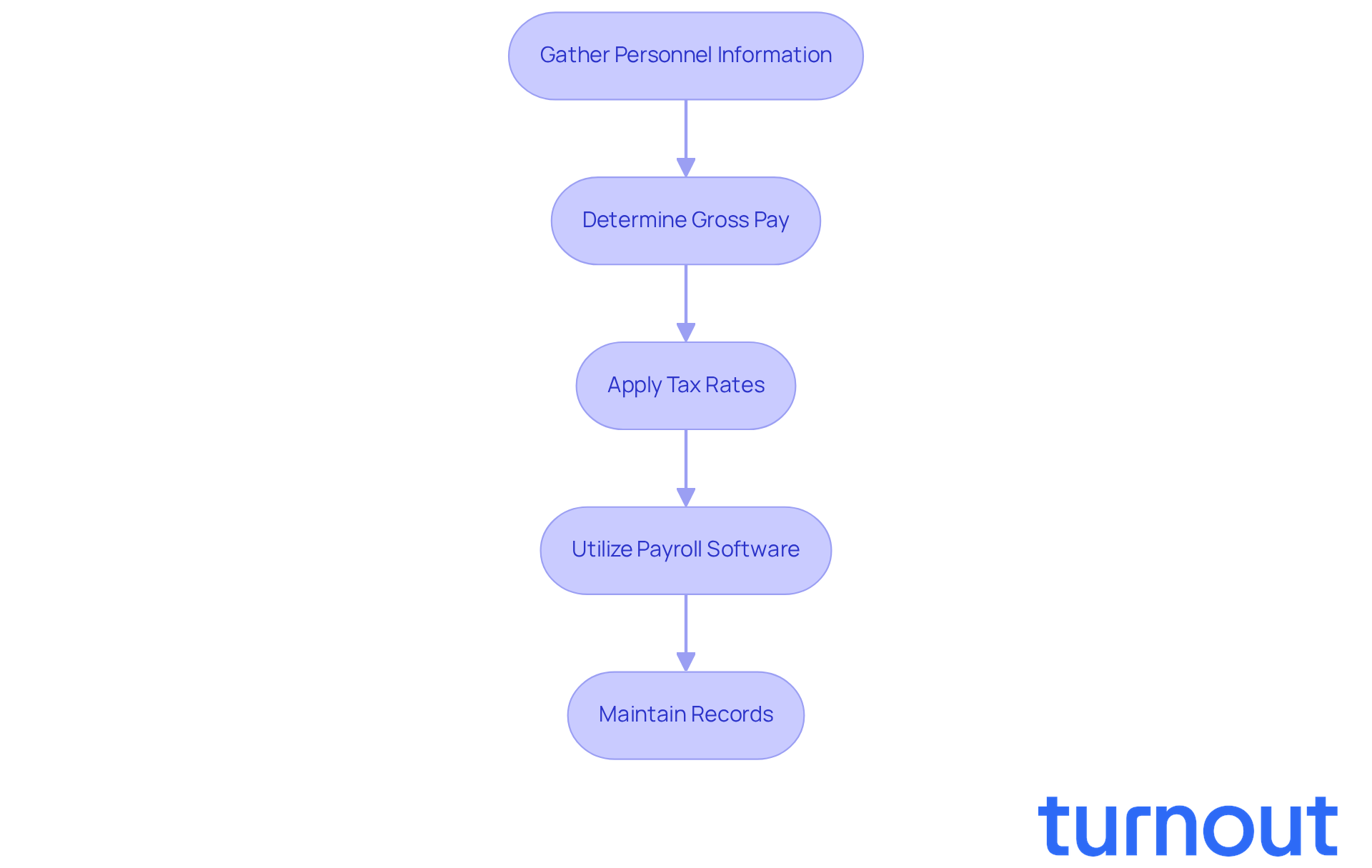
In 2026, calculating and tracking employment tax liabilities may seem overwhelming, but we're here to help. By following these essential steps, you can navigate this process with confidence:
-
Gather Personnel Information: Start by collecting necessary data, including each staff member's Form W-4, which indicates their withholding allowances. This foundational step is crucial for ensuring accurate tax calculations.
-
Determine Gross Pay: Next, calculate the total earnings for each employee, including regular wages, overtime, and bonuses. Understanding gross pay is vital for accurately assessing employment tax liabilities.
-
Apply Tax Rates: Use the current federal and state tax rates to determine how much to withhold for federal income tax, Social Security, and Medicare. Staying informed about tax rate changes is essential for compliance.
-
Utilize Payroll Software: Consider implementing payroll software that automates calculations and tracks liabilities. This can enhance accuracy and efficiency. In fact, as of 2026, around 80% of employers are expanding their payroll teams, many opting for automated systems to reduce errors.
-
Maintain Records: Finally, keep detailed records of all payroll transactions, including tax withholdings and payments made to tax authorities. This practice not only facilitates audits and regulatory checks but also helps mitigate risks linked to payroll errors, which affect 20% of payroll cycles each year.
By following these steps, you can approach the complexities of employment tax liabilities more confidently and clearly. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and taking these actions can lead to a smoother experience.
Understand Compliance Requirements for Employment Taxes
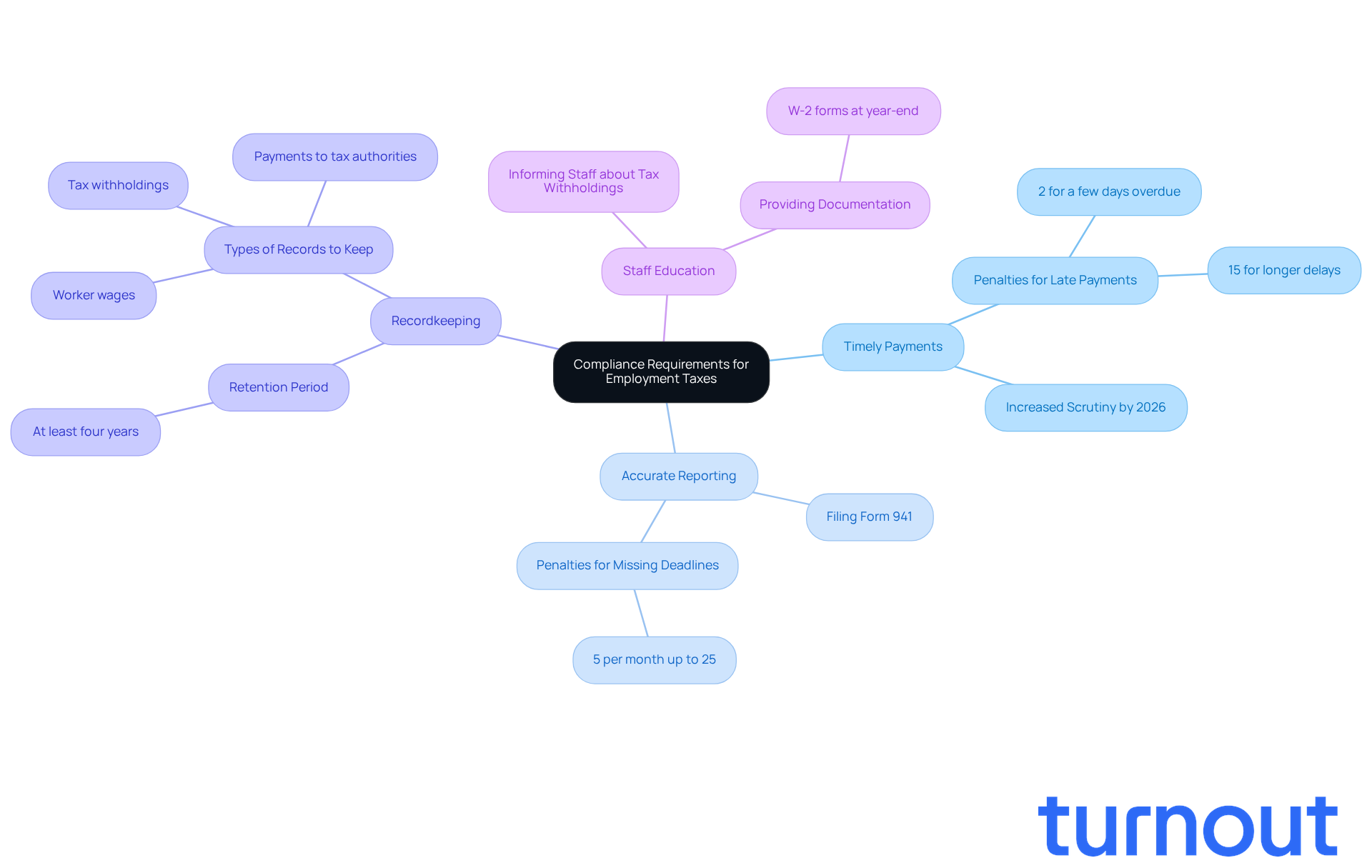
Employers, we understand that navigating compliance requirements regarding employment taxes can feel overwhelming. Here are some essential points to keep in mind:
-
Timely Payments: Paying employment taxes on time is crucial. Late payments can lead to significant penalties, starting at 2% for just a few days overdue and escalating to 15% for longer delays. As we approach 2026, companies will face increased scrutiny, and the consequences for late payments could be severe, with fees accumulating quickly if deadlines are missed.
-
Accurate Reporting: Filing tax forms, like Form 941 for quarterly federal tax returns, must be done accurately and punctually. Missing a deadline can incur extra charges of 5% per month, up to a total of 25%. It's vital for employers to prioritize accurate reporting. While recent statistics show improved adherence rates among businesses in 2026, many still encounter penalties due to simple oversights.
-
Recordkeeping: Keeping thorough records of worker wages, tax withholdings, and payments to tax authorities is essential. We recommend retaining these records for at least four years to ensure compliance and facilitate any necessary audits.
-
Staff Education: It's important to inform your staff about their tax withholdings and provide necessary documentation, like W-2 forms at year-end. This clarity helps employees understand their tax responsibilities and fosters a culture of compliance within your organization.
Experts agree that proactive communication with tax authorities can significantly reduce risks. Timely payments and accurate reporting are key to maintaining good standing. As one compliance specialist wisely noted, "The sooner you act, the better your chances of evading the worst payroll tax consequences." By following these guidelines, you can effectively navigate the complexities associated with employment tax liabilities. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we're here to help.
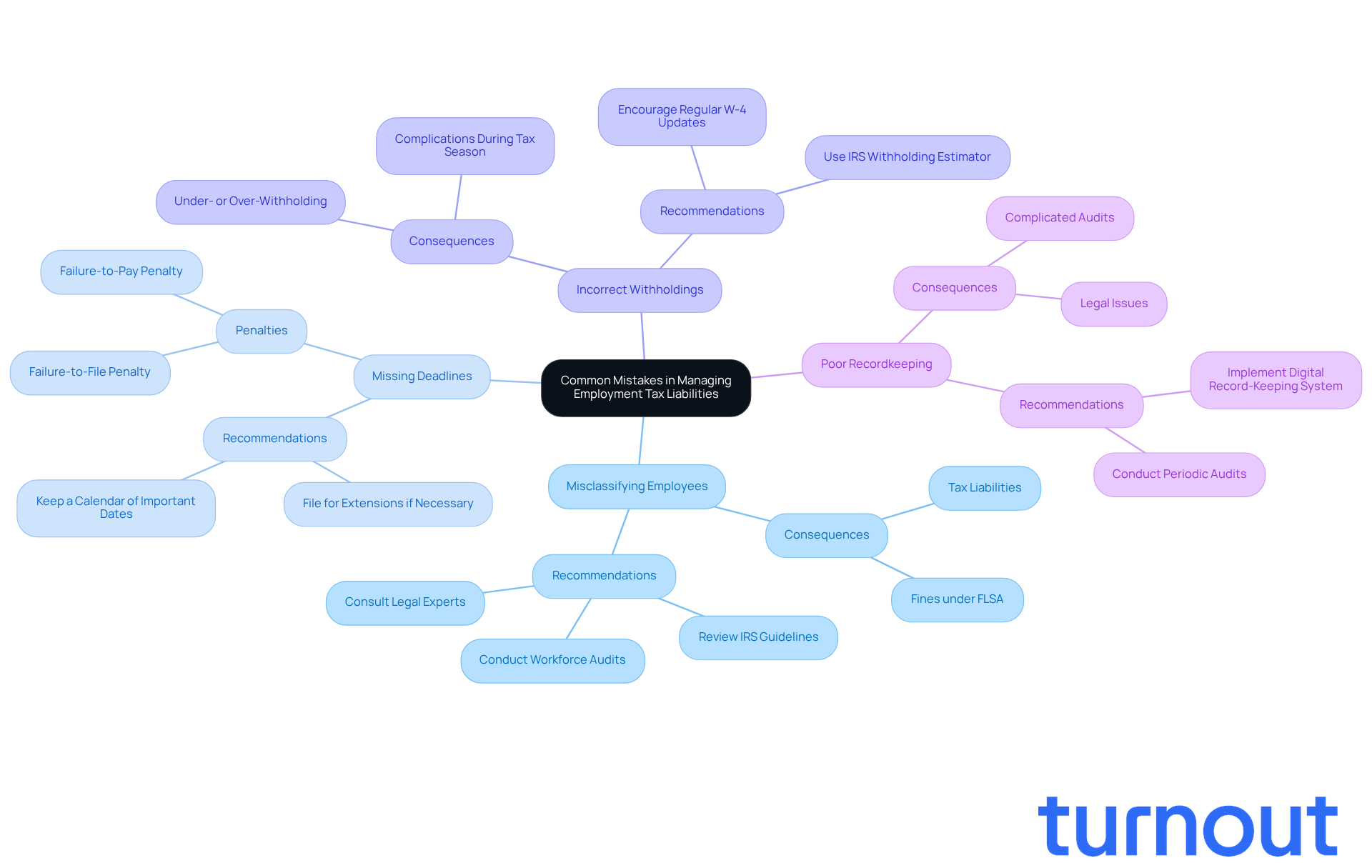
Identify Common Mistakes in Managing Employment Tax Liabilities
Common mistakes employers make when managing employment tax liabilities can feel overwhelming, but understanding them is the first step toward better management:
- Misclassifying Employees: It's easy to mistakenly classify employees as independent contractors, which can lead to significant tax liabilities. This misclassification not only complicates tax reporting but can also result in employment tax liabilities and fines under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). Companies that inaccurately classify workers may incur employment tax liabilities, owed payments, interest, and fines that can add up quickly, sometimes reaching thousands of dollars. In fact, a study by the American Payroll Association reveals that 40% of small businesses encounter IRS fines for payroll mistakes each year, averaging $845. We understand how daunting this can be, but staying informed can help you avoid these pitfalls.
Missing payment or form deadlines can result in employment tax liabilities, leading to fines and interest fees that can feel like a heavy burden. The IRS imposes a failure-to-file charge of 5% of the unpaid fees for each month the return is delayed, up to a maximum of 25%. If employment tax liabilities remain unpaid after the deadline, a failure-to-pay penalty of 0.5% per month applies, compounding the financial strain on employers. Remember, keeping a calendar of important dates can help you stay on track.
-
Incorrect Withholdings: Not applying the correct tax rates or failing to update staff information can lead to under- or over-withholding. This can create complications during tax season, especially with the revised W-4 form introduced in 2024, which adds complexity to how workers communicate their withholding preferences. Encourage your employees to regularly review and update their W-4 forms to maintain accurate tax withholding. You're not alone in this; many employers face similar challenges.
-
Poor Recordkeeping: Insufficient documentation can complicate audits and regulatory checks, leading to potential legal issues. We recommend implementing a robust digital record-keeping system and conducting periodic audits of payroll records to ensure compliance and efficiency. It's essential to maintain payroll records for three years per FLSA to avoid disputes and repercussions. Taking these steps can provide peace of mind.
Neglecting state and local taxes can lead to unforeseen employment tax liabilities and fines. Many states have their own tax deadlines and requirements, which can differ from federal regulations. Staying informed about local tax laws is crucial to avoid costly penalties. Remember, you're not navigating this alone; there are resources available to help you stay compliant.
Conclusion
Navigating employment tax liabilities can feel overwhelming, and we understand that managing these responsibilities is crucial for your business's success. By grasping these obligations, you not only ensure compliance but also foster financial stability. Employers must accurately withhold and remit various taxes, including federal income tax, Social Security, Medicare, and federal unemployment tax. Recognizing the complexities of these obligations is essential to avoid costly penalties and maintain smooth operations.
In this guide, we've shared key insights on defining employment tax liabilities, exploring their types, and outlining effective strategies for calculation and compliance. We encourage you to:
- Gather necessary personnel information
- Apply correct tax rates
- Utilize payroll software
- Maintain thorough records
It's common to feel uncertain about these processes, but being aware of common mistakes - like misclassifying employees and incorrect withholdings - can significantly mitigate risks associated with employment taxes.
In conclusion, staying informed and proactive about your employment tax obligations is not just a legal requirement; it’s a vital part of your business's success. By implementing best practices and seeking assistance when needed, you can navigate these complexities with confidence. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Embracing a culture of compliance will protect your business from penalties and foster trust and transparency within your workforce. We're here to help you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are employment tax liabilities?
Employment tax liabilities are the taxes that employers are responsible for deducting from their workers' wages and contributing on their behalf. This includes federal income tax, Social Security tax, Medicare tax, and federal unemployment tax (FUTA).
What specific taxes are included in employment tax liabilities?
Employment tax liabilities include federal income tax, Social Security tax, Medicare tax, and federal unemployment tax (FUTA).
What are the rates for Social Security and Medicare taxes for the tax year 2026?
For the tax year 2026, Social Security tax is set at 6.2% on wages up to a taxable maximum of $176,100, while Medicare tax is 1.45% of gross wages.
How does federal unemployment tax (FUTA) work?
Employers contribute to FUTA, which varies between 0.6% to 6% depending on state obligations. This tax funds unemployment benefits for workers who have lost their jobs.
Why is it important for employers to understand employment tax liabilities?
Understanding employment tax liabilities is essential for adhering to tax regulations, avoiding penalties, and ensuring accurate withholding amounts for employees. Misclassification of workers can lead to significant consequences, including fines and back wages.
What is a 'Paycheck Checkup'?
A 'Paycheck Checkup' is a suggestion from the IRS to help employers ensure accurate withholding amounts for their workers, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
How can employers maintain financial stability regarding employment tax liabilities?
By accurately calculating and remitting employment tax liabilities on time, employers fulfill their legal obligations, maintain financial stability, and avoid costly disruptions to their business operations.




