Overview
Understanding the tax implications of Zelle transactions is crucial, especially when they involve payments for goods or services. These transactions must be reported to the IRS, regardless of whether you receive a 1099-K form. We understand that navigating tax obligations can feel overwhelming, but it’s essential to distinguish between personal and business transactions.
Maintaining accurate records is not just a good practice; it’s a vital step in ensuring compliance with tax laws. You deserve to feel confident in your financial decisions. By being aware of reporting thresholds, you can avoid potential issues down the line.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you understand these responsibilities and ensure that you are prepared. Taking these steps can bring you peace of mind and help you focus on what truly matters.
Introduction
Navigating the intricacies of digital payments can feel overwhelming, especially with the rise of platforms like Zelle that enable quick money transfers directly between bank accounts. We understand that while this service offers convenience, it also raises important questions about tax obligations, particularly as the IRS updates its reporting requirements.
It’s common to feel uncertain about which transactions are taxable and how to accurately report them to avoid penalties. So, what should Zelle users know to ensure compliance and safeguard themselves against potential tax pitfalls? We're here to help you through this journey.
Understand Zelle and Its Tax Reporting Landscape
Navigating the world of digital payments can feel overwhelming, but we're here to help. The digital payment platform allows users to transfer and receive funds directly between bank accounts, usually within minutes. Unlike other payment applications, this service operates directly through participating banks rather than as a third-party processor. This distinction is important because it exempts the service from certain IRS reporting requirements that apply to other platforms like Venmo or PayPal.
As of 2025, this payment service does not provide Form 1099-K, which is commonly used to report earnings from payment processors. It's essential to understand that while transfers via the platform may not be disclosed to the IRS, you are still required to declare any taxable earnings received through it, raising the question of whether Zelle is taxable. For instance, if you are self-employed and receive payments for services through this digital payment platform, you must report that revenue on your tax return, even without a 1099-K form.
Keeping thorough records of all your Zelle activities throughout the year is crucial for accurate tax reporting and compliance with IRS guidelines. Remember, while personal payments from friends and family are not taxable, it is important to consider if Zelle is taxable for any business-related payments, as those are considered taxable income. Therefore, it’s vital to separate personal and business transactions to avoid confusion and potential penalties for unreported earnings.
Failing to report income from the payment service can lead to serious consequences, including fines, interest fees, and even allegations of tax evasion. To safeguard yourself, consider keeping a distinct business bank account to accurately determine total earnings from deposits. Additionally, the One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBBA) has introduced changes to tax reporting obligations that may impact Zelle users, underscoring the importance of monitoring your business earnings closely.
If you're self-employed, you'll need to file Form 1040 Schedule C to report your business income and claim tax deductions. Consulting with tax professionals can also help you manage your tax filing and minimize the taxes you owe, as their fees are likely tax-deductible. Lastly, remember to make estimated tax payments quarterly to avoid penalties, with due dates in 2025 being:
- April 15
- June 16
- September 15
- January 15, 2026
You are not alone in this journey, and taking these steps can help you feel more secure and informed.
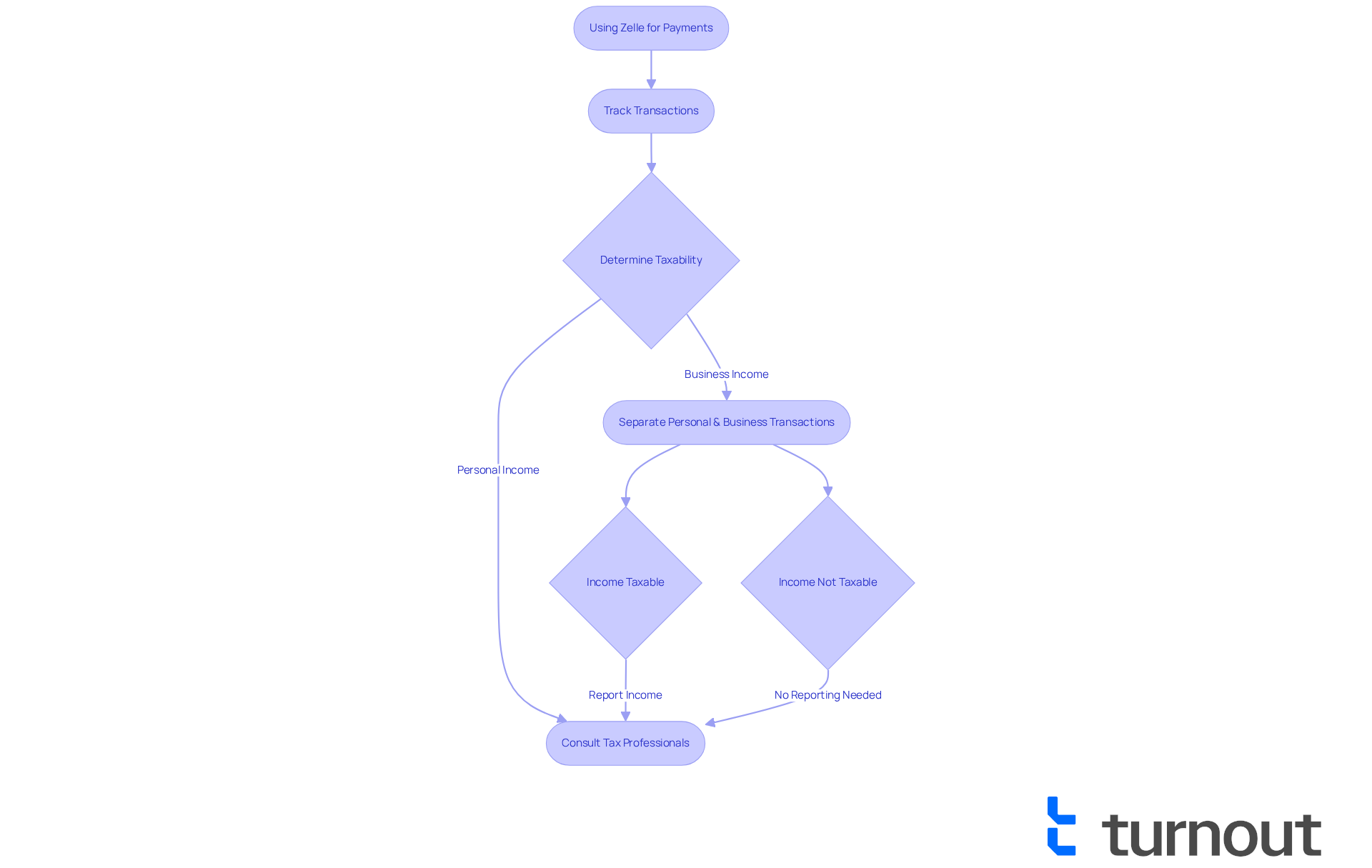
Identify Taxable Transactions: Key Criteria for Zelle Users
Understanding whether a Zelle transaction is taxable, or specifically, is Zelle taxable, can feel overwhelming, but we're here to help you navigate this important aspect of your finances. To clarify, consider these key criteria:
-
Nature of the Payment: Payments made for goods or services are generally taxable. For instance, if you receive payment for freelance work or selling products, you must report this revenue to the IRS.
-
Personal vs. Business Transactions: It's common to feel confused about what counts as taxable. Personal payments, like splitting a dinner bill with friends or receiving a gift, are not taxable. However, payments received for business purposes raise the question of whether is Zelle taxable, as they are considered taxable income. If you use a digital payment service to collect payments for services rendered, you may wonder, is Zelle taxable, and those amounts must be reported. Keeping your business and personal transactions separate is crucial for complying with tax laws.
-
Total Amount: Starting in 2025, if your total business earnings from the payment service exceed $600 in a year, you need to declare this revenue on your tax return. Even though the payment service may not issue a 1099-K form, the IRS requires that all earnings be reported. Remember, during an audit, the IRS can track bank activities, so maintaining accurate records of all transactions is essential. Additionally, receiving large payments that seem inconsistent with personal use may raise flags with the IRS. Organizing your records early can help prevent confusion about your taxable earnings.
We understand that tax matters can be daunting, but with careful attention and organization, you can manage your Zelle transactions confidently.
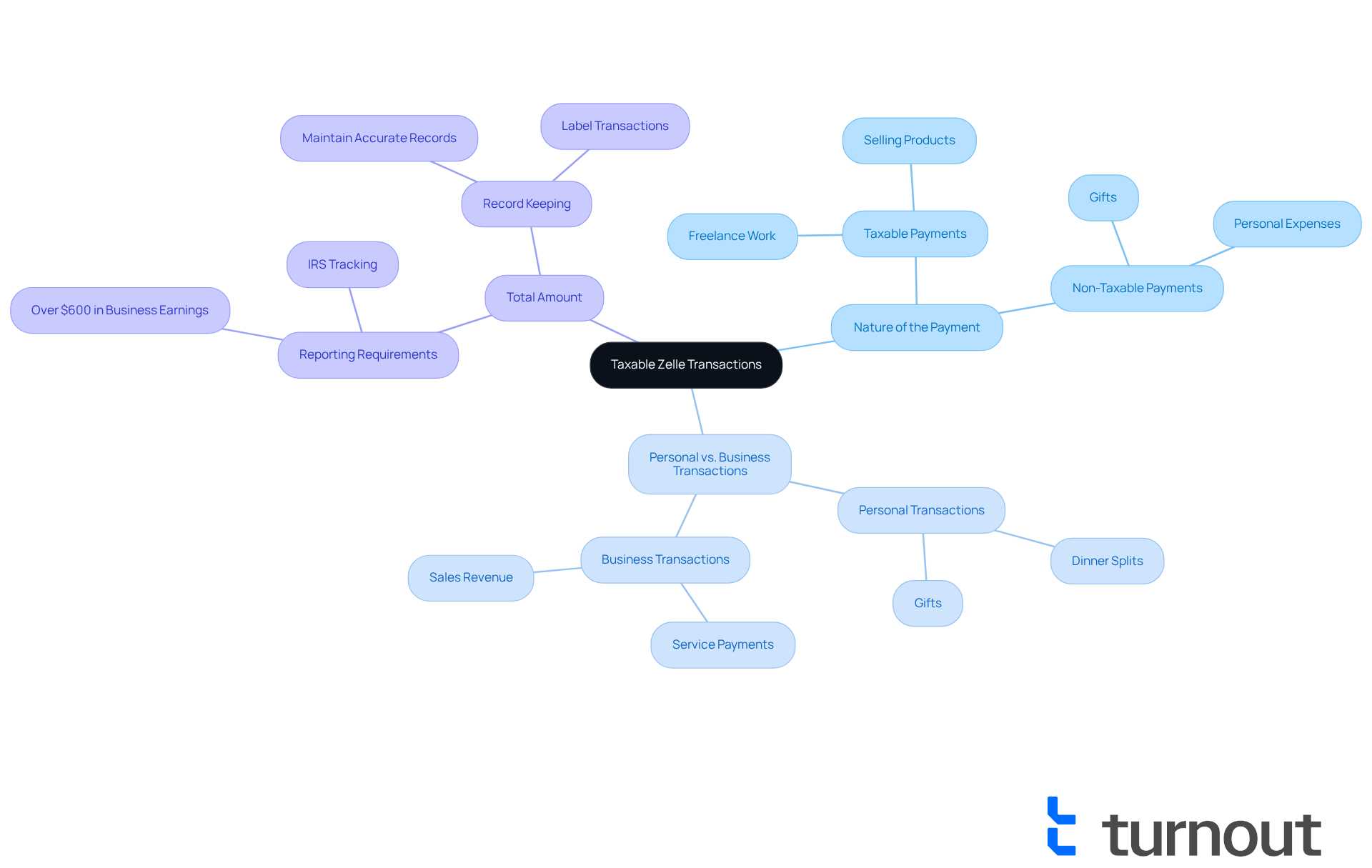
Report Your Zelle Income: Step-by-Step Instructions
Reporting your Zelle earnings can feel overwhelming, but we're here to help. Follow these steps to navigate the process with confidence:
-
Gather Your Records: Start by collecting all relevant documentation. This includes your bank statements, invoices, and receipts related to your business revenue. Having everything in one place will ease your mind.
-
Determine Taxable Amounts: Next, identify which transactions are taxable. Remember, if your total earnings from digital payments, including any amount that is zelle taxable, and other sources reach $400 or more within a year, you must declare it. Personal payments from friends and family are not considered taxable business earnings, so don’t worry about those.
-
Complete Your Tax Return: When it’s time to fill out your tax return, report your digital payment income on the appropriate line for business income. If you are self-employed, this will typically go on Schedule C of Form 1040. It’s a straightforward process once you have your records ready.
-
Keep Detailed Records: Maintaining thorough documentation of your transactions and related business expenses is crucial. As a business using Zelle, knowing if is Zelle taxable will help you manage your records for annual tax returns and quarterly estimated taxes. This diligence will also help verify your earnings if the IRS inquires.
-
Consult a Tax Expert: If you feel uncertain about declaring your earnings or if your situation is complex, consider seeking advice from a tax expert. Many self-employed freelancers and small business owners find comfort in consulting tax professionals to ensure compliance. Remember, consistent monitoring and reconciling your activities can aid in managing cash flow and avoiding inconsistencies.
Neglecting to report qualifying business earnings from digital payments can lead to penalties and increased scrutiny from the IRS. But you are not alone in this journey; with the right support and guidance, you can navigate your tax obligations successfully.
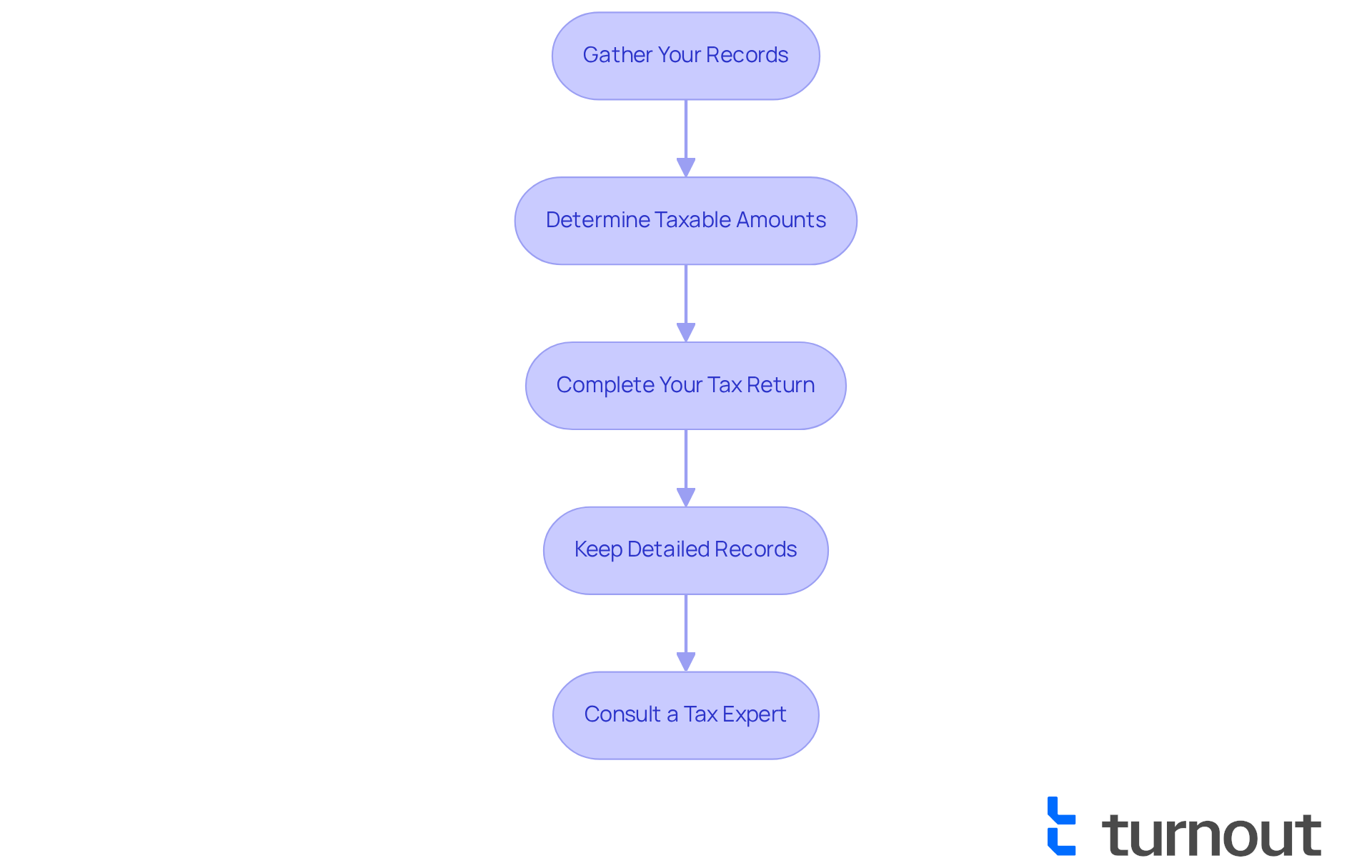
Avoid Common Mistakes: Best Practices for Zelle Tax Reporting
To help you avoid common mistakes when reporting Zelle transactions, let’s explore some best practices that can ease your journey:
-
Separate Personal and Business Activities: We understand that distinguishing between personal and business activities can be challenging. However, this separation is essential. It not only makes tracking easier but also guarantees precise reporting of your taxable earnings.
-
Document Everything: Keeping detailed records of all transactions is crucial. Note the purpose of each payment. This documentation is vital for accurate reporting and can serve as protection in the event of an audit.
-
Be Aware of Reporting Thresholds: It’s common to feel overwhelmed by tax regulations. Familiarize yourself with the reporting thresholds for taxable earnings. Starting in 2025, if your total earnings from the payment service surpass $600, you must declare it, even if you do not obtain a 1099-K form. Remember, you must report all taxable income received via Zelle, leading to the question: is Zelle taxable, as Zelle does not issue 1099-K forms?
-
Review IRS Guidelines: Staying informed can alleviate many concerns. Regularly consult the IRS website for updates on tax reporting requirements related to digital payments. This proactive approach can help you avoid potential pitfalls.
-
Seek Professional Advice: If you encounter uncertainties or complex situations, remember that you are not alone in this journey. It is wise to consult a tax professional. Their expertise can ensure that you meet all reporting requirements accurately and efficiently.
By following these best practices, you can navigate the complexities of Zelle transactions with confidence. We're here to help you every step of the way.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of Zelle and its tax implications can feel overwhelming, especially for those engaged in both personal and business transactions. While Zelle provides a convenient way to transfer funds, it’s vital to understand the tax responsibilities that come with its use. This knowledge is essential for ensuring compliance and avoiding penalties. Remember, the distinction between personal and business payments is crucial, as only the latter qualifies as taxable income. This necessitates careful record-keeping and reporting.
We want to highlight some key insights that can help you on this journey:
- Maintaining thorough documentation of all Zelle transactions is necessary.
- It’s also important to recognize when payments are taxable.
- Be aware of the upcoming reporting requirements set for 2025.
- Keeping your personal and business activities separate is a wise practice.
- Familiarizing yourself with IRS guidelines is beneficial.
- Considering consulting tax professionals for tailored advice can provide you with peace of mind.
By following these steps, you can confidently navigate your tax obligations and mitigate potential issues with the IRS.
Ultimately, being proactive about Zelle transactions and their tax implications fosters financial clarity. It empowers you to manage your income responsibly. As the landscape of digital payments evolves, staying informed and organized will be key to ensuring compliance with tax laws. Embracing these best practices will help you avoid common mistakes and maintain peace of mind as you engage with this increasingly popular payment platform. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Zelle and how does it work?
Zelle is a digital payment platform that allows users to transfer and receive funds directly between bank accounts, typically within minutes. It operates through participating banks rather than as a third-party processor.
Does Zelle provide Form 1099-K for tax reporting?
No, as of 2025, Zelle does not provide Form 1099-K, which is commonly used to report earnings from payment processors.
Are transfers via Zelle reported to the IRS?
While transfers via Zelle may not be disclosed to the IRS, users are still required to declare any taxable earnings received through the platform.
Do I need to report payments received through Zelle if I am self-employed?
Yes, if you are self-employed and receive payments for services through Zelle, you must report that revenue on your tax return, even without a 1099-K form.
Are personal payments made through Zelle taxable?
Personal payments from friends and family are not taxable, but business-related payments received through Zelle are considered taxable income.
What should I do to ensure accurate tax reporting for Zelle transactions?
It's crucial to keep thorough records of all your Zelle activities throughout the year and to separate personal and business transactions to avoid confusion.
What are the consequences of failing to report income from Zelle?
Failing to report income can lead to serious consequences, including fines, interest fees, and potential allegations of tax evasion.
What steps can I take to safeguard myself when using Zelle for business transactions?
Consider keeping a distinct business bank account to accurately track total earnings from deposits and consult with tax professionals for guidance on tax filing.
What form do self-employed individuals need to file to report business income?
Self-employed individuals need to file Form 1040 Schedule C to report their business income and claim tax deductions.
When are the due dates for estimated tax payments in 2025?
The due dates for estimated tax payments in 2025 are April 15, June 16, September 15, and January 15, 2026.




