Introduction
Navigating the complex world of state disability taxation can feel overwhelming. We understand that many individuals rely on these essential support systems, and knowing whether state disability benefits are taxable is crucial. This knowledge directly impacts your financial planning and compliance with tax regulations.
With different rules across states and the potential for significant tax implications, it’s common to feel uncertain. How can you ensure you’re fully informed and prepared? This article will guide you through the essential steps and resources needed to clarify the tax status of state disability benefits. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you take control of your financial situation.
Understand the Basics of State Disability Taxation
Navigating the complexities of state disability taxation can feel overwhelming. But understanding a few key concepts can make a significant difference in your journey.
Definition of State Support Programs: State support programs are financial aid initiatives offered by state governments to individuals who can’t work due to physical or mental conditions. These programs vary widely from state to state, and millions of Americans rely on them for support.
It's important to understand whether state assistance for disabilities is state disability taxable or non-taxable. This depends on factors like where the funds come from and your total earnings. Familiarizing yourself with terms like 'taxable income' and 'non-taxable income' can help clarify your situation.
Federal vs. State Taxation: While federal tax laws provide a general framework, each state has its own rules regarding the taxation of disability assistance. Understanding whether state disability is taxable is crucial for accurate tax reporting and compliance.
Consulting Resources: We encourage you to utilize resources like IRS Publication 907, which outlines tax highlights for individuals with impairments. Consulting with tax professionals can also offer personalized insights tailored to your specific circumstances.
By grasping these fundamentals, you’ll feel more equipped to evaluate your tax situation concerning state assistance. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help.
Identify Taxable vs. Non-Taxable Disability Benefits
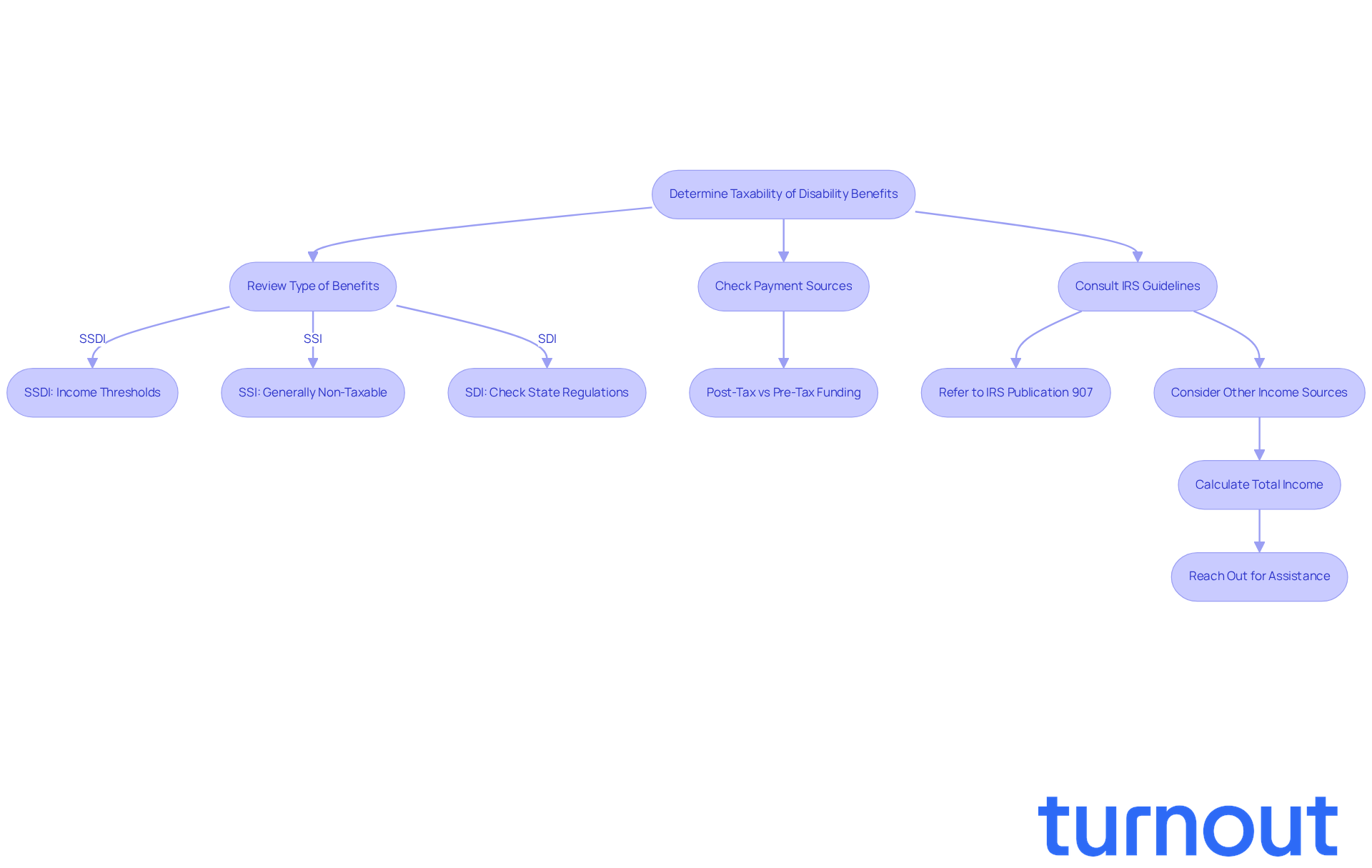
Determining whether your disability benefits are taxable, specifically if state disability is taxable, can feel overwhelming, but we're here to help you navigate this process with care. Follow these steps to gain clarity:
-
Review the Type of Benefits: Different types of disability benefits come with different tax implications.
- Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI): If your combined income exceeds certain thresholds, SSDI benefits may be taxable. For single filers, this threshold is $25,000, and for married couples filing jointly, it’s $32,000. If you surpass these limits, up to 85% of your SSDI payments could be taxed. It’s important to note that currently, 50% of Social Security recipients' payments are taxed. Understanding your tax obligations, such as whether state disability is taxable, is crucial, and organizations like Turnout can assist you in navigating these complexities without needing legal representation.
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI): Thankfully, SSI payments are generally not taxable, providing essential financial support without tax implications.
- State Disability Insurance (SDI): Most states do not tax SDI payments, leading to the question of whether state disability is taxable. Be sure to check your state’s regulations to be informed.
-
Check Payment Sources: The tax implications of assistance payments from employer-sponsored plans can depend on how premiums were paid. If benefits were funded with post-tax dollars, they’re typically non-taxable. However, those funded with pre-tax dollars may be taxable.
-
Consult IRS Guidelines: It’s wise to refer to IRS guidelines, especially Publication 907, which outlines specific tax rules related to impairments. This resource can clarify how your benefits are treated under current tax laws. If you’re uncertain about your eligibility or tax obligations, consider reaching out to Turnout for assistance. They can help you understand your options, including support from IRS-licensed enrolled agents.
-
Consider Extra Earnings: If you have other sources of income, like dividends or interest, this could affect the taxability of your assistance payments. Calculate your total income to see if it exceeds the thresholds, as higher income can lead to a larger portion of your SSDI payments being taxable. Also, keep in mind the new $6,000 tax deduction for individuals aged 65 and older in 2026, which may offer potential tax relief for seniors.
By carefully assessing these elements, you can determine which of your assistance payments are taxable. This understanding will help you stay compliant with tax laws while optimizing your financial resources. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey-Turnout is here to support you.
Gather Necessary Documentation for Tax Assessment
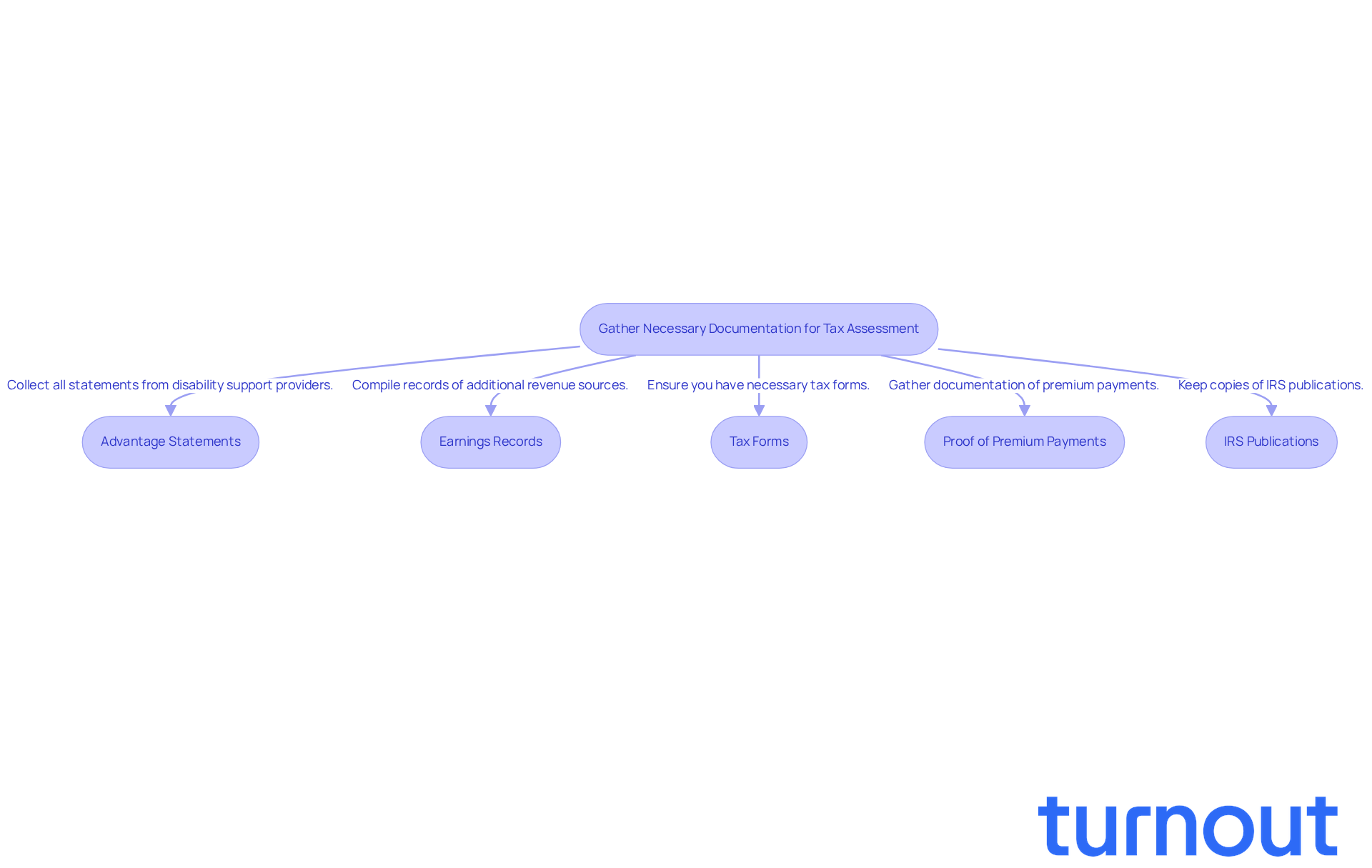
Preparing for your tax assessment regarding disability benefits can feel overwhelming, but you’re not alone in this journey. To help you navigate this process, gather the following documentation:
-
Advantage Statements: Collect all statements from your disability support providers, including SSDI, SSI, and state disability assistance. Each year, SSDI recipients receive Form SSA-1099, which outlines the total SSDI payments received during the prior year. These documents detail the amounts received during the tax year, which are crucial for accurate reporting.
-
Earnings Records: Compile records of any additional revenue sources, such as wages, dividends, or interest. This information is essential, as it can affect whether your disability assistance is state disability taxable, especially if your total earnings surpass certain limits. Did you know that up to 50% of SSDI payments may be subject to tax, leading to the question of whether is state disability taxable if combined earnings exceed $25,000 for individual filers?
-
Tax Forms: Make sure you have the necessary tax forms, like Form 1040 or 1040-SR, along with any relevant schedules that may apply to your situation. These forms are vital for reporting your earnings and advantages accurately.
-
Proof of Premium Payments: If your advantages come from an employer-sponsored plan, gather documentation showing how premiums were paid (pre-tax vs. post-tax). This distinction can significantly affect your taxable income.
-
IRS Publications: Keep copies of IRS publications concerning disability assistance and taxation, such as Publication 915. These resources provide guidance on how to report your entitlements and understand tax implications. Remember, SSI payments are not subject to federal taxes, and it is important to know if state disability is state disability taxable, as they do not need to be reported on tax returns.
By organizing these documents ahead of time, you can simplify the tax filing process and ensure that you accurately report your assistance payments. This preparation reduces the chance of mistakes or issues with your tax return. Remember, tax returns are due by April 15, 2026, even if some tax documents are missing. Direct deposits from the IRS typically arrive in three weeks or less.
We’re here to help! With the support of trained nonlawyer advocates and IRS-licensed enrolled agents, you can navigate these processes with confidence, receiving expert guidance without the need for legal representation.
Navigate Bureaucratic Processes for Tax Determination
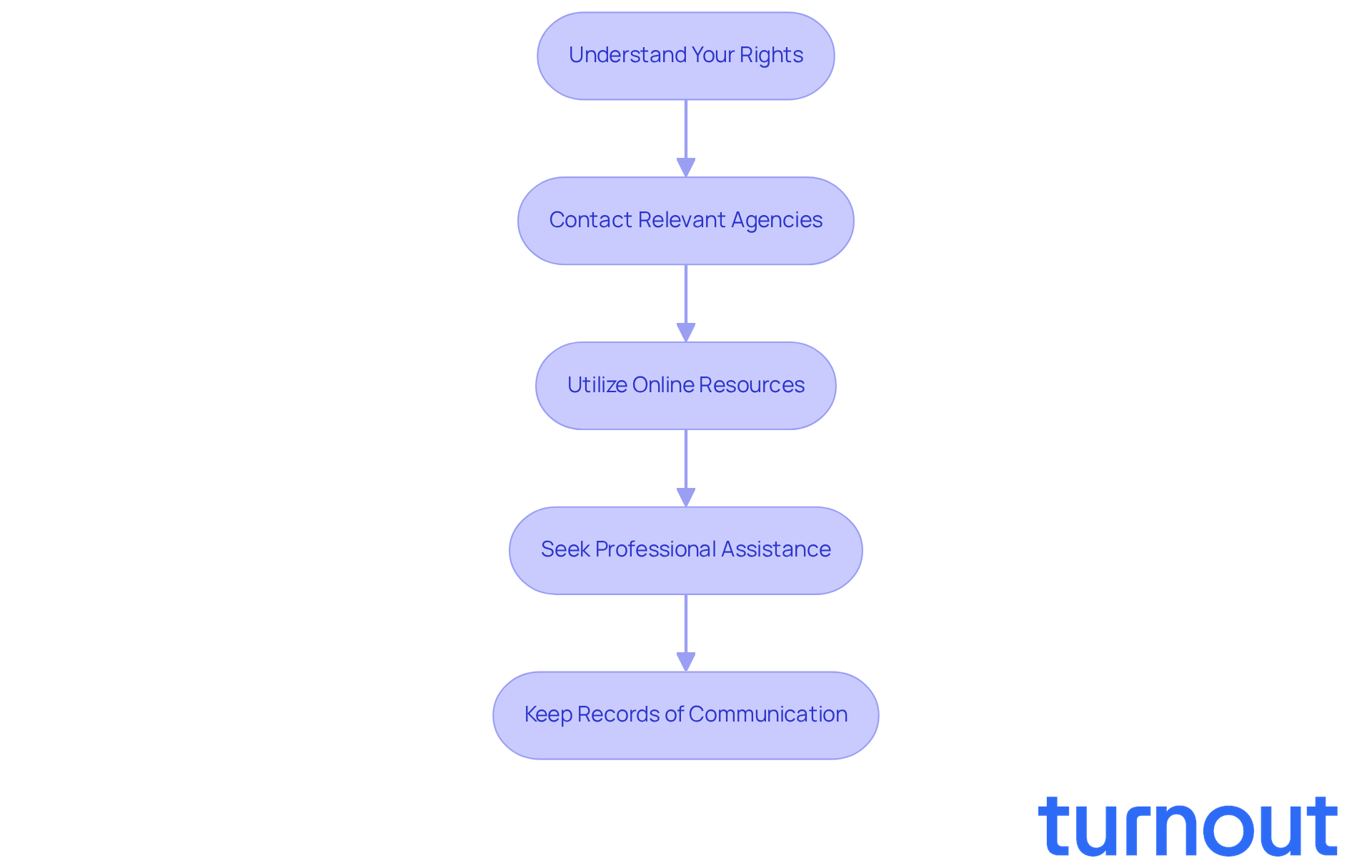
Navigating the bureaucratic processes involved in understanding whether state disability is taxable for benefits can feel overwhelming. But don’t worry; we’re here to help you through it. Here are some steps to guide you:
-
Understand Your Rights: It’s important to know your rights as a taxpayer with impairments. The IRS has resources specifically for you, including IRS Publication 5066-A. This publication outlines the services provided by Low Income Taxpayer Clinics (LITCs) to help you understand your entitlements and obligations.
-
Contact Relevant Agencies: If you have questions about your assistance payments and whether state disability is taxable, reach out to the IRS or your state tax agency. When you call, have your documentation ready to make the process smoother.
-
Utilize Online Resources: Take advantage of online tools and resources. The IRS website and your state tax agency’s site offer comprehensive information about filing requirements and deadlines that are relevant to your situation.
-
Seek Professional Assistance: If the process feels daunting, consider consulting a tax expert who specializes in support for those with disabilities. Turnout provides access to IRS-licensed enrolled agents and various tools designed to assist you in navigating the complex tax laws related to impairment allowances. Many taxpayers with impairments are seeking professional tax assistance, highlighting the importance of expert guidance in this area.
-
Keep Records of Communication: It’s wise to document all your interactions with tax agencies. Keep track of dates, names of representatives, and details discussed. This record-keeping can be invaluable if you need to follow up or dispute any issues that arise.
By following these steps, you can confidently navigate the bureaucratic processes related to determining if state disability is taxable for your benefits. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
Conclusion
Understanding whether state disability benefits are taxable is essential for anyone relying on these vital financial supports. We know that the complexities surrounding taxation can feel overwhelming. But with a clear grasp of the fundamental concepts, you can navigate your tax obligations with confidence.
In this guide, we’ve highlighted key points to help you determine the taxability of state disability benefits. It’s important to distinguish between taxable and non-taxable benefits, like SSDI and SSI. Gathering necessary documentation and navigating bureaucratic processes are crucial steps for ensuring compliance and optimizing your financial resources. Consulting IRS guidelines and seeking professional assistance can further clarify your personal circumstances and tax obligations.
Ultimately, being informed about state disability taxation isn’t just about fulfilling legal requirements; it’s about empowering you to make sound financial decisions. By taking the time to understand the rules and seeking help when needed, you can maximize your benefits while staying compliant with tax laws. Remember, the journey may be complex, but support is available. Taking proactive steps can make a significant difference in achieving peace of mind regarding your financial future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are state support programs?
State support programs are financial aid initiatives offered by state governments to individuals who cannot work due to physical or mental conditions. These programs vary widely from state to state, and millions of Americans rely on them for support.
Are state disability benefits taxable?
Whether state assistance for disabilities is taxable or non-taxable depends on factors such as the source of the funds and your total earnings. Understanding terms like 'taxable income' and 'non-taxable income' is essential for clarifying your situation.
How do federal and state taxation differ regarding disability assistance?
Federal tax laws provide a general framework, but each state has its own rules regarding the taxation of disability assistance. Understanding your state's specific regulations is crucial for accurate tax reporting and compliance.
What resources can help me understand state disability taxation?
Resources such as IRS Publication 907 outline tax highlights for individuals with impairments. Additionally, consulting with tax professionals can provide personalized insights tailored to your specific circumstances.
Why is it important to understand state disability taxation?
Grasping the fundamentals of state disability taxation equips you to evaluate your tax situation concerning state assistance, ensuring accurate reporting and compliance with tax laws.




