Introduction
Navigating the complexities of financial assistance can feel overwhelming, especially for those relying on Supplemental Security Income (SSI) due to disabilities. We understand that while SSI provides crucial support for vulnerable populations, many recipients often wonder if their benefits are taxable. This concern is valid and important. Understanding the tax implications of SSI is essential not just for effective financial management, but also for maximizing the support available to you.
With potential changes on the horizon, it’s common to feel uncertain about your tax responsibilities. How can you ensure that you’re making informed decisions and avoiding unexpected liabilities? We’re here to help you through this journey, providing the guidance you need to navigate these challenges with confidence.
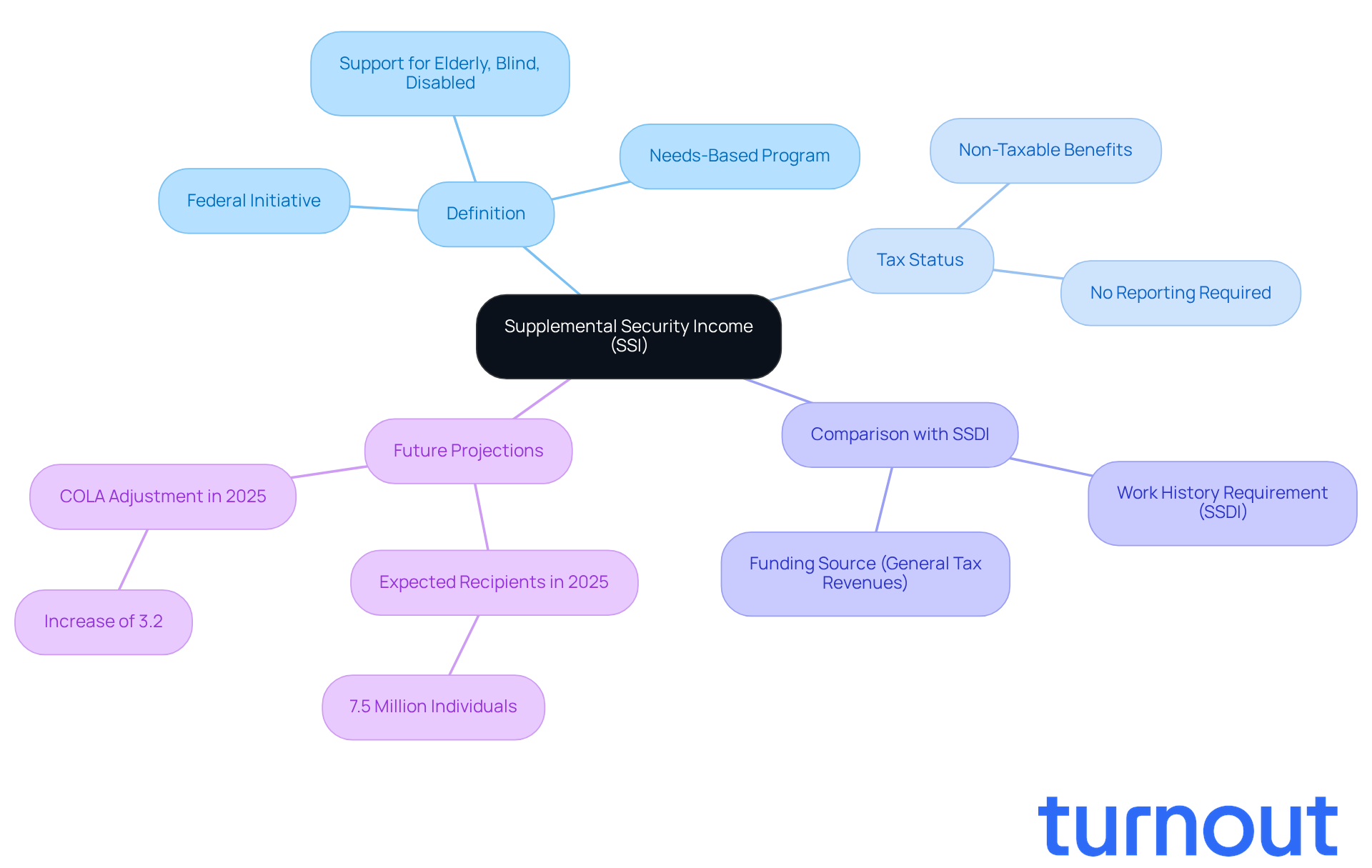
Define SSI Disability and Its Tax Status
Supplemental Security Income (SSI) is a vital federal initiative aimed at providing financial support to those who are elderly, blind, or disabled and have limited resources. We understand that navigating financial challenges can be overwhelming, especially when facing disabilities. Unlike Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI), which depends on your work history, SSI is a needs-based program funded through general tax revenues.
One of the most reassuring aspects of SSI is that it raises the question of whether SSI disability is taxable, as its benefits are not considered taxable earnings under federal law. This means you won’t have to report SSI payments on your tax returns, which is crucial for those already dealing with financial hardships. In 2025, around 7.5 million individuals are expected to receive SSI assistance, underscoring the program's importance in supporting vulnerable groups.
Financial experts emphasize that understanding if SSI disability is taxable is essential for beneficiaries. It can help you manage your finances more effectively and maximize the support you receive. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We're here to help you navigate these challenges and ensure you get the assistance you deserve.
Identify Taxable Conditions for SSI Benefits
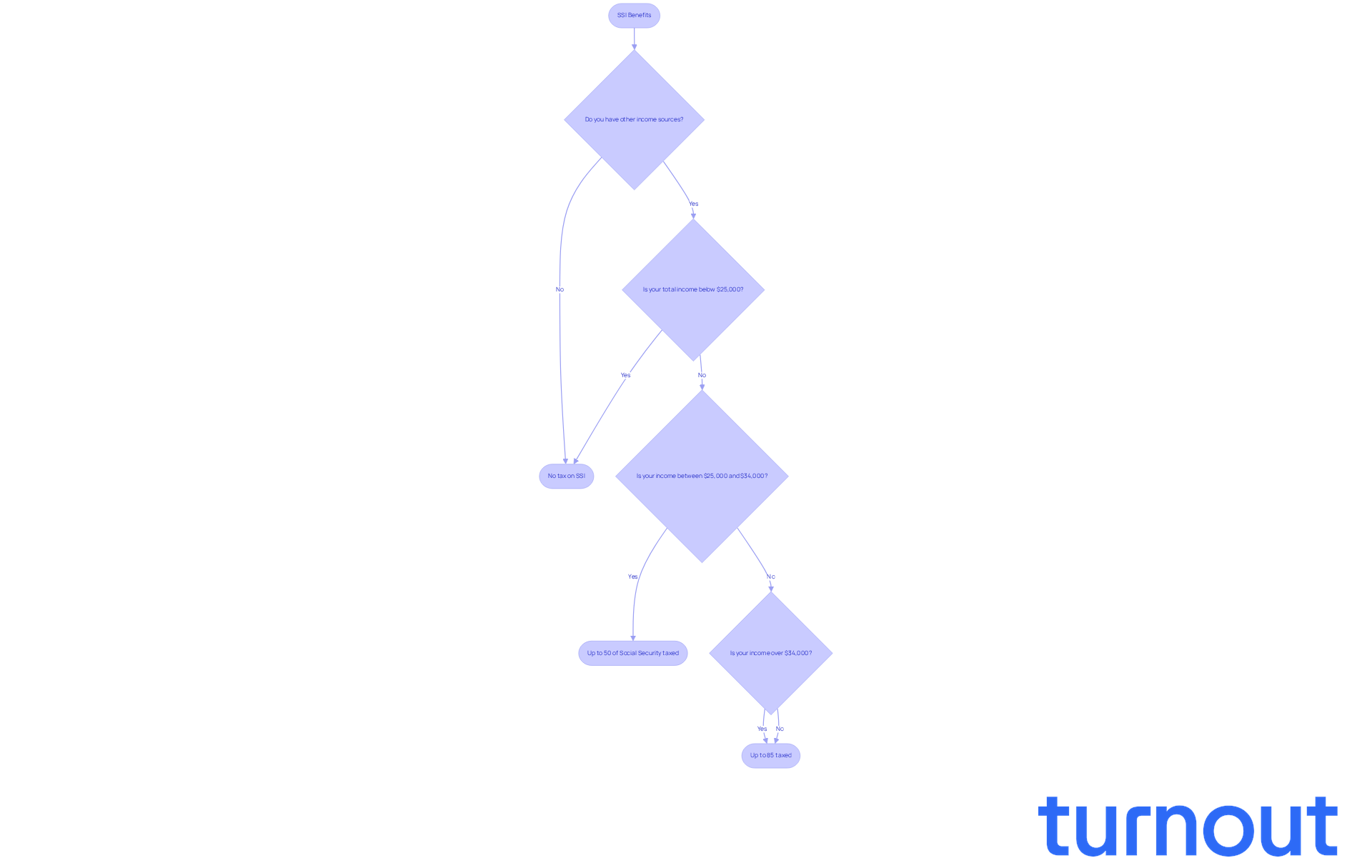
While Supplemental Security Income (SSI) payments themselves aren’t taxable, it’s important for recipients to know that is SSI disability taxable and how other income sources can impact their overall tax situation. Many SSI recipients also earn wages, receive pensions, or get additional assistance, which can influence their tax responsibilities. In December 2024, around 21.6% of SSI recipients under age 18 reported other unearned earnings. This highlights how crucial it is to understand how these additional sources can affect tax obligations.
We understand that tracking overall earnings can feel overwhelming. However, exceeding certain limits with additional income may require you to file a tax return, which brings up the question of whether is SSI disability taxable, even if your SSI assistance remains non-taxable. For instance, individual taxpayers with provisional earnings between $25,000 and $34,000 may have up to 50% of their Social Security payments taxed. Those with provisional earnings over $34,000 could see up to 85% taxed. This sliding scale emphasizes the need for thoughtful financial planning.
Moreover, the question of whether is SSI disability taxable can vary significantly based on the source of the benefits and your overall financial situation. Understanding these nuances is essential for effective tax management. While SSI is designed to support low-earning individuals, other income sources can complicate tax obligations, potentially moving you into higher tax brackets. Regular consultations with tax professionals can help you navigate these complexities and optimize your financial outcomes. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Examine SSI in Relation to Other Income and Tax Regulations
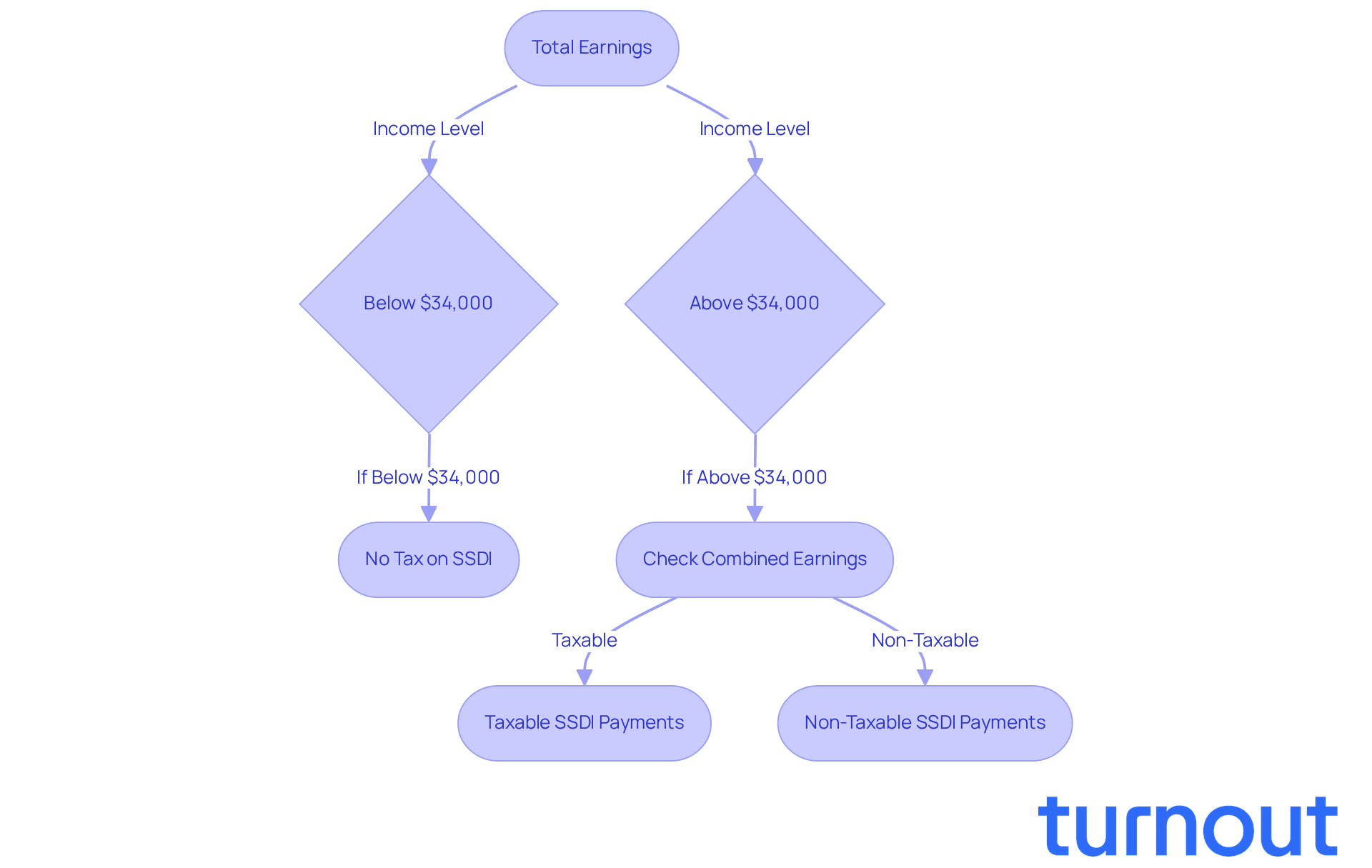
Navigating the connection between Supplemental Security Income (SSI) and other revenue sources can feel overwhelming. We understand that while SSI itself isn’t subject to federal taxation, it raises the question of whether SSI disability is taxable, as other financial streams like Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) can be. If your total earnings exceed certain thresholds, SSDI payments may be taxable.
The IRS defines combined earnings as the sum of adjusted gross revenue, nontaxable interest, and half of the Social Security payments you receive. For instance, if you’re an individual taxpayer with total earnings over $34,000, you might face taxation on as much as 85% of your SSDI payments. This means that if you’re receiving both SSI and SSDI, it’s crucial to keep an eye on your total earnings to determine if SSI disability is taxable and to avoid unexpected tax obligations.
It’s common to feel concerned about these financial limits, especially since they haven’t been adjusted for inflation. More recipients are finding themselves subject to taxation over time. Understanding these nuances is essential for effective financial management and planning.
Additionally, it’s important to note that Social Security benefits were exempt from federal earnings tax until 1984. The 2025 Act introduced a temporary senior deduction for individuals aged 65 and older, which could influence your tax obligations. We encourage you to prioritize ongoing education about tax laws that affect seniors. Seeking professional advice can also help you navigate the complexities of Social Security taxation.
Turnout is here to support you in this journey. We utilize trained nonlawyer advocates for SSD claims and IRS-licensed enrolled agents for tax relief. Our goal is to ensure you can effectively navigate these complex financial systems without the need for legal representation. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
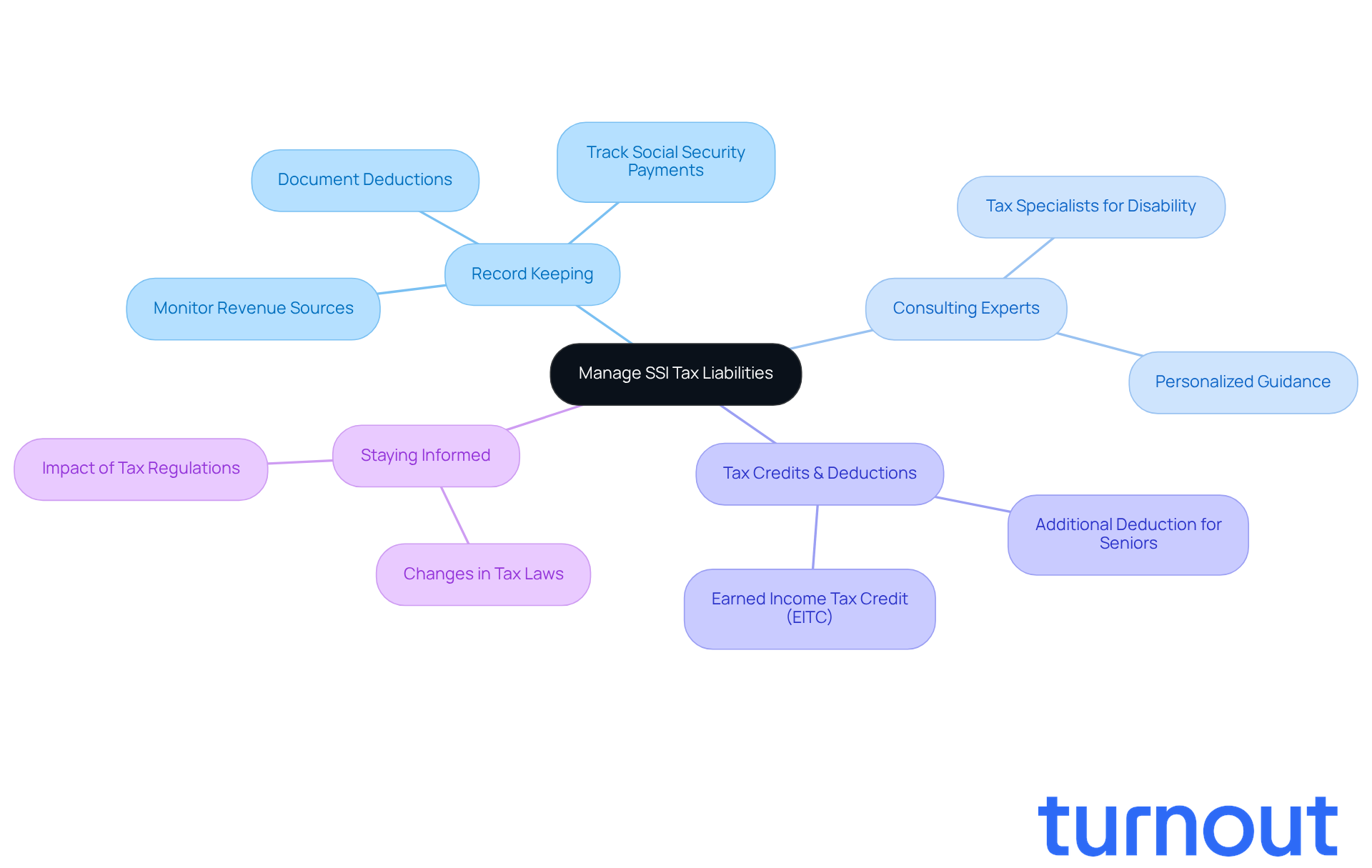
Manage SSI Tax Liabilities: Strategies and Considerations
Managing tax liabilities related to understanding whether SSI disability is taxable along with other earnings can feel overwhelming, but there are key strategies that can help you navigate this journey with confidence. First and foremost, keeping precise records of all your revenue sources is essential. This means monitoring your Social Security payments, any extra earnings, and relevant deductions. Did you know that in 2025, around 57.4 percent of recipient families are expected to owe taxes, raising the question of whether their assistance is SSI disability taxable? This highlights just how important careful record-keeping is.
It's common to feel uncertain about tax filing, especially when projections show that 72 percent of beneficiary families will file an income tax return and wonder if SSI disability is taxable through 2030. Consulting with a tax expert who specializes in disability assistance can provide you with personalized guidance tailored to your unique circumstances. These specialists can help you navigate the complexities of tax regulations, ensuring you optimize your benefits while minimizing tax liabilities. For instance, Patrick Purcell from the Social Security Administration noted that the question of whether SSI disability is taxable can decrease the net Social Security earnings received by higher-income recipients.
Additionally, exploring tax credits and deductions that may apply to you is crucial. The Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) can offer substantial financial relief. In fact, statistics show that households in the second earnings quartile paid less than 0.5 percent of their advantages as tax in 2010, a figure expected to rise to 4.3 percent by 2050. This changing landscape of tax obligations is something to keep in mind.
Staying informed about changes in tax laws and regulations is vital, as these can directly impact your financial planning and obligations. For example, the extra $6,000 deduction for seniors under the OBBB legislation aims to assist older Americans, but it may not benefit households with taxable income below the enhanced standard deduction. Understanding these nuances can empower you to make informed decisions about your tax responsibilities, including whether SSI disability is taxable. Remember, a key distinction to keep in mind is whether SSI disability is taxable, as SSI benefits themselves are not taxable.
You're not alone in this journey. We're here to help you navigate these challenges and ensure you have the support you need.
Conclusion
Understanding the tax implications of Supplemental Security Income (SSI) is crucial for beneficiaries navigating their financial responsibilities. We understand that this can be overwhelming. While SSI benefits themselves are not considered taxable income, the overall tax landscape can become complex when additional earnings come into play. It’s important to recognize how other income sources can impact your tax obligations, ensuring that you feel well-informed about your financial situation.
Key insights discussed include the non-taxable nature of SSI benefits and the potential tax liabilities associated with other income. It’s essential to keep precise records. Remember, while SSI offers vital support, you must remain vigilant about your total earnings to avoid unexpected tax burdens. Consulting with tax professionals and staying updated on relevant tax laws are vital steps in managing these complexities effectively.
Ultimately, understanding whether SSI disability is taxable goes beyond mere compliance; it empowers you to make informed financial decisions. By actively engaging with resources and seeking expert advice, you can optimize your benefits and minimize tax liabilities. Embracing this knowledge not only fosters financial stability but also ensures that the support provided by SSI continues to uplift those in need. You are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Supplemental Security Income (SSI)?
Supplemental Security Income (SSI) is a federal program that provides financial support to individuals who are elderly, blind, or disabled and have limited resources.
How does SSI differ from Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)?
SSI is a needs-based program that does not depend on work history, while SSDI is based on an individual's work history and contributions to Social Security.
Is SSI disability taxable?
No, SSI disability benefits are not considered taxable earnings under federal law, so you do not need to report SSI payments on your tax returns.
How many individuals are expected to receive SSI assistance in 2025?
Approximately 7.5 million individuals are expected to receive SSI assistance in 2025.
Why is it important for SSI beneficiaries to understand their tax status?
Understanding whether SSI disability is taxable can help beneficiaries manage their finances more effectively and maximize the support they receive.




