Overview
Understanding your SSDI benefits is crucial, especially when it comes to taxes. Many recipients worry about how their total earnings might affect their benefits. If you're a single filer, the threshold is set at $25,000, while for married couples filing jointly, it’s $32,000. Exceeding these limits can mean that a portion of your benefits may be taxable.
It’s important to know that if your earnings fall between these thresholds, up to 50% of your benefits could be subject to taxation. This potential tax liability can significantly impact your financial well-being. We understand that navigating these tax implications can feel overwhelming, but it's essential for effective financial planning.
You're not alone in this journey. Many people share similar concerns, and seeking clarity can help you make informed decisions. Remember, understanding these details can empower you to take control of your financial future. We're here to help you through this process.
Introduction
Understanding the intricacies of Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is essential for millions of Americans who rely on this vital financial support. We understand that as the number of SSDI recipients continues to grow, so does the complexity surrounding the tax implications of these benefits.
With specific income thresholds determining whether SSDI payments are taxable, it’s common to feel overwhelmed by the daunting task of navigating these regulations.
How can you ensure you are informed and prepared to manage your financial obligations while maximizing the support you receive? We're here to help you through this journey.
Define SSDI: Overview of Social Security Disability Insurance
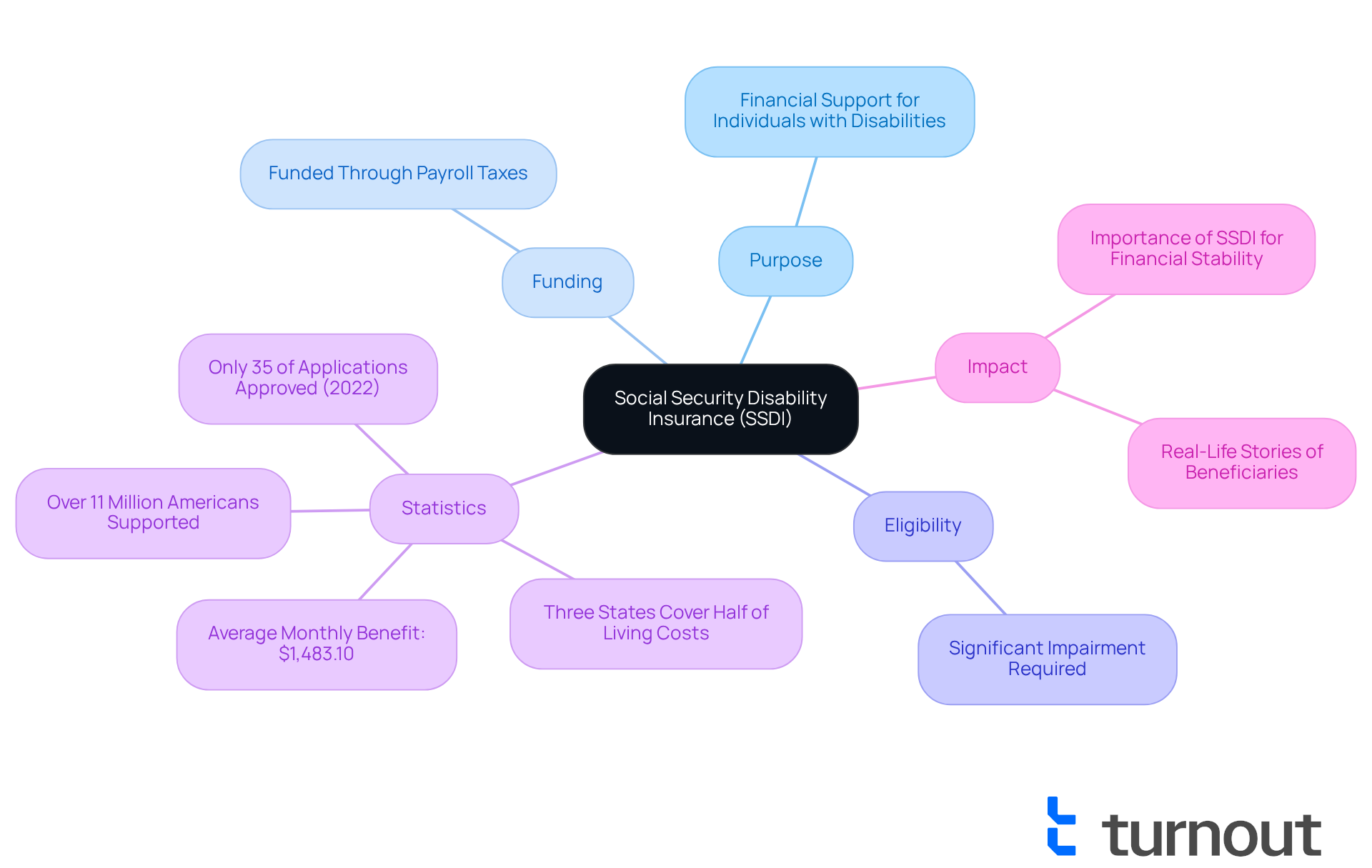
Social Security Disability Insurance is a vital federal program designed to provide financial support to individuals who are unable to work due to qualifying disabilities. Funded through payroll taxes, this initiative aims to assist those who have contributed to the Social Security system and have now found themselves facing the challenges of disability. We understand that navigating this process can be overwhelming, and to qualify, applicants must show that their disability significantly impairs their ability to engage in substantial gainful activity (SGA).
As of 2025, Social Security Disability Insurance supports over 11 million Americans, offering crucial financial assistance during tough times. The average monthly benefit for disabled workers stands at approximately $1,483.10. While this amount is essential, it often falls short of covering living expenses. In fact, only three states provide average disability benefits that meet even half of the cost of living. This reality underscores the ongoing financial struggles many beneficiaries face.
The importance of Social Security Disability Insurance cannot be overstated; it serves as a lifeline for individuals grappling with the difficulties of disability, ensuring they have access to essential resources. Real-life stories illustrate the program's impact: countless beneficiaries rely solely on disability benefits for their survival, highlighting how this program fosters financial stability for individuals with disabilities.
As our work environment evolves, particularly with the rise of the gig economy, the need for robust support systems like disability insurance remains crucial. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we are here to help you navigate these challenges and find the support you need.
Determine Taxability: Are SSDI Benefits Taxable?
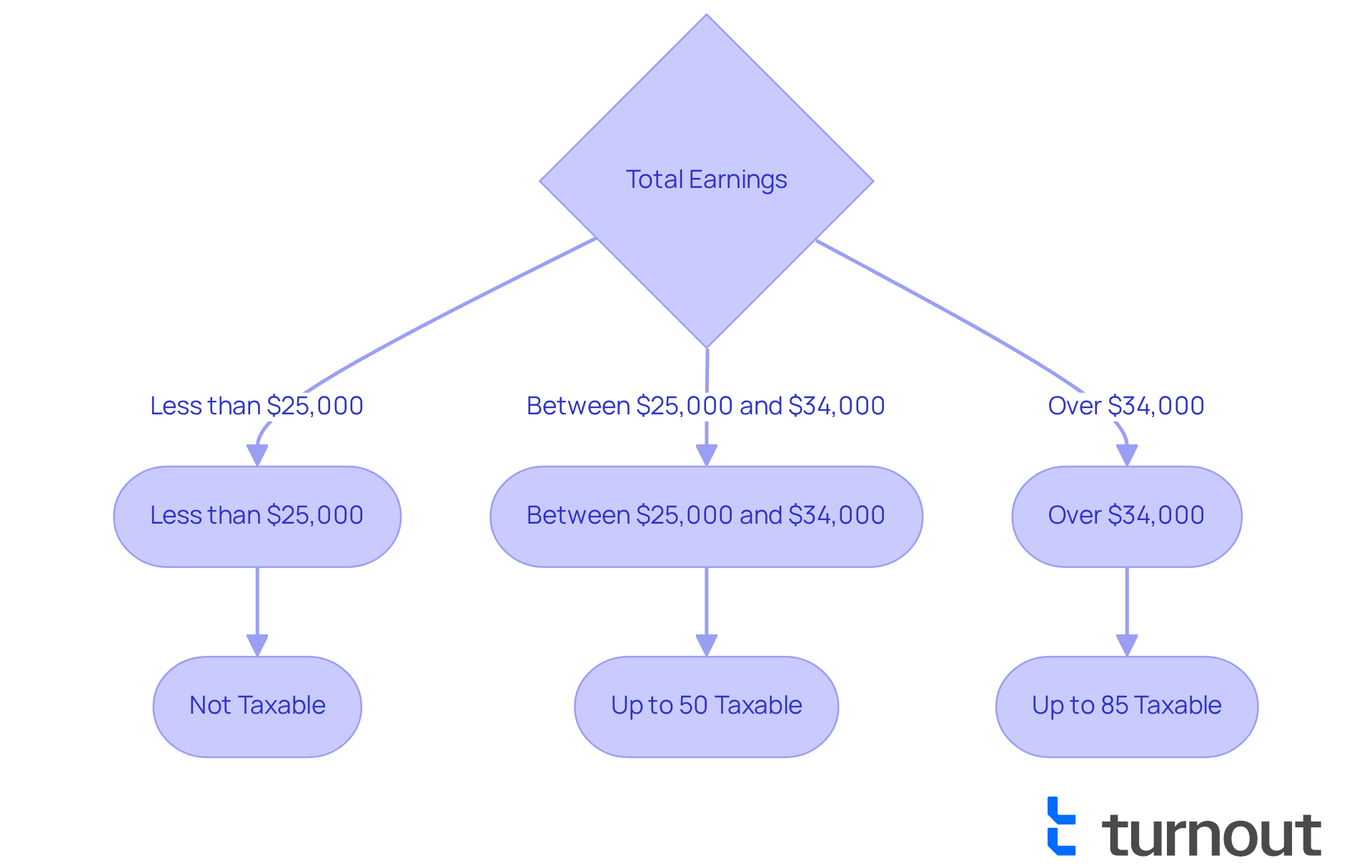
Navigating the world of disability assistance can be overwhelming, especially when trying to determine if SSDI is taxable. If your total earnings exceed certain limits, you might question whether SSDI is taxable, since part of your disability assistance may be subject to taxation. For single filers, this threshold is set at $25,000, and for married couples filing jointly, it’s $32,000. If your earnings fall below these thresholds, your disability assistance remains tax-exempt.
We understand that comprehending these limits is crucial for accurately disclosing your earnings and avoiding unexpected tax obligations. In fact, many individuals receiving disability support face these tax implications, often questioning, is SSDI taxable, with approximately 50% experiencing taxation on their payments based on their earnings. Recent IRS guidelines emphasize the importance of determining total earnings, which includes half of the disability payments along with other income sources like pensions and wages. As we approach 2025, these guidelines will continue to be essential for ensuring compliance and effective tax planning.
It's also important to note that 41 states, along with Washington, D.C., do not impose taxes on Social Security earnings. Recipients can choose withholding options of 7%, 10%, 12%, or 22% for their assistance payments.
We’re here to help you navigate these complexities. Turnout offers valuable tools and services, including trained nonlegal advocates and IRS-licensed enrolled agents. They can assist you in understanding your rights and options regarding disability claims and tax relief, ensuring you don’t have to face this journey alone.
Explore Tax Conditions: When Are SSDI Benefits Taxed?
Navigating disability support payments can be challenging, especially when trying to determine if SSDI is taxable. We recognize that many recipients may feel overwhelmed by the complexities of taxation based on overall earnings, which include wages, pensions, interest, and other revenue sources. It's important to know that the question of whether SSDI is taxable arises if your total earnings exceed certain limits, as the IRS requires you to report a portion of your disability payments as taxable income.
For instance, if your total earnings fall between $25,000 and $34,000, up to 50% of your benefits may be subject to taxation, raising the question of whether SSDI is taxable. If your earnings are higher, it raises the question of whether SSDI is taxable, as up to 85% could be taxable. This means that you could receive benefits as high as $81,000, including retroactive payments, without incurring taxes if that is your only source of income.
To navigate these regulations effectively, it’s crucial to keep precise financial records. We encourage you to seek advice from tax experts who can provide personalized guidance tailored to your situation. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
Additionally, if you are receiving Social Security Disability Insurance, it's essential to understand that supplemental payments made to family members from a wage earner's record are considered earnings for those individuals. This could potentially affect their tax responsibilities as well. We understand that these details can feel daunting, but with the right support and information, you can manage your financial situation confidently.
Assess Financial Impact: Implications of SSDI Taxation on Recipients
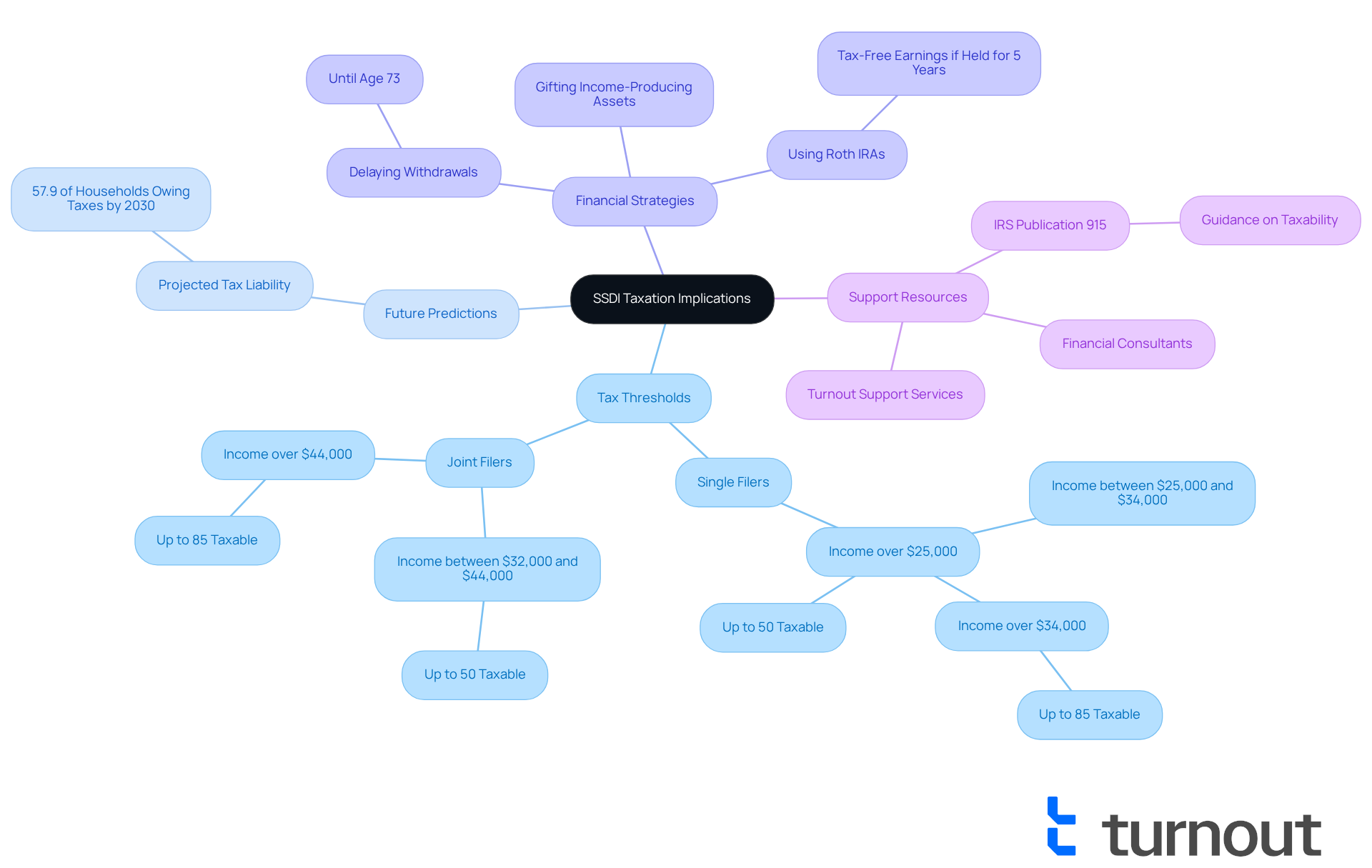
Understanding whether SSDI is taxable can significantly affect your financial well-being. If your allowances are subject to taxation, you might find that your net earnings decrease, making it harder to manage essential costs. For instance, if you're single and your total earnings exceed $25,000, up to 50% of your benefits may be taxed. Joint filers with a combined income over $44,000 could see up to 85% of their benefits taxed. Alarmingly, forecasts indicate that by 2030, 57.9% of beneficiary households are expected to owe tax on their benefits, which raises the question of whether SSDI is taxable among disability support recipients.
Understanding if SSDI is taxable is crucial for effective financial planning. We understand that tax season can be overwhelming, so it's important to set aside funds to meet potential tax liabilities. This way, you won’t be caught off guard. Seeking guidance from financial consultants can provide you with tailored strategies to handle your disability benefits and reduce tax obligations. For example, consider delaying withdrawals from retirement accounts until age 73 and utilizing tax-advantaged accounts like Roth IRAs. These can help shield your earnings from taxation if held for a sufficient period.
Moreover, many beneficiaries of disability benefits successfully manage their financial situations after taxes by adopting prudent budgeting techniques and exploring alternative revenue streams. Take Dana, a single woman, for example. After applying the senior bonus deduction, she effectively managed her taxable income. By being knowledgeable and strategic about your finances, you can enhance your financial stability despite the challenges posed by disability benefits taxation.
Additionally, Turnout offers valuable support in navigating these complexities, ensuring that you can access the necessary resources and assistance for tax relief and financial management. The recent passage of the "One Big, Beautiful Bill" also provides significant tax relief to nearly 90% of Social Security beneficiaries, further impacting the financial landscape for SSDI recipients. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and support is available to help you thrive.
Conclusion
Understanding the tax implications of Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is essential for recipients seeking financial stability. We recognize that navigating these complexities can be overwhelming. This article has explored whether SSDI benefits are taxable, highlighting the importance of knowing income thresholds and their potential impact on your financial well-being. With millions relying on SSDI, clarity around its taxability can significantly influence how you manage your finances.
Key points discussed include:
- The income limits that determine taxability
- The percentage of benefits that may be taxed based on total earnings
- The states that do not impose taxes on SSDI
It's common to feel uncertain about these details, but accurate financial record-keeping and seeking professional tax advice can help you navigate these complexities effectively. As we look to the future, it's likely that more beneficiaries may face tax obligations, making proactive financial planning a necessity.
Ultimately, awareness and preparation are crucial for SSDI recipients. By understanding the tax rules and implementing strategic budgeting, you can mitigate the financial impact of potential taxation on your benefits. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. Staying informed and seeking assistance can empower you to manage your finances confidently and ensure you continue to receive the support you need.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)?
Social Security Disability Insurance is a federal program that provides financial support to individuals who are unable to work due to qualifying disabilities. It is funded through payroll taxes and aims to assist those who have contributed to the Social Security system.
Who qualifies for SSDI?
To qualify for SSDI, applicants must demonstrate that their disability significantly impairs their ability to engage in substantial gainful activity (SGA).
How many people does SSDI support?
As of 2025, Social Security Disability Insurance supports over 11 million Americans.
What is the average monthly benefit for SSDI recipients?
The average monthly benefit for disabled workers receiving SSDI is approximately $1,483.10.
Do SSDI benefits cover living expenses?
While SSDI benefits are essential, they often fall short of covering living expenses. Only three states provide average disability benefits that meet even half of the cost of living.
Why is SSDI important for individuals with disabilities?
SSDI serves as a lifeline for individuals facing the challenges of disability, ensuring they have access to essential resources and financial stability during tough times.
How does SSDI impact beneficiaries' lives?
Many beneficiaries rely solely on SSDI benefits for their survival, highlighting the program's critical role in fostering financial stability for individuals with disabilities.
What is the relevance of SSDI in the context of the gig economy?
As the work environment evolves with the rise of the gig economy, the need for robust support systems like disability insurance remains crucial for individuals facing disabilities.




