Introduction
Understanding the complexities of Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is crucial for millions of Americans who rely on this essential program. We know that SSDI serves as a vital safety net, providing financial support to those unable to work due to qualifying disabilities. Yet, many beneficiaries find themselves grappling with an important question: Are SSDI benefits taxable?
This article delves into the intricacies of SSDI taxation, offering insights into federal and state tax implications. We’ll explore how your filing status can affect your tax liability and share strategies to help minimize your tax burdens. With so much at stake and the rules often confusing, it’s common to feel overwhelmed. How can you ensure that you’re making informed decisions about your benefits and obligations?
You are not alone in this journey. Together, we can navigate these financial waters with clarity and confidence.
Define Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) and Its Purpose
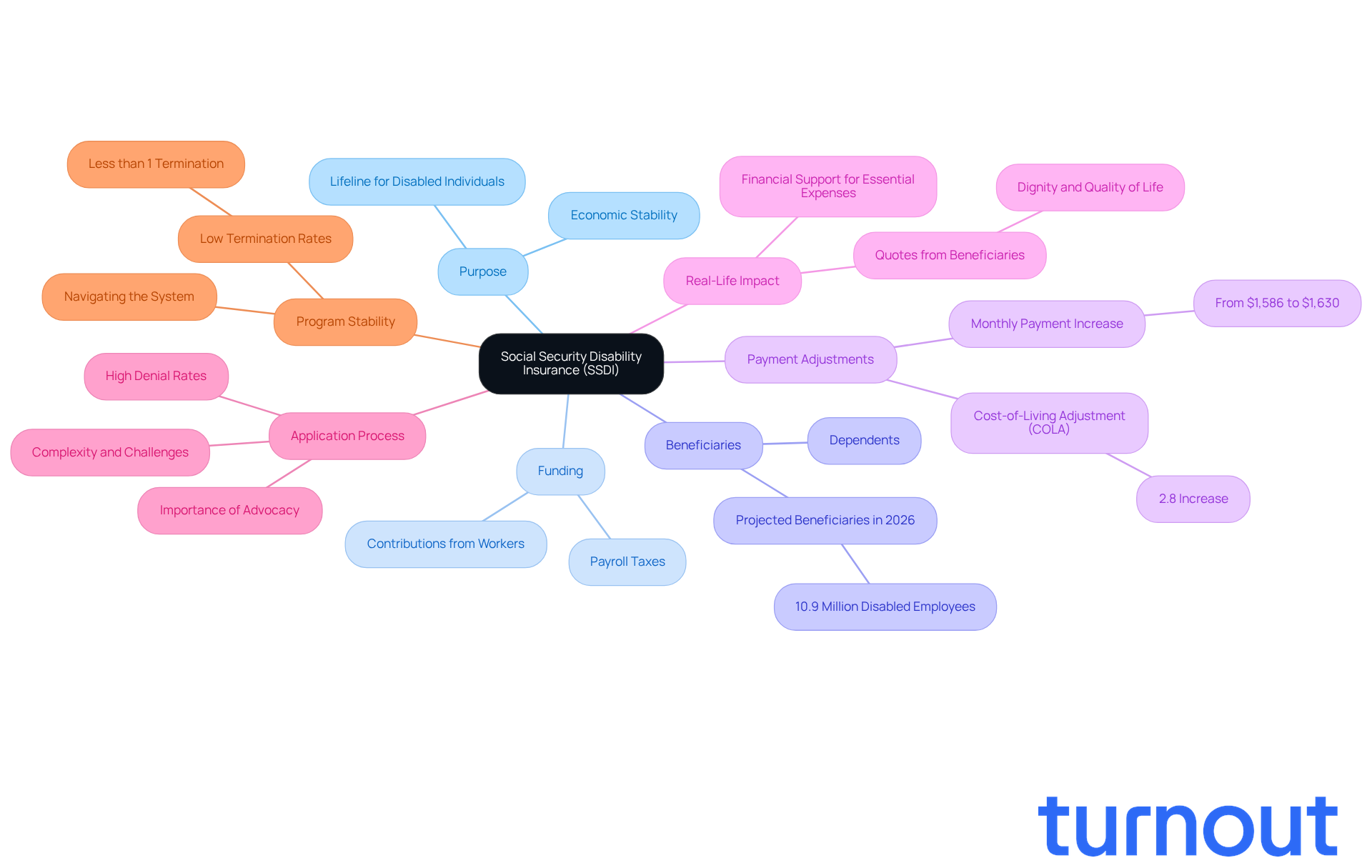
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is more than just a federal program; it’s a lifeline for those who can’t work due to qualifying disabilities. Funded through payroll taxes, SSDI aims to replace a portion of lost income for individuals who have contributed to the Social Security system throughout their careers. This program is crucial for those facing medical conditions that are expected to last at least one year or lead to death, ensuring they have the resources they need during tough times.
In 2026, approximately 10.9 million disabled employees and their dependents are projected to receive disability benefits. This highlights how essential the program is in providing economic stability. The typical monthly disability payment is expected to rise from $1,586 in 2025 to $1,630 in 2026, thanks to a 2.8% cost-of-living adjustment (COLA). This adjustment helps beneficiaries keep up with rising living costs, including housing, food, and medical care.
Real-life stories illustrate the profound impact of SSDI on individuals' lives. Many beneficiaries share how this financial support has been vital in covering essential expenses, allowing them to focus on their health and recovery. As one financial consultant noted, "Social Security Disability Insurance not only offers a lifeline for those unable to work but also helps preserve their dignity and quality of life during challenging times."
The goal of SSDI is to ensure that disabled Americans have access to the financial resources they need, reinforcing its role as a crucial part of the social safety net. However, we understand that navigating the SSDI application process can be daunting. Consulting knowledgeable advocates, like those at Turnout, can significantly enhance your chances of approval. While Turnout is not a law firm and does not provide legal representation, they offer trained nonlawyer advocates to assist clients. They provide tools and services to help you manage these processes without needing legal representation, ensuring you can access the benefits you deserve.
It’s also reassuring to know that less than 1 percent of recipients evaluated have their assistance terminated, underscoring the program's stability. As more Americans rely on disability insurance, understanding its benefits and navigating the application process becomes increasingly important. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Identify When SSDI Benefits Are Taxable Under Federal Law
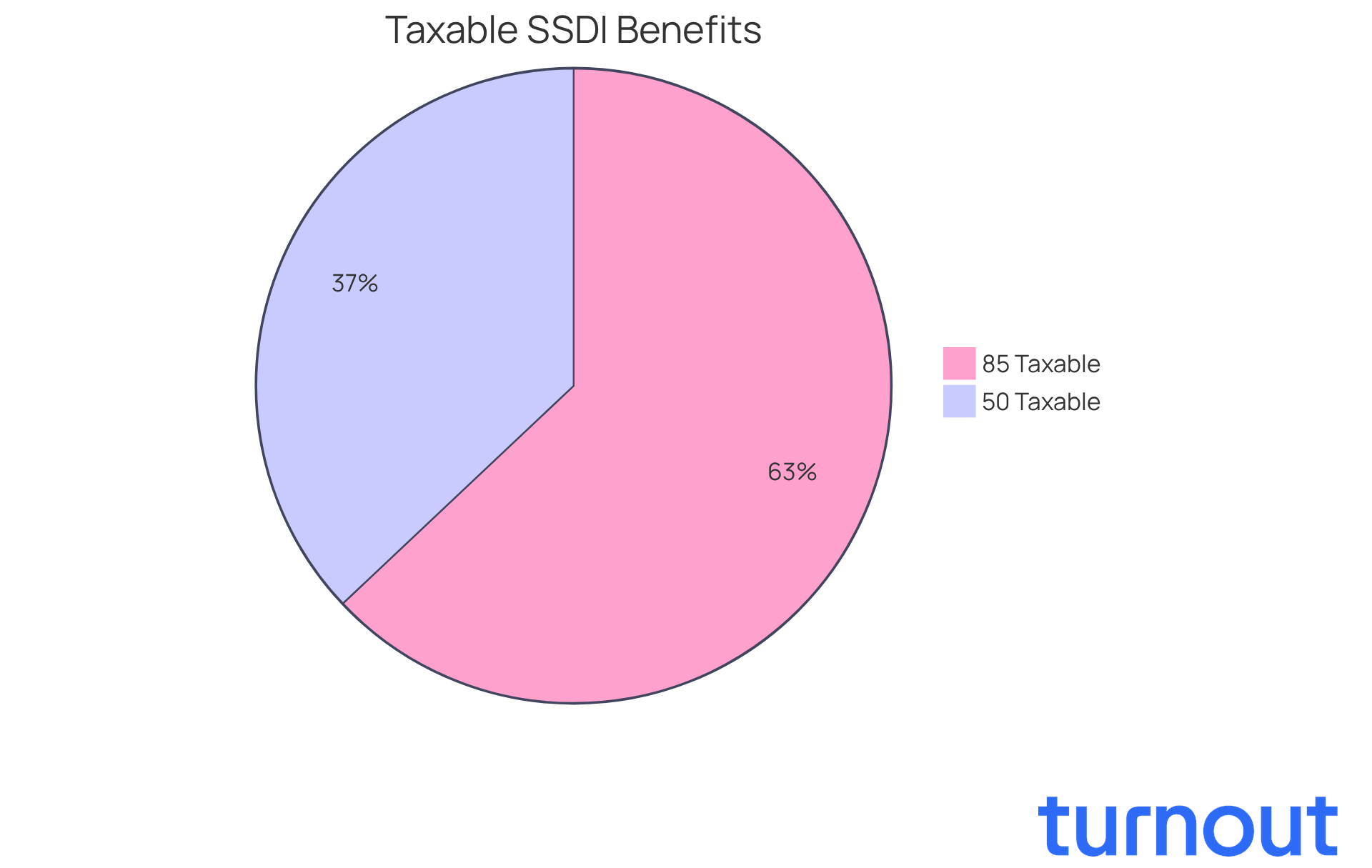
Navigating disability support can be challenging, particularly when trying to understand whether is ss disability taxable. If your total earnings exceed certain limits, you might find yourself wondering if is ss disability taxable on your disability payments. For the tax year 2026, if half of your disability payments, combined with all other earnings, surpass $25,000 for single filers or $32,000 for married couples filing jointly, you could owe taxes on a portion of your benefits.
It's important to know that the IRS states that up to 50% of your disability payments may be included in your taxable earnings, which raises the question of is ss disability taxable within these financial ranges. For those with higher earnings, this can increase to 85%. We understand that these numbers can feel overwhelming, but grasping these thresholds is crucial for effective tax planning and managing your financial obligations.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We're here to help you navigate these complexities and ensure you make informed decisions. Take a moment to reflect on your situation and consider how understanding these limits can empower you to manage your finances better.
Examine How Filing Status Affects SSDI Taxability
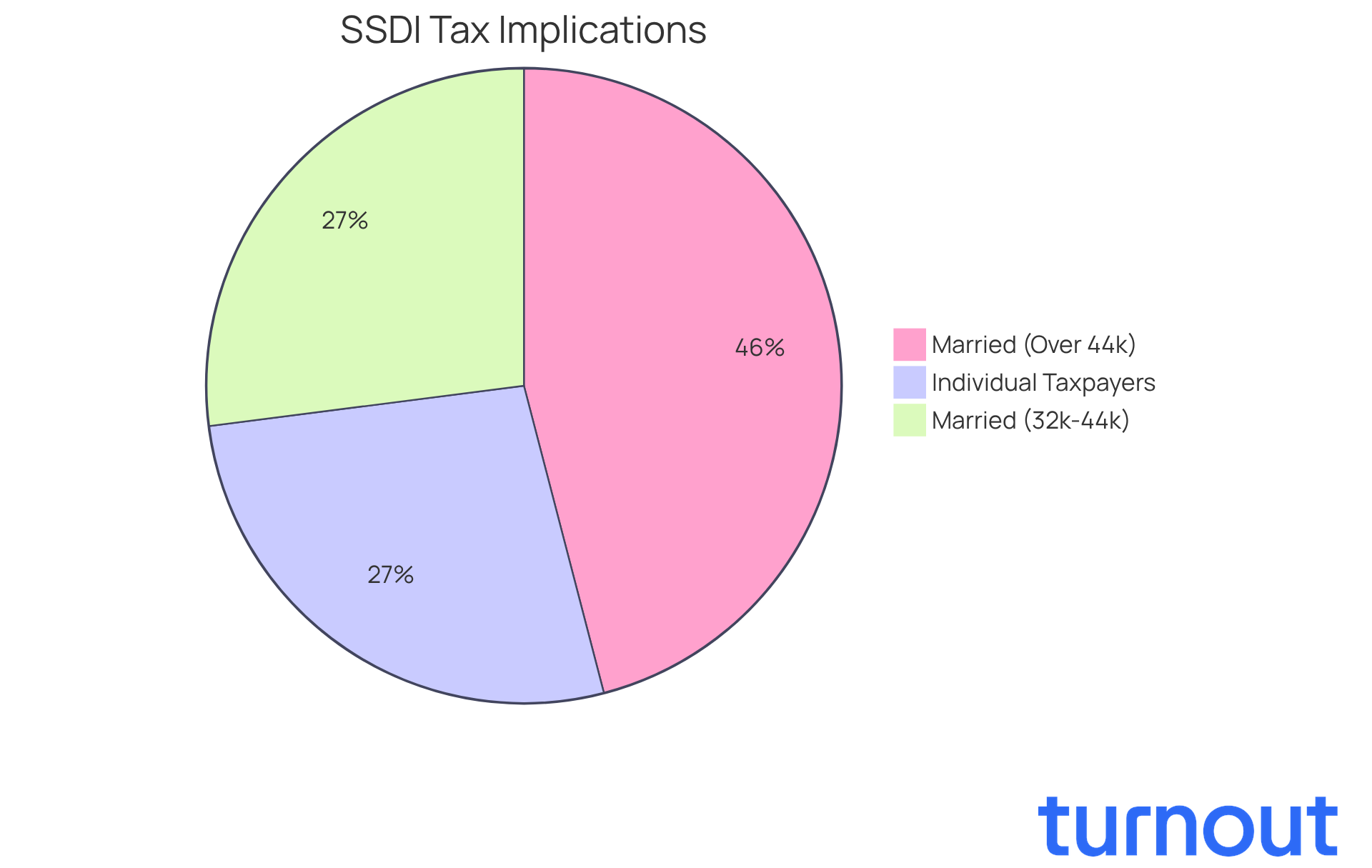
Your filing status can significantly impact the tax implications of your disability payments. We understand that navigating these complexities can be overwhelming. For individual taxpayers, if your total earnings exceed $25,000, you might discover that up to 50% of your SSDI payments is SSDI taxable. In contrast, married couples filing jointly benefit from a higher threshold of $32,000. However, if their total earnings surpass $44,000, it may indicate that SSDI is taxable, as up to 85% of their assistance may become taxable.
According to the Social Security Administration, about 50% of Social Security recipients' benefits are SSDI taxable. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for accurate tax reporting and financial planning. As we look ahead to 2026, discussions about potential changes to tax regulations affecting disability beneficiaries are ongoing. This makes it more important than ever to stay informed about these thresholds.
Additionally, the White House Council of Economic Advisors notes that the bonus deduction will increase the share of seniors who won’t have to pay taxes on Social Security from 64% to 88%. Moreover, forecasts suggest that the proportion of families liable for income tax on their benefits will rise from 10.4% in 2010 to 12.1% by 2025. This highlights the evolving tax environment concerning whether SSDI is taxable for beneficiaries.
At Turnout, we’re here to help you navigate these complexities. We offer tools and services to ensure you understand your benefits and tax obligations without the need for legal representation. Remember, you are not alone in this journey.
Calculate the Taxable Amount of SSDI Benefits
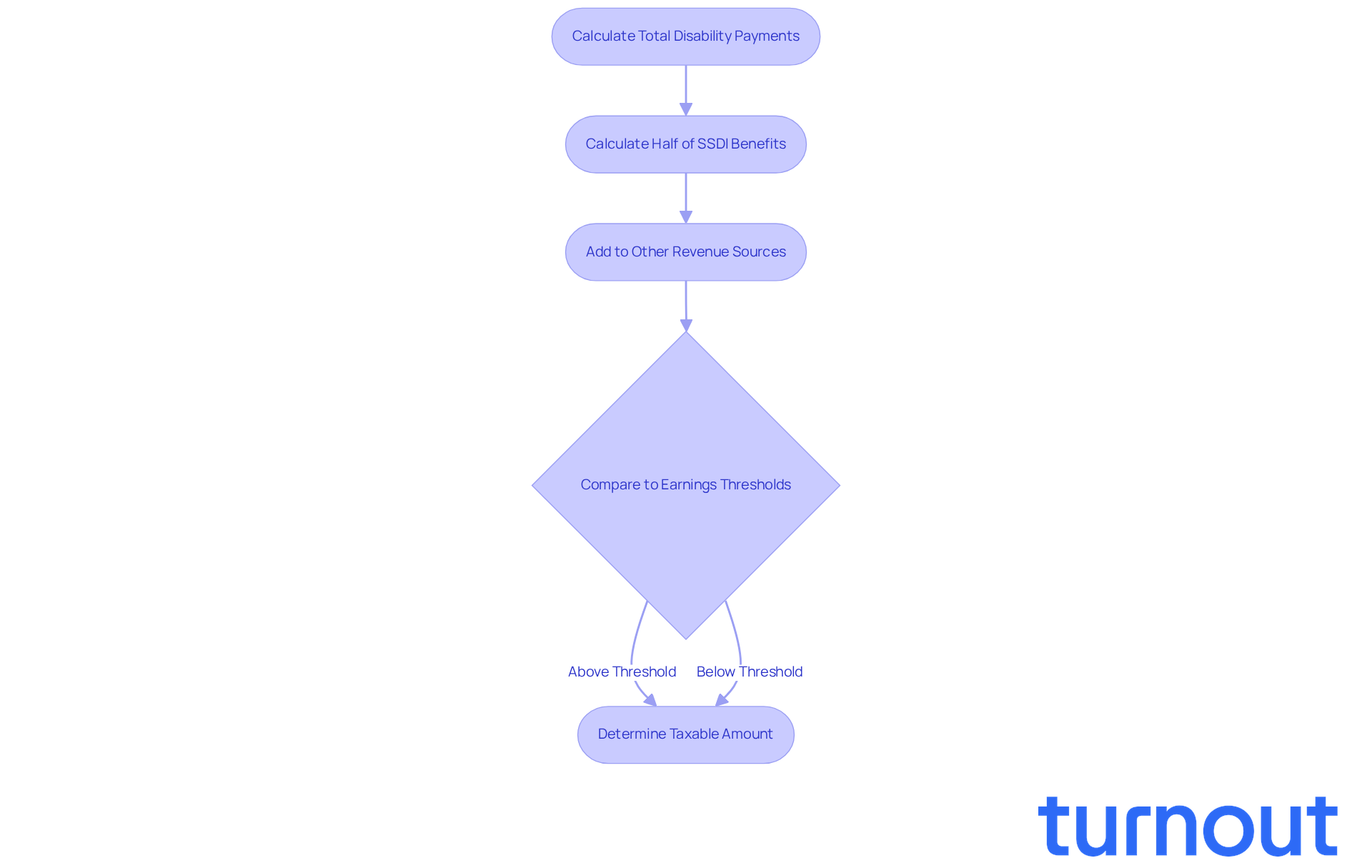
Determining whether is ss disability taxable for your disability payments can feel overwhelming, but we’re here to help you navigate this process with care. Here’s a simple guide to follow:
- Calculate your total disability payments received during the tax year.
- Calculate half of your SSDI benefits.
- Add this amount to all other sources of revenue, including tax-exempt interest.
- Compare the total to the earnings thresholds based on your filing status.
It’s common to feel uncertain about these calculations. If your total surpasses the threshold, you may need to consider if is ss disability taxable by including a portion of your disability assistance in your taxable earnings. For example, if your total earnings are $30,000 as a single filer, you might need to declare 50% of your disability payments as taxable income.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Turnout is here to assist you in understanding your financial obligations. Our trained nonlawyer advocates can provide guidance on SSD claims and help you understand how is ss disability taxable. We want to ensure you have the support you need, without the necessity for legal representation.
Explore State Tax Rules for SSDI Benefits
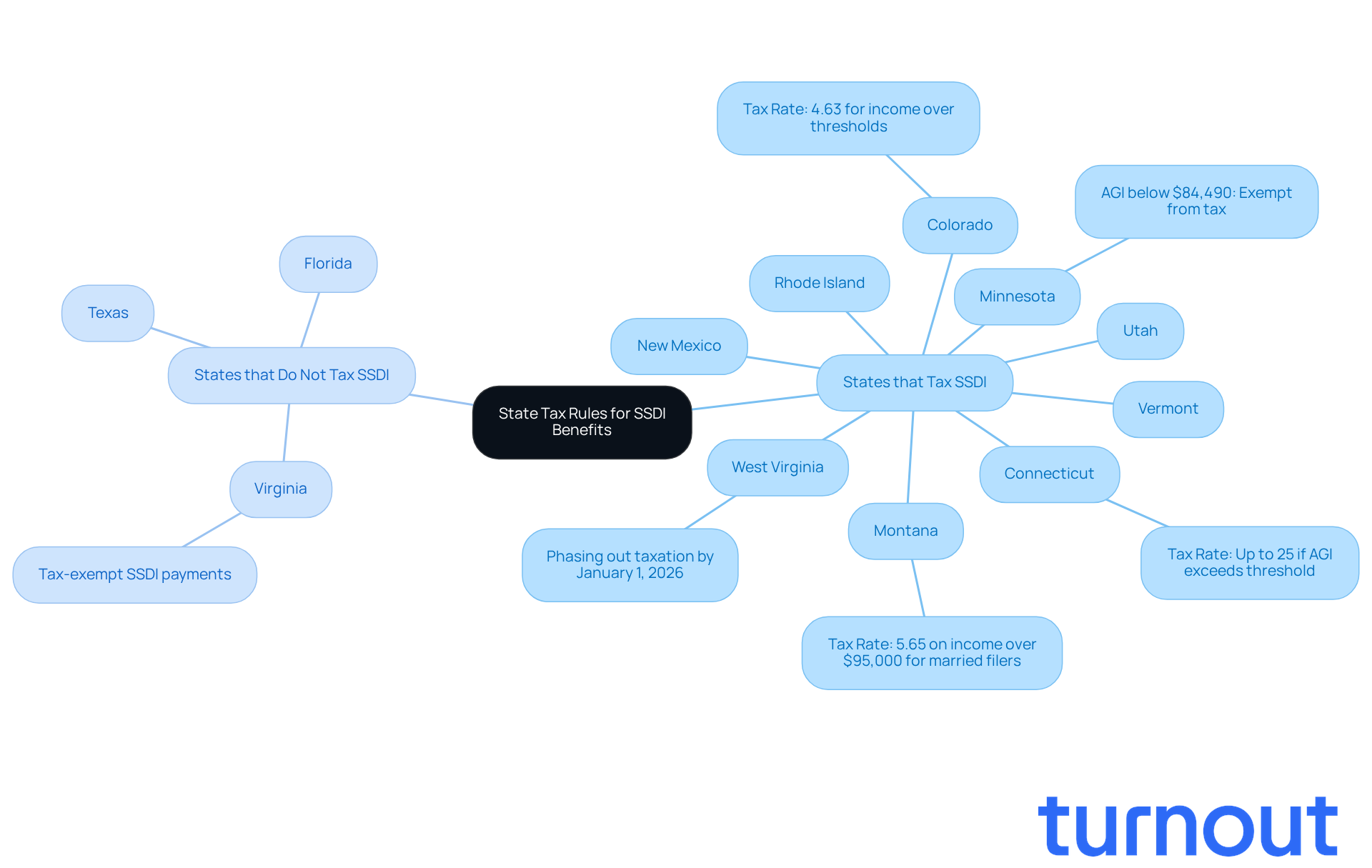
The confusion surrounding state tax regulations often leads people to wonder, is ss disability taxable, and these regulations can vary significantly across the United States. As we look ahead to 2026, it’s important to note that about 12 states impose some form of taxation, which raises the question of whether is ss disability taxable. For instance, it is important to know whether is ss disability taxable in states like:
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Minnesota
- Montana
- New Mexico
- Rhode Island
- Utah
- Vermont
- West Virginia
as these benefits are taxed. In contrast, states such as Florida and Texas do not impose any state tax on disability payments.
Understanding your state's tax regulations is crucial to determine if ss disability is taxable for those who receive disability benefits. For example, in Minnesota, individual taxpayers with an adjusted gross income (AGI) below $84,490 are exempt from state taxation, which raises the question of whether is ss disability taxable. Meanwhile, in Colorado, the tax rate can reach 4.63% for those whose earnings exceed certain thresholds, prompting inquiries about whether ss disability is taxable. Some states even offer exemptions or deductions specifically for disability benefit recipients, prompting the inquiry of whether is ss disability taxable, which can significantly ease their overall tax burden.
At Turnout, we’re dedicated to helping individuals navigate these complexities. Our trained nonlawyer advocates are here to support you with SSD claims, ensuring you understand your rights and options regarding state tax implications. For instance, if you’re in Colorado, you should understand whether is ss disability taxable, as your disability payments may be taxed if your total income exceeds $25,000. On the other hand, a recipient in Virginia enjoys tax-exempt disability payments, which leads to the question of whether is ss disability taxable. Consulting with a Turnout advocate can help you optimize your tax situation, allowing you to keep as much of your benefits as possible.
We understand that dealing with taxes can be overwhelming, but you are not alone in this journey. Let us help you find clarity and peace of mind.
Implement Strategies to Minimize SSDI Tax Liability
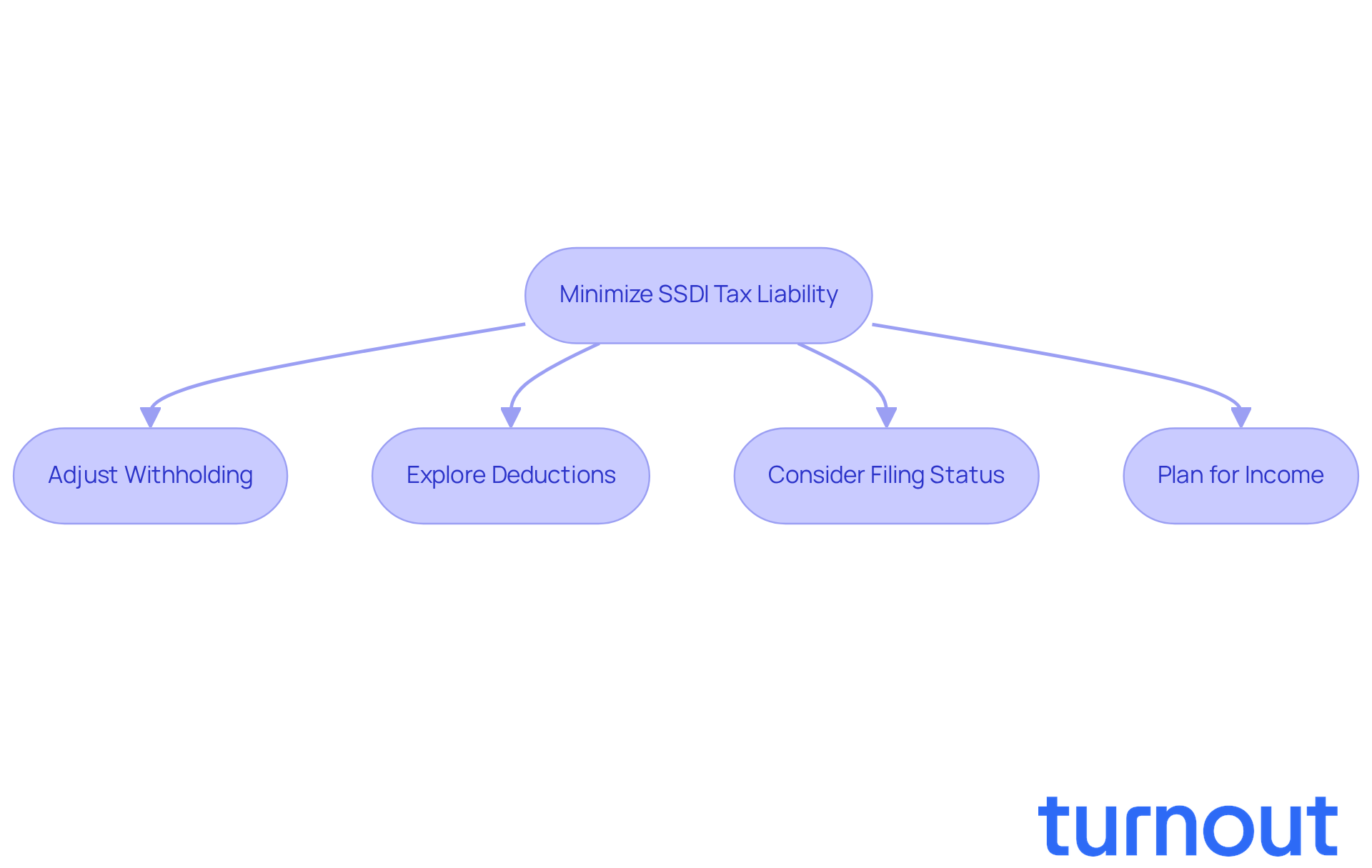
To effectively minimize your SSDI tax liability, it’s important to consider some supportive strategies that can make a difference:
-
Adjust Withholding: Have you thought about using IRS Form W-4V? This allows you to request federal tax withholding from your disability payments. It’s a proactive step that can help you manage your tax bill throughout the year, so you’re not caught off guard when tax season arrives.
-
Explore Deductions: Investigating potential tax deductions can be beneficial. Many SSDI recipients find that medical expenses are a common deduction that can significantly lower earnings, raising the question of whether SSDI is taxable. Staying informed about what deductions you might qualify for is crucial for optimizing your tax situation.
-
Consider Filing Status: Evaluating your filing status is another key step. Could a different status help lower your tax liability? For instance, filing a joint tax return with a partner might offer additional advantages, especially if their earnings are lower.
-
Plan for Income: If you have other sources of income, timing can be everything. In 2026, for example, non-blind disability recipients can earn up to $1,690 monthly without affecting their support. This flexibility allows you to manage your earnings strategically.
By implementing these strategies, SSDI recipients can navigate their tax obligations more effectively and determine if SSDI is taxable, potentially reducing their overall tax burden. Financial experts emphasize the importance of proactive tax planning. Understanding your tax situation and making informed decisions can lead to significant savings. As Joe Elsasser, a certified financial planner, wisely notes, "With tax changes come tax planning opportunities." Engaging with a tax advisor can further enhance your strategy, ensuring you maximize available benefits while remaining compliant with tax regulations. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Conclusion
Understanding the tax implications of Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is crucial for beneficiaries like you who are striving to manage financial obligations effectively. We recognize that while SSDI is a vital source of income for those unable to work due to disabilities, it can also be subject to taxation under certain conditions. Knowing the thresholds for taxable income, including how your filing status impacts this, is essential for making informed financial decisions.
Key insights to consider include:
- The specific income limits that determine when SSDI benefits become taxable
- The varying state tax rules that may apply
- The strategies available to help minimize your tax liability
By taking proactive steps, such as adjusting your withholding and exploring available deductions, you can navigate your tax responsibilities more effectively and potentially reduce your overall tax burden.
Ultimately, staying informed about SSDI tax rules and actively engaging with resources, like nonlawyer advocates, can empower you to maximize your benefits while ensuring compliance with tax regulations. Remember, awareness and strategic planning are vital for maintaining your financial stability and quality of life amidst the complexities of the tax system. You're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)?
SSDI is a federal program designed to provide financial support to individuals who are unable to work due to qualifying disabilities. It is funded through payroll taxes and aims to replace a portion of lost income for those who have contributed to the Social Security system.
Who qualifies for SSDI benefits?
Individuals who have medical conditions expected to last at least one year or lead to death may qualify for SSDI benefits.
How many people are projected to receive SSDI benefits in 2026?
Approximately 10.9 million disabled employees and their dependents are projected to receive disability benefits in 2026.
What is the typical monthly disability payment for SSDI recipients?
The typical monthly disability payment is expected to rise from $1,586 in 2025 to $1,630 in 2026, due to a 2.8% cost-of-living adjustment (COLA).
How does SSDI help beneficiaries?
SSDI provides financial support that helps beneficiaries cover essential expenses, allowing them to focus on their health and recovery during challenging times.
What role do advocates play in the SSDI application process?
Advocates, such as those at Turnout, can assist individuals in navigating the SSDI application process, improving their chances of approval. While Turnout does not provide legal representation, they offer trained nonlawyer advocates to help clients access the benefits they deserve.
Are SSDI benefits stable?
Yes, less than 1 percent of SSDI recipients evaluated have their assistance terminated, indicating the program's stability.
Are SSDI benefits taxable?
Yes, SSDI benefits can be taxable. For the tax year 2026, if half of your disability payments combined with other earnings exceed $25,000 for single filers or $32,000 for married couples filing jointly, you may owe taxes on a portion of your benefits.
How much of SSDI benefits may be taxable?
The IRS states that up to 50% of disability payments may be included in taxable earnings, which can increase to 85% for those with higher earnings.
How can individuals manage their SSDI benefits and taxes effectively?
Understanding the income thresholds for SSDI taxation is crucial for effective tax planning and managing financial obligations. Seeking assistance from knowledgeable advocates can also help individuals navigate these complexities.




