Introduction
Understanding the complexities of Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is essential for millions of Americans who depend on this crucial support system during tough times. We know that navigating financial challenges can be overwhelming, and the question of whether disability benefits are taxable can add to that stress. This concern can significantly affect your overall tax obligations, and it’s common to feel uncertain about what to expect.
Many SSDI recipients may find themselves surprised by unexpected tax burdens due to specific income thresholds that determine tax liability. It’s important to be informed and prepared for these complexities. What strategies can you employ to ensure you’re ready for the tax implications of your benefits?
We’re here to help you understand your options and navigate this journey with confidence.
Define Social Security Disability Insurance and Its Purpose
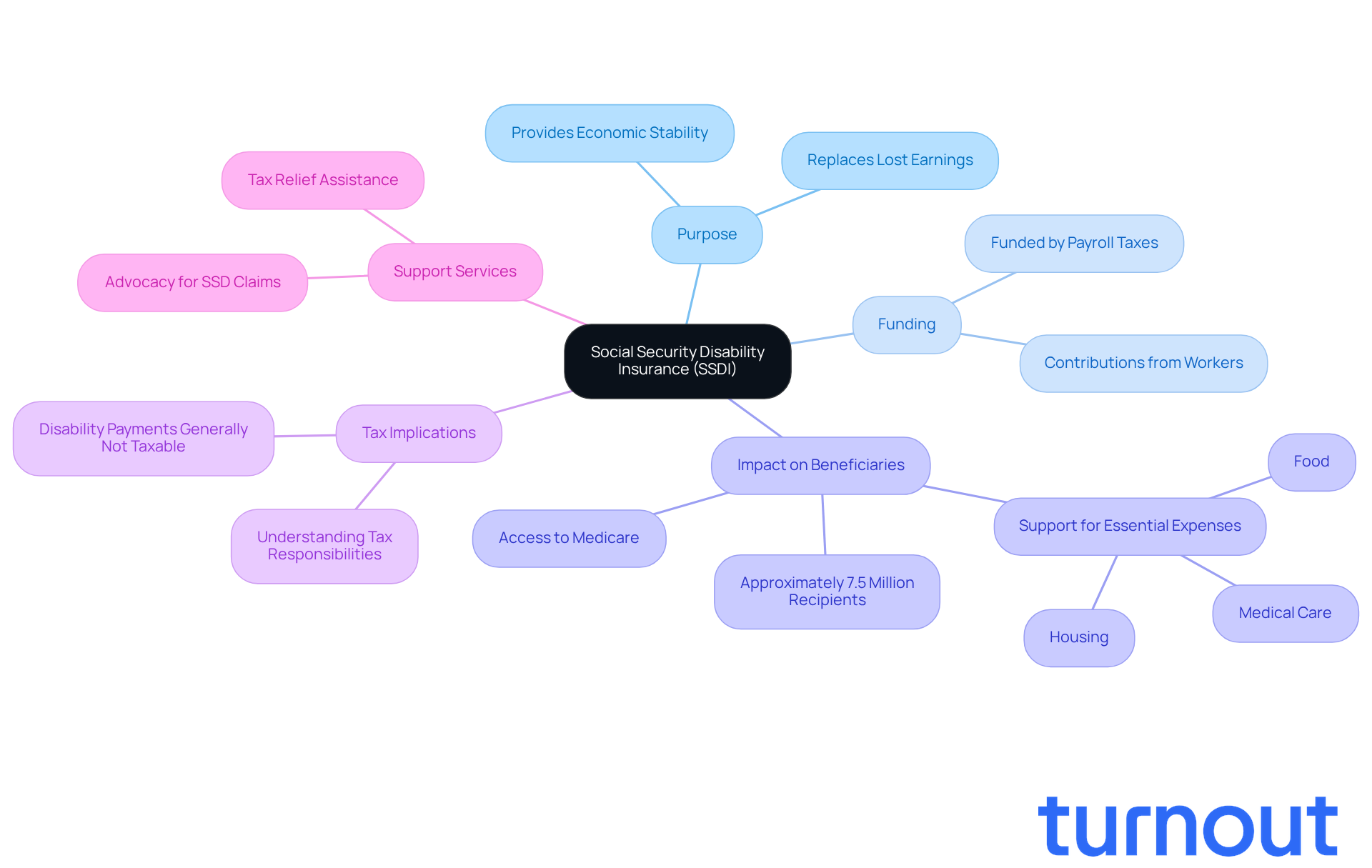
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) is more than just a federal program; it’s a lifeline for those unable to work due to medical conditions that are expected to last at least a year or lead to death. Funded by payroll taxes, SSDI aims to replace lost earnings for individuals who have contributed to the Social Security system through their work history. As of 2026, approximately 7.5 million Americans rely on this support, underscoring its vital role in providing economic stability during challenging health crises.
The primary goal of SSDI is to ensure that recipients have a reliable source of income during times of disability, which can be life-altering. Beyond financial assistance, qualifying for SSDI can open doors to essential services like Medicare after a waiting period. Understanding the interconnected benefits of SSDI is crucial, particularly in determining if disability social security taxable impacts tax responsibilities. While most recipients find that their disability payments are not taxable, it is important to understand if disability social security is taxable for effective financial planning.
Navigating the complexities of SSD claims and tax relief can be overwhelming, but Turnout is here to simplify that process. We understand that seeking assistance can feel daunting, which is why we offer trained nonlawyer advocates for SSD claims and IRS-licensed enrolled agents for tax debt relief. Our qualified support is designed to guide you through each step with care and understanding.
Real-life stories illustrate the profound impact SSDI has on beneficiaries. For many, these benefits are a crucial support system, helping them manage essential expenses like housing, food, and medical care. Financial experts emphasize the importance of SSDI as a safety net, particularly for those unable to work due to unforeseen circumstances. As the program evolves, it is essential for all recipients to stay informed about the benefits and whether disability social security is taxable. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Explore Taxability of Social Security Disability Benefits
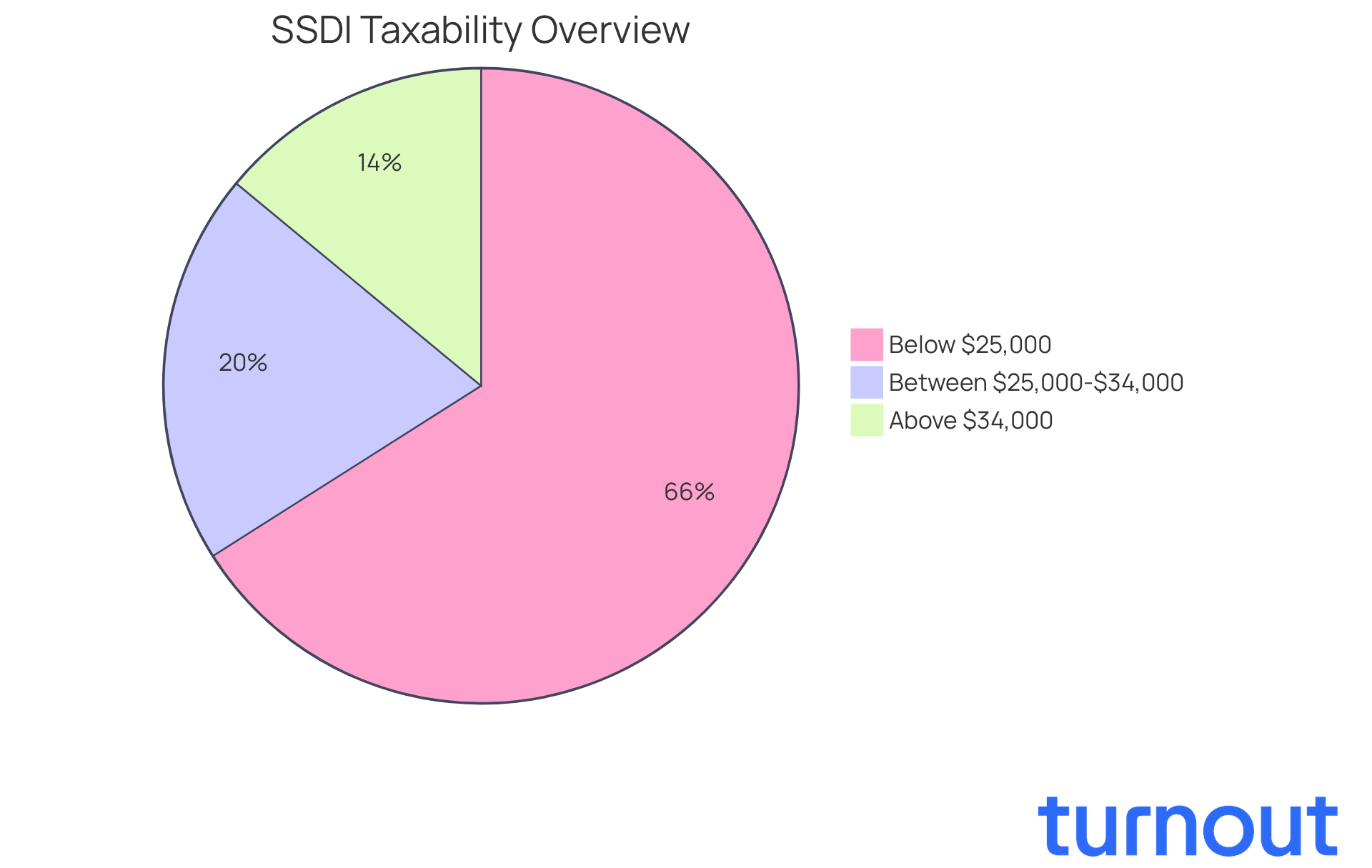
It can feel overwhelming to understand whether is disability social security taxable, especially when considering your overall earnings. We know that navigating these financial waters can be challenging. According to IRS guidelines, if your total earnings exceed certain limits - $25,000 for individual filers and $32,000 for couples filing jointly - it raises the question of whether is disability social security taxable, as up to 50% of your SSDI payments may be subject to taxation.
If you find yourself earning more than $34,000 as a single filer or $44,000 as a married couple, it’s important to consider whether is disability social security taxable, as up to 85% of your assistance could be liable for taxes. This is why accurately calculating your total earnings is crucial, particularly in understanding if disability social security taxable affects your tax liability.
By understanding these thresholds, you can effectively plan your finances and avoid unexpected tax burdens during filing season, particularly regarding whether is disability social security taxable. It’s reassuring to know that around two-thirds of Social Security Disability Insurance recipients fall below the earnings thresholds, which raises the question of whether is disability social security taxable. This means many may not encounter tax responsibilities on their payments, especially when considering if disability social security is taxable. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help you navigate these complexities.
Analyze Factors Affecting Tax Calculation on SSDI Benefits
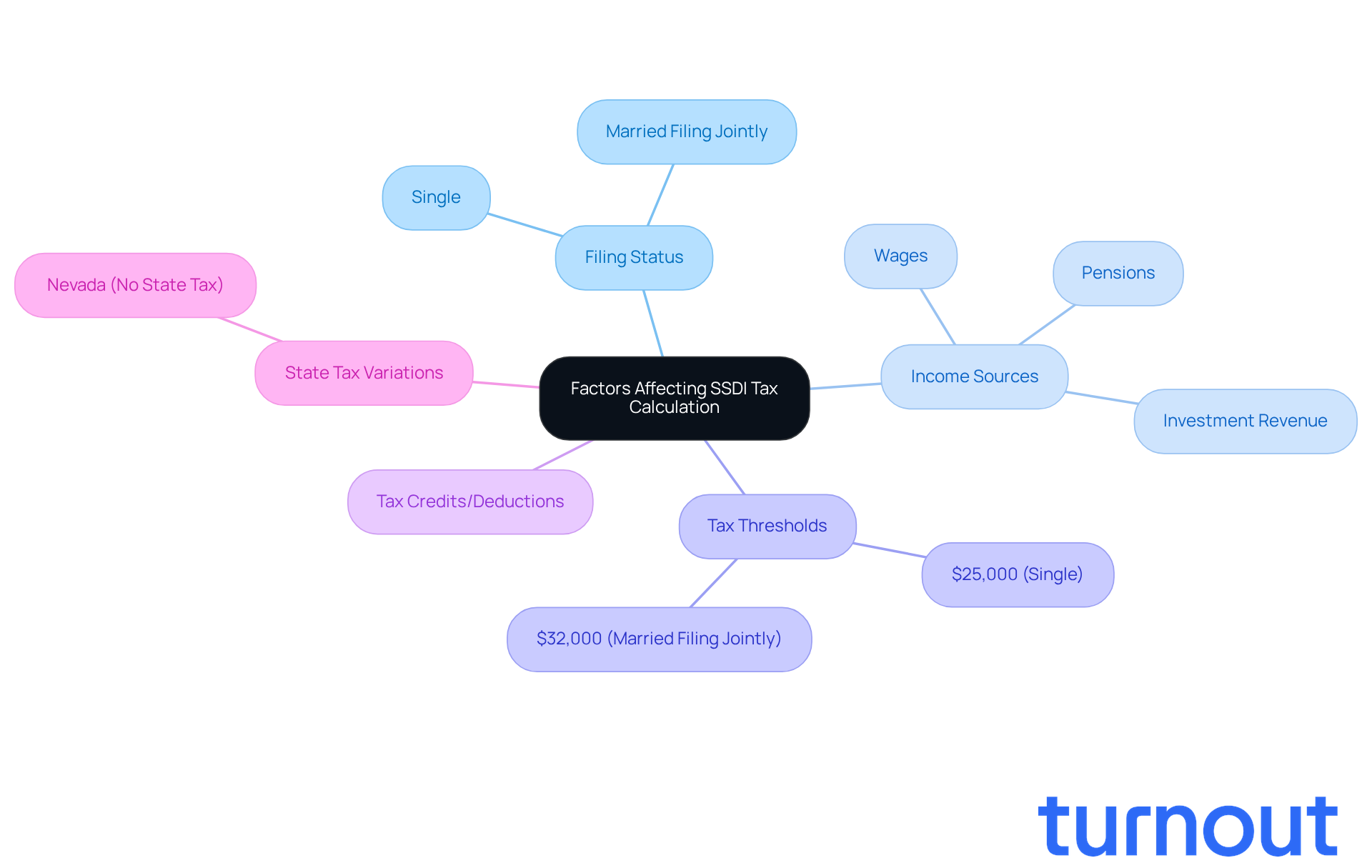
Navigating whether disability Social Security is taxable can feel overwhelming. We understand that multiple factors come into play, such as your filing status - whether you're single or married filing jointly - along with other income sources like wages, pensions, or investment revenue. Did you know that if your total earnings exceed certain thresholds - $25,000 for individuals and $32,000 for married couples filing jointly - up to 50% or even 85% of your Social Security Disability payments may be taxable, leading to the question, is disability Social Security taxable? This means that significant income from other sources can increase your overall tax burden.
Moreover, it's important to recognize that SSDI benefits might be reduced due to workers' compensation or other public disability benefits, adding another layer of complexity to your tax situation. Understanding how tax credits and deductions can lower your taxable income is crucial for effective tax planning. Keeping accurate records of all your income sources is essential; it not only helps with compliance but also optimizes your tax situation.
It's worth noting that in Nevada, disability payments are not taxable, thanks to the absence of state tax.
At Turnout, we’re here to help you navigate these complexities. Our trained nonlawyer advocates can assist you, especially if you have multiple income streams that could affect your tax obligations. Consulting with a tax expert knowledgeable about disability benefits can provide you with valuable insights. As Merryl Jones, a Second Chance Lawyer, wisely states, "Let’s make sure your voice is heard and your future protected." You're not alone in this journey; we're here to support you every step of the way.
Implement Strategies for Managing SSDI Tax Obligations
Managing your SSDI tax obligations can feel overwhelming, especially when you're trying to determine if disability social security is taxable, but you’re not alone in this journey. Here are some strategies to help you navigate this process with confidence:
-
Monitor Your Earnings: It’s important to keep an eye on all your revenue sources. By doing so, you can ensure you stay below taxable thresholds. For instance, if you’re an individual filer, you won’t pay any fees on your allowances if your total earnings are below $25,000. If you’re married and filing jointly, you can earn up to $32,000 without facing charges.
-
Adjust Withholding: If you think you might owe taxes, consider requesting federal withholding from your SSDI payments. This proactive step can help you avoid a hefty tax bill when the year ends. Remember, almost 90% of Social Security recipients won’t pay federal taxes on their payments, but it is crucial to understand if disability social security taxable applies to your specific situation.
-
Utilize Deductions: Take the time to explore available tax deductions and credits that could apply to you. Medical expenses or education credits can significantly lower your taxable earnings. For example, in Colorado, taxpayers aged 65 and older can subtract federally taxed Social Security benefits from their taxable income.
-
Consult a Tax Professional: Engaging a tax advisor who understands disability benefits can provide you with tailored strategies and ensure you comply with tax laws. Many SSDI beneficiaries have successfully reduced their tax burdens by seeking professional advice.
By implementing these strategies, you can navigate your tax obligations with greater ease and potentially lessen your overall tax burden. Remember, we’re here to help you through this process.

Conclusion
Understanding the nuances of Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) and its tax implications is essential for those seeking financial stability. We know that navigating these waters can be overwhelming. While many recipients may not face tax liabilities on their SSDI payments, various income thresholds and external factors can influence this outcome. Recognizing these elements empowers you to make informed financial decisions and plan effectively for your tax obligations.
Key insights from this article highlight the importance of:
- Monitoring total earnings
- Understanding filing statuses
- Consulting tax professionals
These steps can help you navigate the complexities of SSDI taxation. By staying informed about income thresholds and potential deductions, you can minimize your tax burdens and ensure compliance with current regulations. These strategies serve as valuable tools to enhance your financial planning and alleviate the stress associated with tax season.
Ultimately, being well-informed about SSDI and its tax responsibilities is crucial. Taking proactive steps, such as adjusting withholdings and utilizing available deductions, can lead to a more secure financial future. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Engaging with resources and support systems, like Turnout, can further assist you in navigating these challenges, ensuring you have the support you need for financial clarity and stability.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)?
SSDI is a federal program designed to provide financial support to individuals who are unable to work due to medical conditions expected to last at least a year or result in death. It is funded by payroll taxes and aims to replace lost earnings for those who have contributed to the Social Security system.
Who benefits from SSDI?
As of 2026, approximately 7.5 million Americans rely on SSDI for economic stability during health crises. The program serves individuals who cannot work due to disabilities.
What is the primary purpose of SSDI?
The primary goal of SSDI is to ensure that recipients have a reliable source of income during times of disability, which can significantly impact their lives.
Are SSDI benefits taxable?
Most SSDI recipients find that their disability payments are not taxable; however, it is important to understand the tax implications for effective financial planning.
What additional benefits can qualifying for SSDI provide?
Qualifying for SSDI can also provide access to essential services like Medicare after a waiting period.
How can individuals navigate the SSDI claims process?
Navigating SSDI claims and tax relief can be complex, but organizations like Turnout offer trained nonlawyer advocates for SSD claims and IRS-licensed enrolled agents for tax debt relief to assist individuals through the process.
Why is SSDI considered a safety net?
SSDI is viewed as a safety net because it helps beneficiaries manage essential expenses, such as housing, food, and medical care, particularly for those unable to work due to unforeseen circumstances.
How can beneficiaries stay informed about SSDI benefits?
It is essential for all SSDI recipients to stay informed about their benefits and any changes, including whether disability social security is taxable, to ensure proper financial planning.




