Overview
If you're wondering whether you might be subject to backup withholding, we understand that this can be a concerning situation. It’s important to evaluate whether you have provided a correct taxpayer identification number (TIN) and if you've received any notifications from the IRS regarding unpaid taxes.
Understanding these criteria is crucial, and we’re here to help you navigate this process. By promptly addressing any discrepancies, you can prevent unexpected tax deductions and ensure compliance with tax regulations. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; many face similar challenges.
Take a moment to reflect: Have you checked your TIN recently? If you find any issues, don’t hesitate to reach out for assistance. Ensuring everything is in order can provide peace of mind and help you avoid potential complications.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of tax obligations can feel overwhelming, like wandering through a maze. This is especially true when it comes to backup withholding—a process that can have a significant impact on your financial well-being. In this guide, we aim to demystify backup withholding, providing you with a clear path to understand if you are subject to these deductions and how to effectively manage your tax responsibilities.
Have you ever received an unexpected notice from the IRS, or worse, found your payments reduced without warning? It's common to feel anxious in these situations. By exploring the criteria for backup withholding, the types of payments it affects, and strategies to prevent or stop it, we hope to equip you with the knowledge you need to protect your income and avoid unnecessary financial pitfalls. Remember, you are not alone in this journey—we're here to help.
Understand Backup Withholding: Definition and Importance
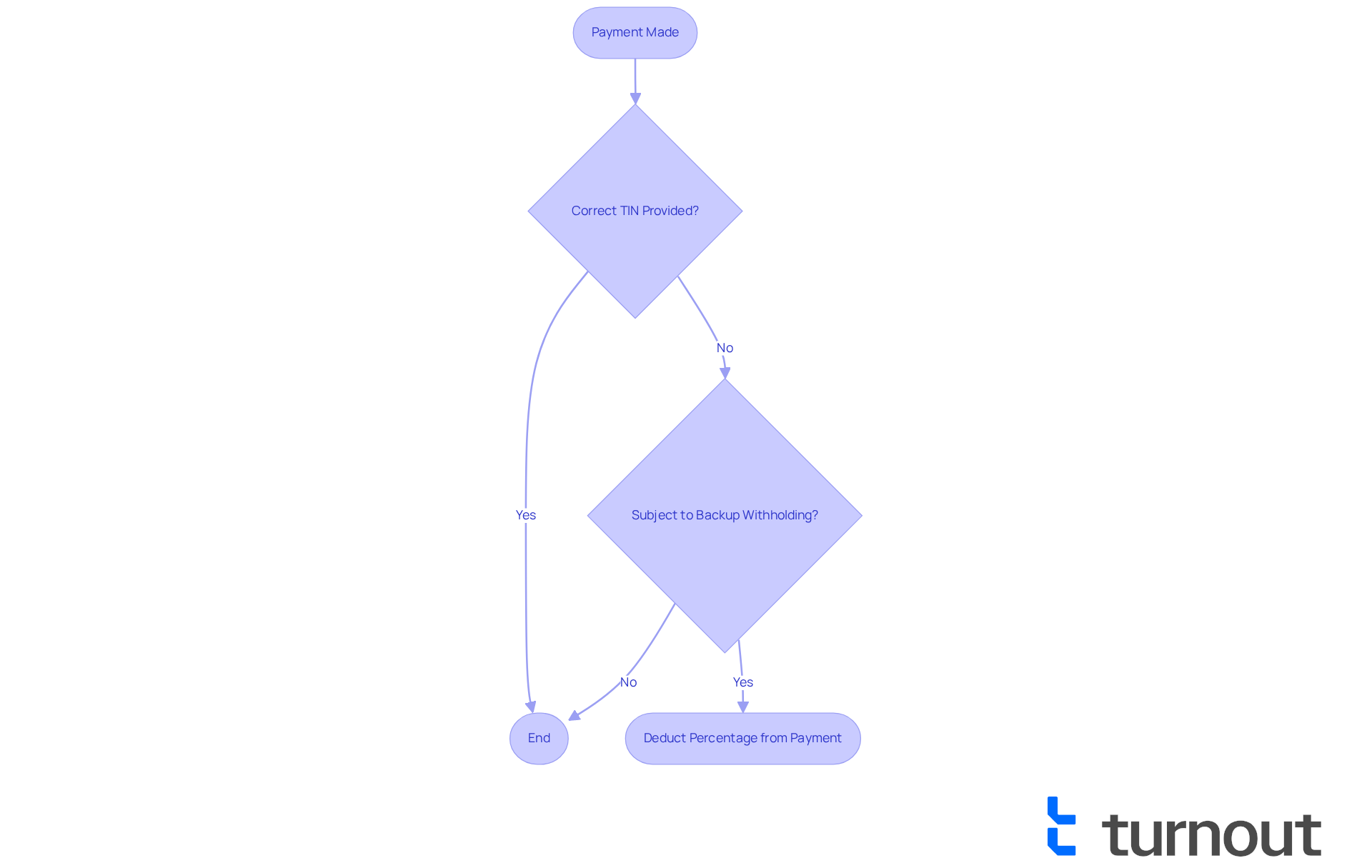
We understand that navigating tax obligations can be challenging. The retained tax is a financial mechanism that requires payers to deduct a certain percentage from payments made to recipients. This often occurs when the recipient does not provide a correct taxpayer identification number (TIN) or is unsure about how to know if you are subject to backup withholding due to specific IRS notifications.
It is vital to understand how to know if you are subject to backup withholding, as this can significantly impact your income and tax obligations. It's common to feel overwhelmed by these requirements. By recognizing when and why tax deductions occur, you can manage your finances more effectively and prevent unforeseen tax obligations.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We're here to help you navigate these complexities with confidence.
Identify Payments Subject to Backup Withholding
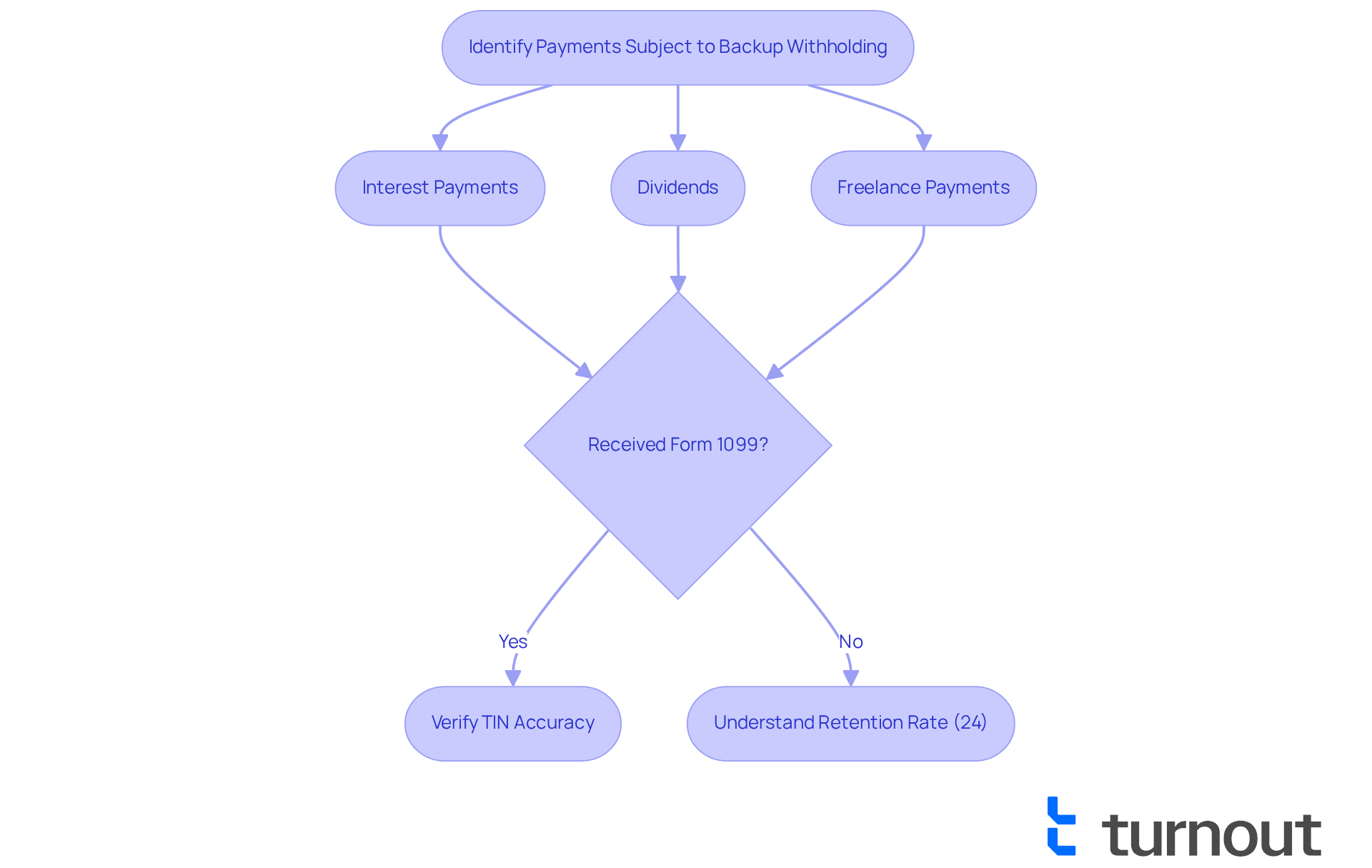
To understand how to know if you are subject to backup withholding, it's important to recognize that payments such as interest payments, dividends, and specific payments made to freelance workers might be affected. We understand that navigating these financial obligations can be overwhelming. If you receive a Form 1099, it may help you understand how to know if you are subject to backup withholding. For instance, independent contractors who receive payments reported on Form 1099-NEC should learn how to know if you are subject to backup withholding, especially if they have unpaid taxes or do not provide an accurate Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN).
It's common to feel concerned about these potential deductions, particularly when considering how to know if you are subject to backup withholding, as many independent contractors encounter retention of funds due to these issues. Currently, the retention rate stands at 24%, which can significantly impact your financial situation. Understanding these payment types is crucial to avoid unexpected tax liabilities during tax season.
Furthermore, if the IRS notifies a payer that a payee's TIN does not match IRS records, it is important to understand how to know if you are subject to backup withholding, which may necessitate additional tax retention. This is why it's so important to confirm that your TIN is correct and up to date. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you navigate these challenges.
Evaluate Your Eligibility: Criteria for Backup Withholding
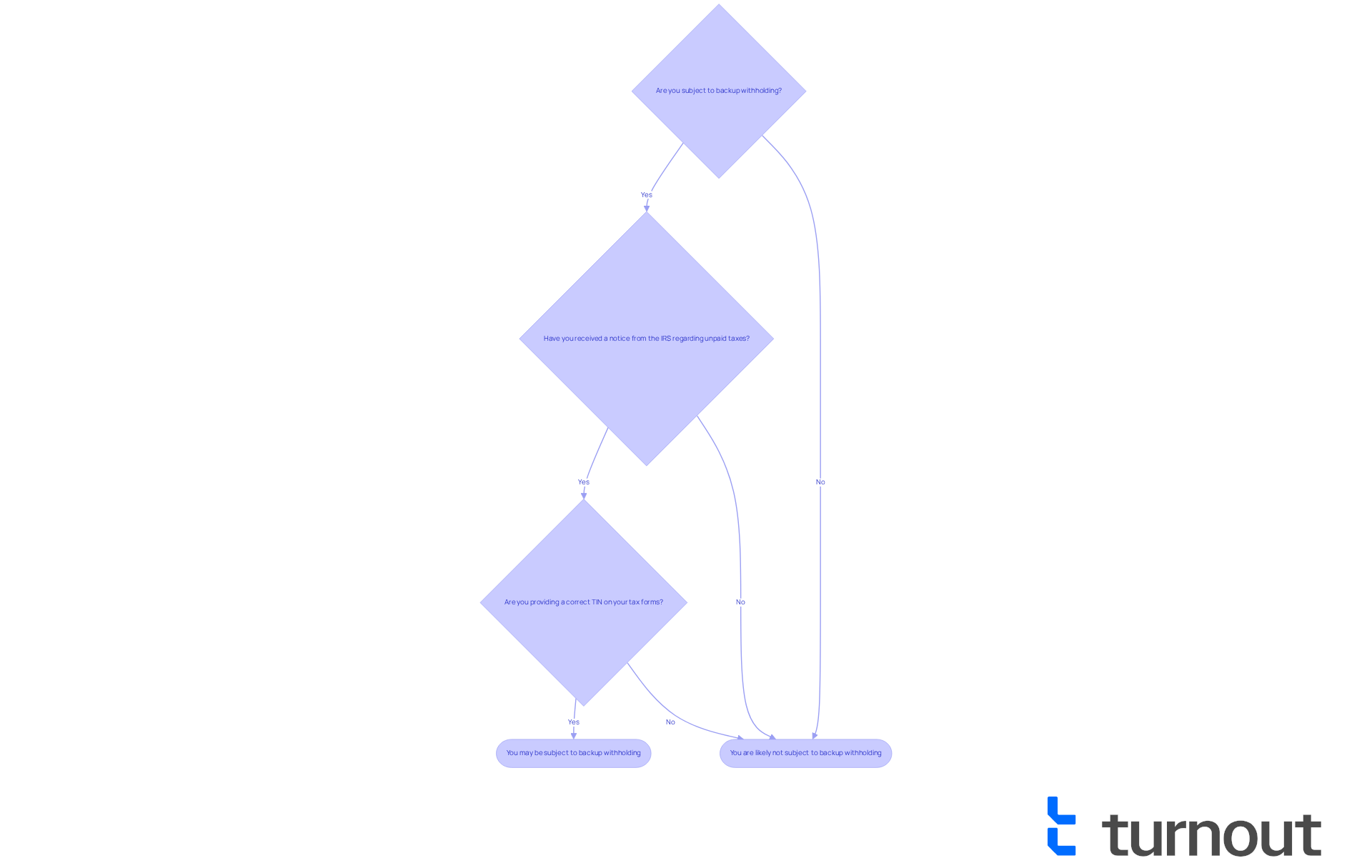
Navigating tax issues can be challenging, and we understand that you may have concerns about how to know if you are subject to backup withholding. To help you, consider these important criteria:
- Have you received a notice from the IRS regarding unpaid taxes?
- Are you providing a correct TIN on your tax forms?
If you’ve been informed by the IRS about how to know if you are subject to backup withholding, it’s crucial to resolve these underlying issues quickly. We’re here to help you grasp these criteria, as doing so can assist you in avoiding unnecessary deductions and ensuring adherence to tax regulations. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and taking these steps can lead to a more secure financial future.
Implement Strategies to Prevent or Stop Backup Withholding
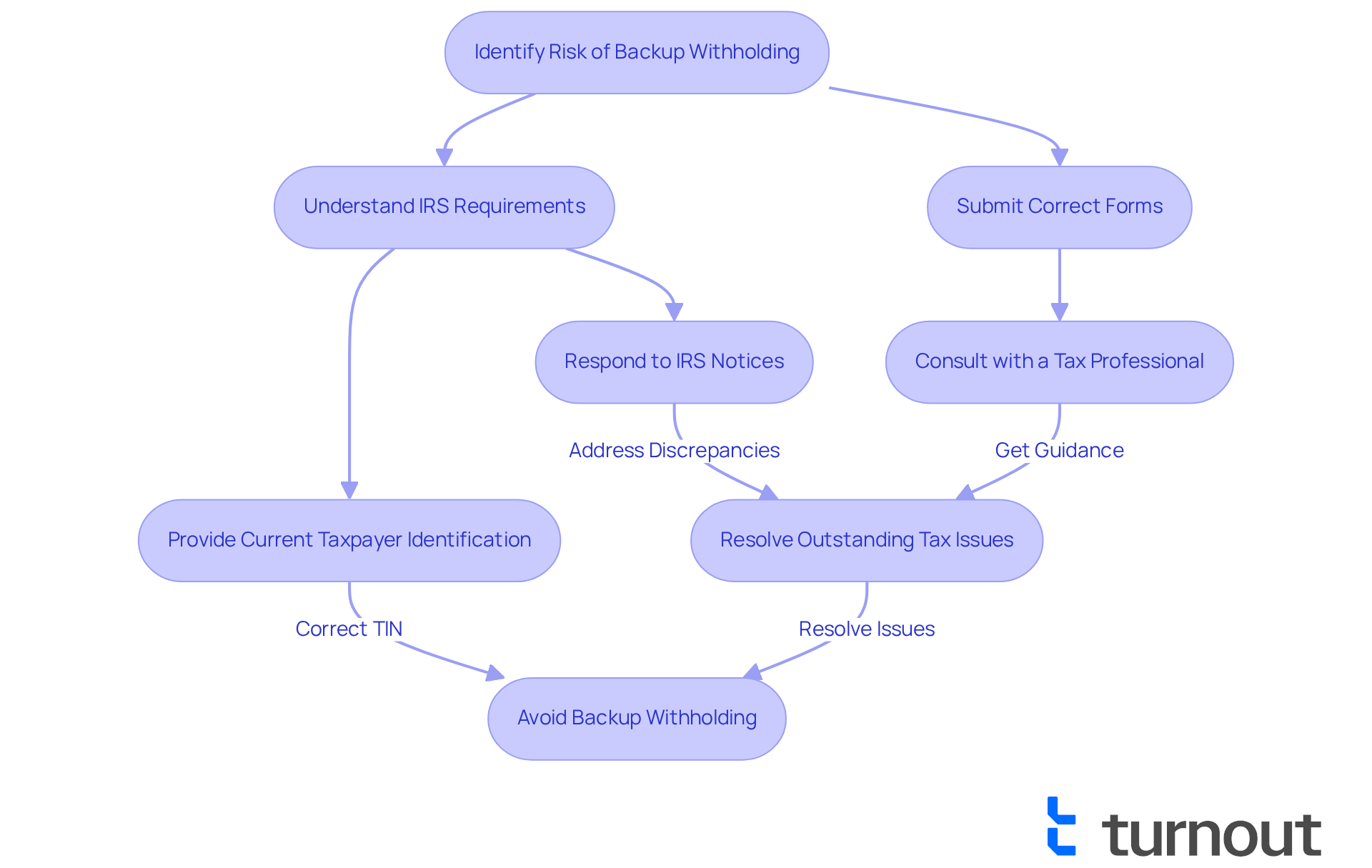
To avoid or halt payment deductions, it’s essential to understand how to know if you are subject to backup withholding and provide precise and current taxpayer identification details to all payers. This includes submitting the correct Form W-9 for U.S. persons or the appropriate Form W-8 for foreign individuals. If you receive a notice from the IRS, respond promptly to address any discrepancies and resolve outstanding tax issues. We understand that receiving such notices can be stressful. Statistics indicate that a significant percentage of taxpayers who act quickly on IRS notices manage to resolve their issues efficiently, minimizing the risk of further complications.
Consulting with a financial advisor or tax professional can also be beneficial. As Sandra Habiger, a Chartered Professional Accountant, states, "Backup retention is undesirable, yes." Nevertheless, it can be avoided or fixed by providing the necessary tax information, including the right taxpayer identification number, by filing the requisite tax forms, or by paying the outstanding balance. These experts can help review your tax situation, ensuring compliance and providing guidance on how to navigate IRS requirements effectively.
Remember, knowing how to know if you are subject to backup withholding can help you avoid it by addressing the underlying issues, such as providing the correct TIN and resolving underreported income. You are not alone in this journey. Addressing any IRS notifications without delay is crucial. We’re here to help you through this process.
Conclusion
Understanding backup withholding is crucial for effectively managing your tax obligations and ensuring your financial security. We understand that navigating the complexities of this tax mechanism can be overwhelming. By grasping its nuances, you can avoid unexpected deductions that might impact your income.
Key insights from this guide emphasize the importance of recognizing payments subject to backup withholding, such as:
- Interest
- Dividends
- Payments to freelancers
It's common to feel uncertain about eligibility criteria, including the necessity of providing a correct taxpayer identification number (TIN) and responding promptly to IRS notifications. Being aware of these aspects is essential for preventing unnecessary tax retention. Implementing strategies like submitting accurate tax forms and consulting with financial professionals can further mitigate the risks associated with backup withholding.
Ultimately, staying informed and proactive is vital in addressing backup withholding issues. By taking the necessary steps to understand and manage your tax obligations, you can safeguard your financial well-being and ensure compliance with IRS regulations. Embracing this knowledge empowers you to navigate your financial journey with confidence, minimizing the potential for unexpected tax liabilities. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is backup withholding?
Backup withholding is a tax mechanism that requires payers to deduct a certain percentage from payments made to recipients, typically when the recipient does not provide a correct taxpayer identification number (TIN).
When does backup withholding occur?
Backup withholding occurs when a recipient is unable to provide a correct TIN or is unsure about their tax status, often due to specific notifications from the IRS.
Why is it important to understand backup withholding?
Understanding backup withholding is crucial as it can significantly impact your income and tax obligations, helping you manage your finances more effectively and avoid unforeseen tax liabilities.
How can I know if I am subject to backup withholding?
You can determine if you are subject to backup withholding by checking if you have received any notifications from the IRS regarding your taxpayer identification number or tax status.




