Overview
It's important to know that you cannot skip filing taxes for a year in Canada unless certain conditions are met. For instance, if your income is below the Basic Personal Amount or if you have no tax liability, you may have some leeway. However, we understand that the thought of taxes can be overwhelming.
Failing to file your taxes can lead to:
- Penalties
- Loss of benefits
- Complications in future tax situations
That's why it's essential to understand your obligations before making any decisions. Remember, you're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help guide you.
Introduction
Navigating the complexities of tax obligations can feel overwhelming for many Canadians. It's common to wonder, "Can I skip filing taxes for a year?" Understanding the nuances of tax requirements is crucial. This knowledge can lead to significant benefits or, conversely, unforeseen penalties. If you find yourself in this situation, you're not alone.
In this article, we will explore:
- Various scenarios that may allow for skipping a year of filing
- The potential consequences of not filing
- The steps you can take to effectively manage your tax status in Canada
Remember, we're here to help you through this journey.
Understand Your Tax Obligations in Canada
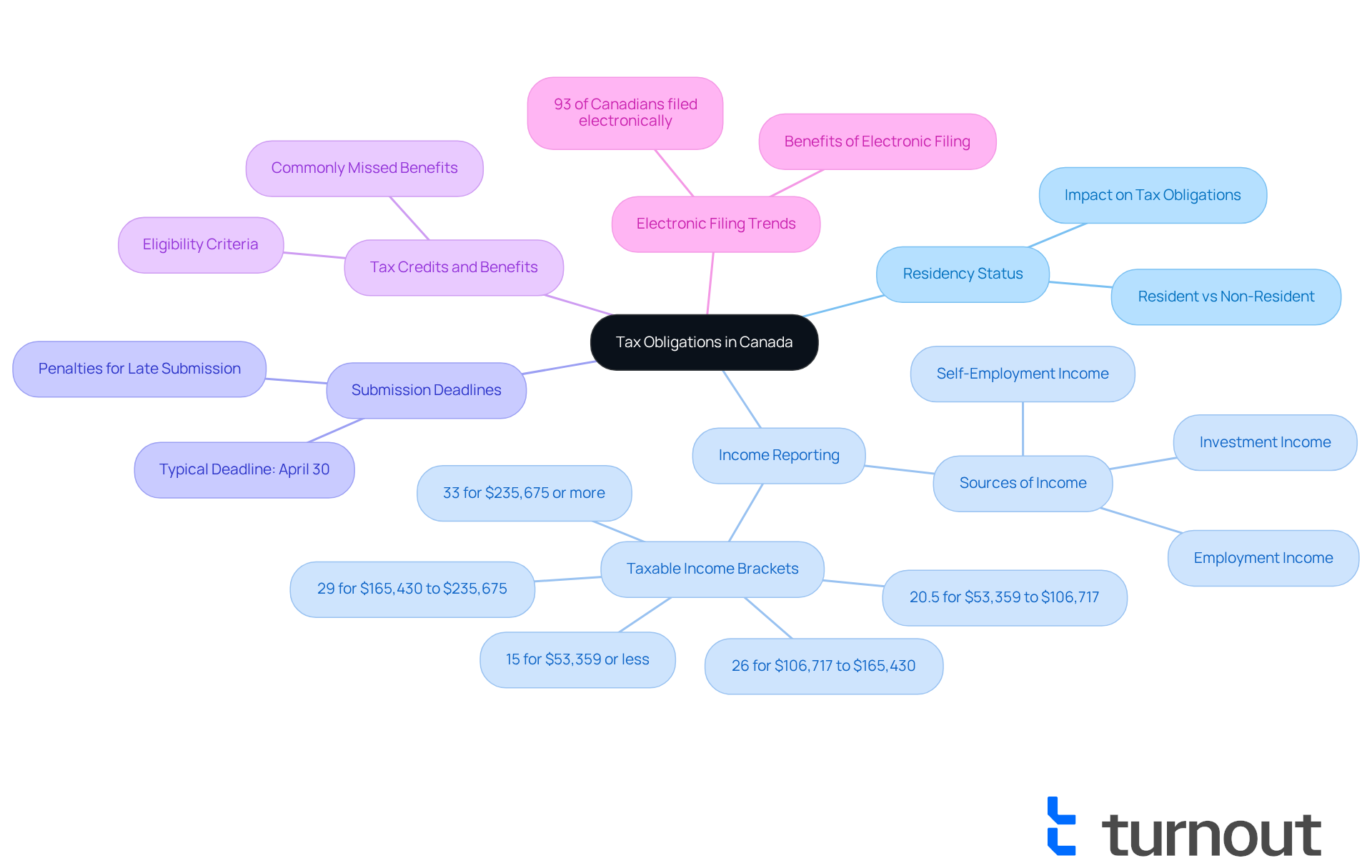
Before considering whether you can skip filing taxes for a year, it’s important to understand your tax obligations in Canada. We know that navigating taxes can be daunting, but all residents must file an annual tax return if they owe taxes or wish to claim benefits or credits. The Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) requires individuals to declare their earnings, even if they are below the taxable threshold. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Residency Status: It’s essential to determine whether you are a resident or non-resident for tax purposes, as this significantly impacts your obligations.
- Income Reporting: Remember, all sources of income—including employment, self-employment, and investment income—must be reported accurately.
- Submission Deadlines: Familiarize yourself with the due dates for submitting your returns to prevent penalties. Typically, the deadline is April 30 for individuals.
Understanding the tax credits and benefits you may be eligible for can help you determine if you can skip filing taxes for a year.
In 2025, approximately 93% of Canadians filed their taxes electronically, reflecting a growing trend towards digital submissions. We understand that many individuals, especially those with low incomes, may feel overwhelmed by the tax submission process. It’s common to miss chances to claim benefits due to a lack of awareness or understanding. By grasping these responsibilities, you can better evaluate your circumstances and the potential consequences of not submitting. Remember, you are not alone in this journey—we're here to help you navigate your tax obligations.
Identify When You Can Skip Filing Taxes
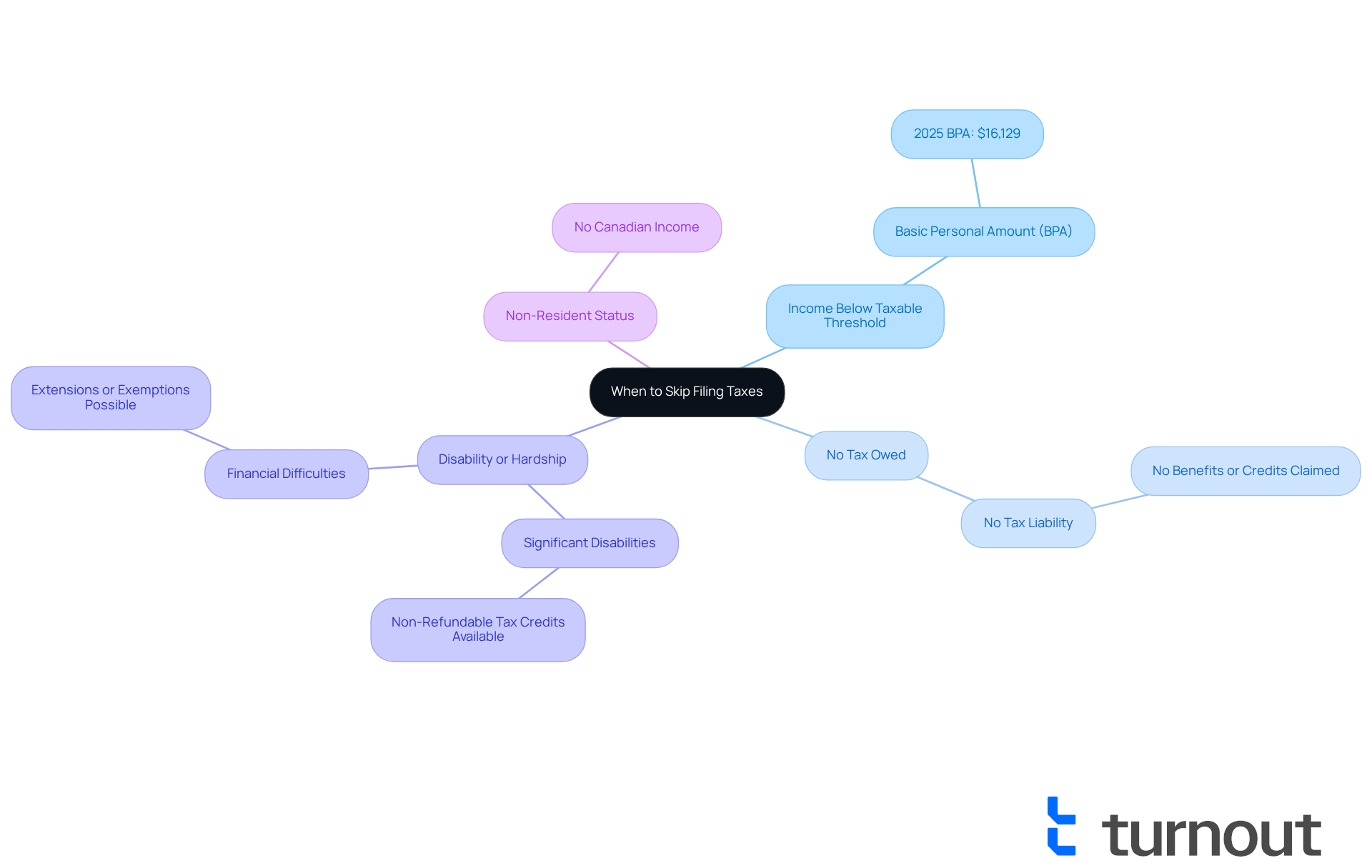
In certain situations, the question arises: can you skip filing taxes for a year, which can be a relief during challenging times. Here are some key scenarios to consider:
- Income Below the Taxable Threshold: If your total income is below the Basic Personal Amount (BPA) set by the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA), you may not need to file. For 2025, the BPA is $16,129. If your income is below this figure, you might find that submitting is not required.
- No Tax Owed: If you have no tax liability and don’t plan to claim any benefits or credits, you may not need to file your taxes.
- Disability or Hardship: We understand that significant disabilities or financial difficulties can create barriers. Individuals facing these challenges may wonder, can you skip filing taxes for a year by qualifying for extensions or exemptions from submission? Many Canadians with disabilities avoid tax submissions due to these hurdles. It’s important to know that non-refundable tax credits are available for those with certified disabilities, which can help reduce any tax liability.
- Non-Resident Status: If you are a non-resident without Canadian income, you are typically not obliged to submit returns.
To ensure compliance with CRA guidelines and to clarify your specific situation, we encourage you to consult the CRA’s resources or seek help from knowledgeable advocates. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. This support can help you navigate the complexities of tax submission and empower you to make informed decisions.
Evaluate the Consequences of Skipping a Tax Year
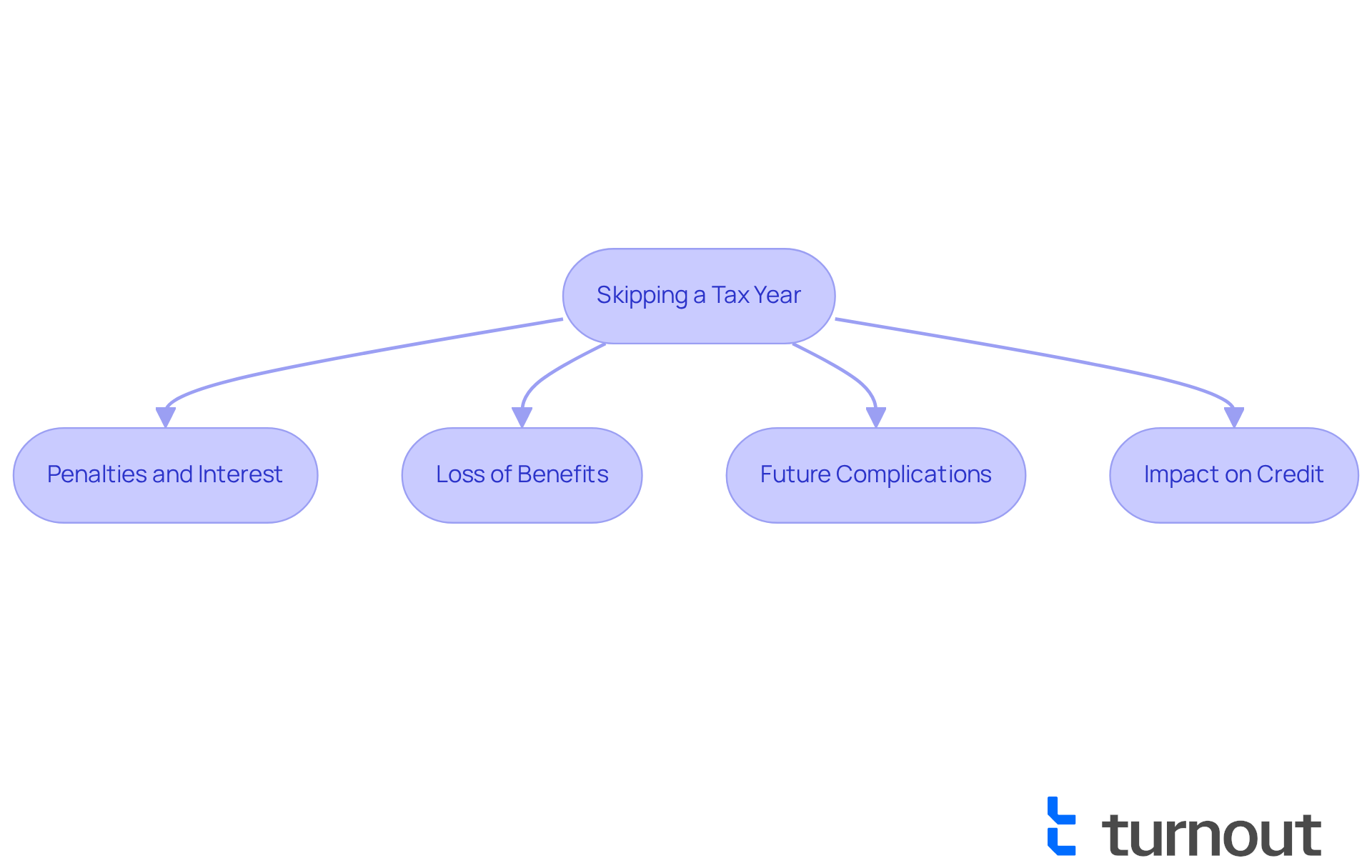
Before deciding whether you can skip filing taxes for a year, it's important to reflect on the potential consequences. We understand that navigating taxes can be overwhelming, and you might feel uncertain about your next steps.
- Penalties and Interest: Failing to file taxes when owed can lead to significant penalties and interest on the unpaid amount. In Canada, the penalty for not filing can reach up to 5% of the unpaid tax, plus an additional 1% for each month the return is late, which can accumulate quickly. For instance, if you owe $1,000 in dues and submit your return three months late, you might face a fine of $8,000. This can feel daunting, but knowing the facts is the first step.
If you are wondering about the loss of benefits, you should know that skipping filing taxes for a year may jeopardize your eligibility for various benefits or credits. For example, individuals depending on social support or disability allowances may see their payments diminished or stopped completely if they do not submit their financial returns, as numerous programs necessitate verification of income. A case study from the Little Rock Port Authority Slackwater Harbor Improvements project illustrates how individuals faced financial setbacks due to unfiled taxes, impacting their access to essential benefits. It's crucial to consider how this could affect your situation, particularly when asking, can you skip filing taxes for a year?
-
Future Complications: Not submitting can complicate future tax situations, particularly if you need to claim carry-forward credits or deductions. This can lead to a more complicated documentation process in subsequent years, potentially resulting in missed opportunities for refunds or credits. Statistics indicate that individuals who neglect to submit their documents frequently encounter a 30% rise in the intricacy of their tax submissions in the subsequent year. We want to help you avoid these challenges.
-
Impact on Credit: Unresolved tax issues can negatively affect your credit score, making it more challenging to secure loans or mortgages. Tax debts that remain unpaid can be reported to credit bureaus, leading to long-term financial repercussions. For example, a study indicated that individuals with unresolved tax issues saw their credit scores drop by an average of 50 points, significantly affecting their borrowing capacity. This is a critical aspect to keep in mind as you make decisions.
Weigh these consequences carefully against your current situation. Remember, you're not alone in this journey; we're here to help you navigate these challenges and make informed decisions.
Follow Steps to Manage Your Tax Filing Status
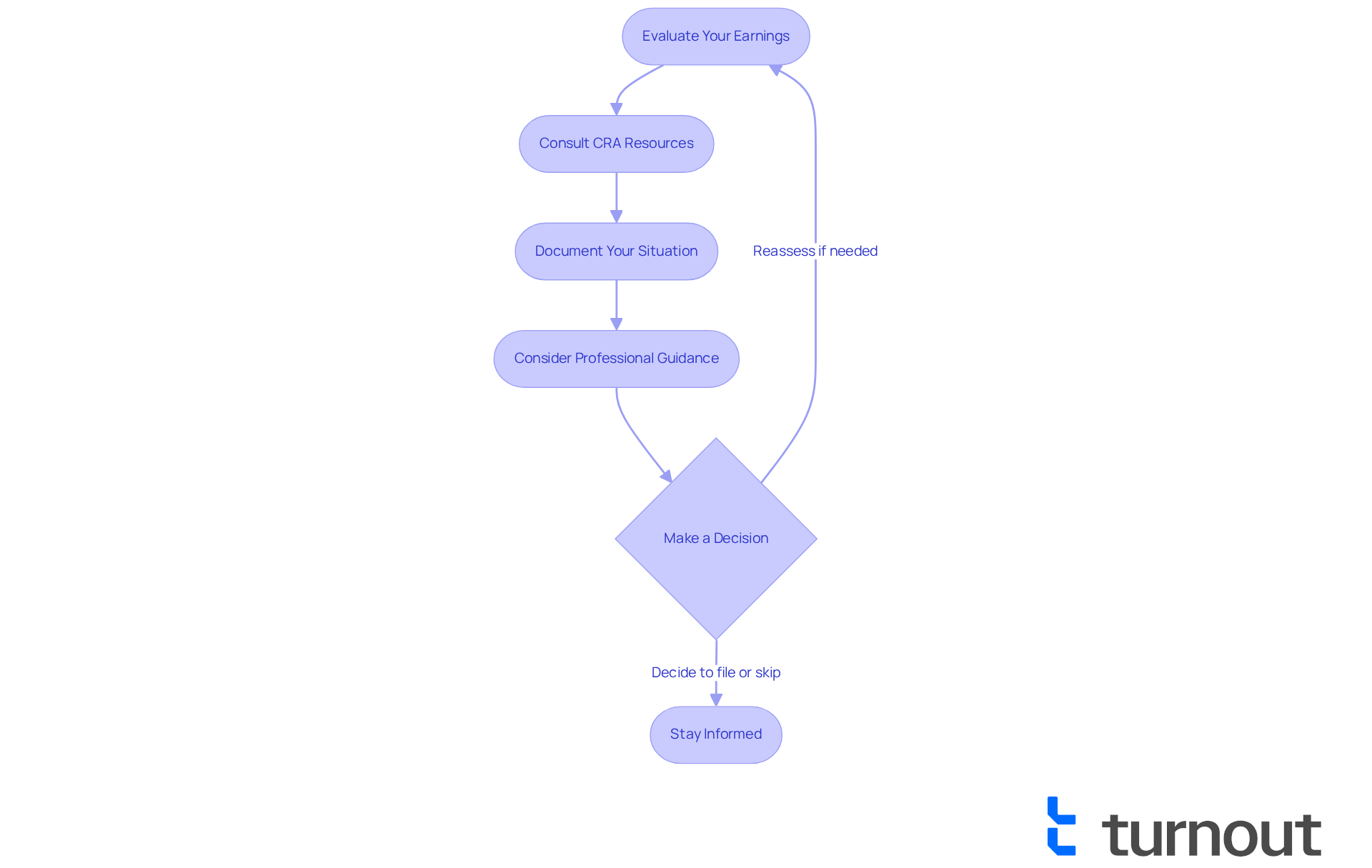
To effectively manage your tax filing status, consider these supportive steps:
-
Evaluate Your Earnings: Start by gathering all your earnings statements. It's important to see if your revenue exceeds the taxable threshold. In Canada, the average tax refund in recent years was about $2,294. This highlights how crucial it is to evaluate your earnings accurately, as you may be eligible for refunds.
-
Consult CRA Resources: We understand that navigating tax information can be overwhelming. Utilize the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) website for detailed information on submission requirements, exemptions, and resources available to you. The CRA has made significant improvements to its digital services, making it easier for you to access necessary information, including online courses and chat support.
-
Document Your Situation: It's common to feel uncertain about your financial circumstances. Keeping thorough records of your situation, including any hardships or disabilities that may affect your tax obligations, can be very helpful. This documentation is crucial if you decide to seek assistance or need to explain your situation to the CRA.
-
Consider Professional Guidance: If you're feeling uncertain about your tax obligations or options, remember that seeking help from a knowledgeable advocate can make a difference. Professional guidance offers tailored advice, ensuring you understand your rights and responsibilities.
-
Make a Decision: After assessing your income and consulting resources, take a moment to decide if you are wondering, can you skip filing taxes for a year. It's important to understand the possible consequences of your decision, including any penalties for late submission. Fortunately, the CRA is offering relief from late-filing penalties until June 2, 2025, which may provide you with some reassurance.
-
Stay Informed: Keep yourself updated on any changes in tax laws or CRA guidelines that may affect your situation. The CRA regularly updates its resources, and being informed can help you navigate your tax responsibilities more effectively.
By following these steps, you're taking control of your tax filing status and making informed decisions regarding your obligations. Remember, you're not alone in this journey, and we're here to help.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of tax obligations in Canada can feel overwhelming, especially when considering the possibility of skipping a tax year. We understand that understanding your tax responsibilities is crucial; failing to file can lead to significant penalties and loss of benefits. It’s important to assess your individual circumstances, including income levels and potential hardships, to make informed decisions about tax filing.
Knowing when filing is not mandatory can relieve some stress. For instance:
- If your income is below the Basic Personal Amount
- If you face disabilities that may hinder compliance
You might not need to file. However, skipping a tax year can have serious consequences, including:
- Financial penalties
- Loss of benefits
- Long-term impacts on your credit score
These insights highlight the necessity of careful evaluation and proactive management of your tax situation.
Ultimately, staying informed and seeking professional guidance can empower you to navigate your tax obligations effectively. Remember, understanding your tax responsibilities is vital, as it directly affects your financial well-being and access to essential benefits. By taking the necessary steps to manage your tax filing status, you can avoid complications and ensure compliance, fostering a more secure financial future. You are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the tax obligations for residents in Canada?
All residents in Canada must file an annual tax return if they owe taxes or wish to claim benefits or credits. This includes declaring all sources of income, even if they are below the taxable threshold.
How does residency status affect tax obligations in Canada?
Your residency status, whether you are a resident or non-resident for tax purposes, significantly impacts your tax obligations.
What types of income need to be reported on tax returns?
All sources of income must be reported accurately, including employment income, self-employment income, and investment income.
When is the deadline for submitting tax returns in Canada?
The typical deadline for submitting tax returns for individuals is April 30.
Can I skip filing taxes for a year?
Understanding your tax credits and benefits eligibility can help you determine if you can skip filing taxes for a year, but generally, you must file if you owe taxes or wish to claim benefits.
How are Canadians filing their taxes in recent years?
In 2025, approximately 93% of Canadians filed their taxes electronically, indicating a growing trend towards digital submissions.
What should I do if I feel overwhelmed by the tax submission process?
It's common to feel overwhelmed, especially for those with low incomes. Understanding your responsibilities and seeking help can assist you in navigating your tax obligations effectively.




