Introduction
The complexities of mental health conditions often lead to a pressing question: can anxiety be classified as a disability? We understand that this is a significant concern for many. With approximately one in three adults in the U.S. experiencing a mental health issue at some point in their lives, it’s crucial to grasp the implications of anxiety disorders within the framework of disability law.
This article delves into the nuances of how anxiety is evaluated against other mental health conditions. We’ll explore the criteria set forth by the Social Security Administration and the Americans with Disabilities Act. It’s common to feel overwhelmed when seeking support and benefits. What does it truly take for anxiety to be recognized as a disability in today’s legal landscape?
You are not alone in this journey. Together, we can navigate these challenges and find the answers you need.
Understanding Anxiety as a Disability
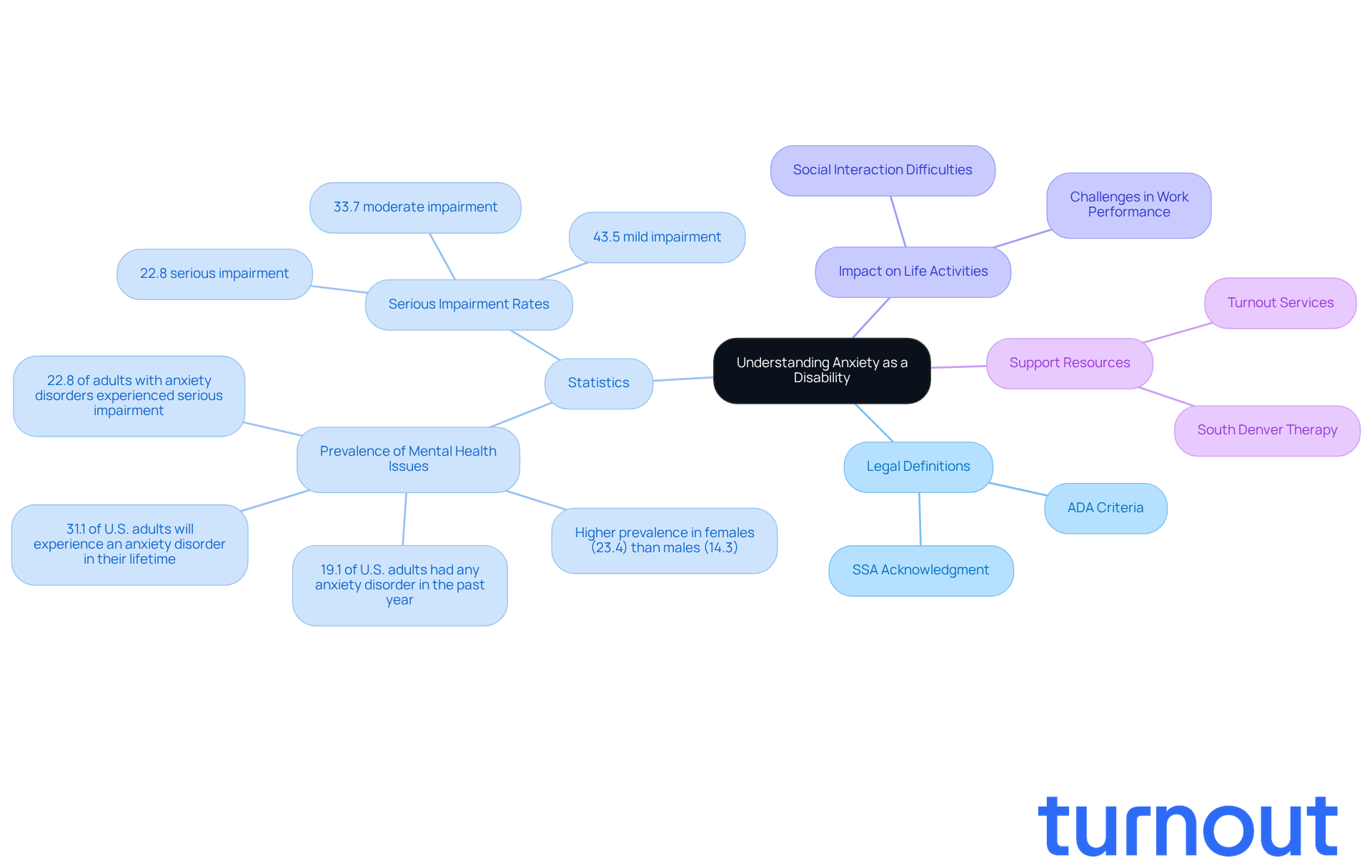
The question of whether can anxiety be a disability arises, especially when anxiety conditions significantly hinder your ability to carry out major life activities. We understand that navigating these challenges can be overwhelming. The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) raises the question of can anxiety be a disability if a mental impairment substantially limits one or more major life activities, such as working, learning, or social interactions.
The Social Security Administration (SSA) acknowledges that can anxiety be a disability, as it may serve as a criterion for disability benefits. If you can demonstrate the severity and impact of your situation, you may qualify for support. Conditions like generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder raise the question of whether can anxiety be a disability, especially if they significantly interfere with your daily functioning.
It's important to note that approximately 31.1% of U.S. adults will encounter a mental health issue at some point in their lives. This statistic highlights just how common these conditions are. Among adults with any emotional disorder, 22.8% experience serious impairment, which can greatly affect their ability to maintain employment. Mental health professionals emphasize that anxiety can lead to substantial challenges in daily life. Many individuals report difficulties in work performance and social interactions.
Understanding these definitions and statistics is crucial for anyone seeking disability benefits, particularly in relation to the question of can anxiety be a disability. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Turnout offers vital resources and services to help you manage the complexities of SSD claims. They provide access to trained nonlawyer advocates who can streamline the process and ensure that you receive the support you need.
Comparing Anxiety and Depression: Disability Criteria
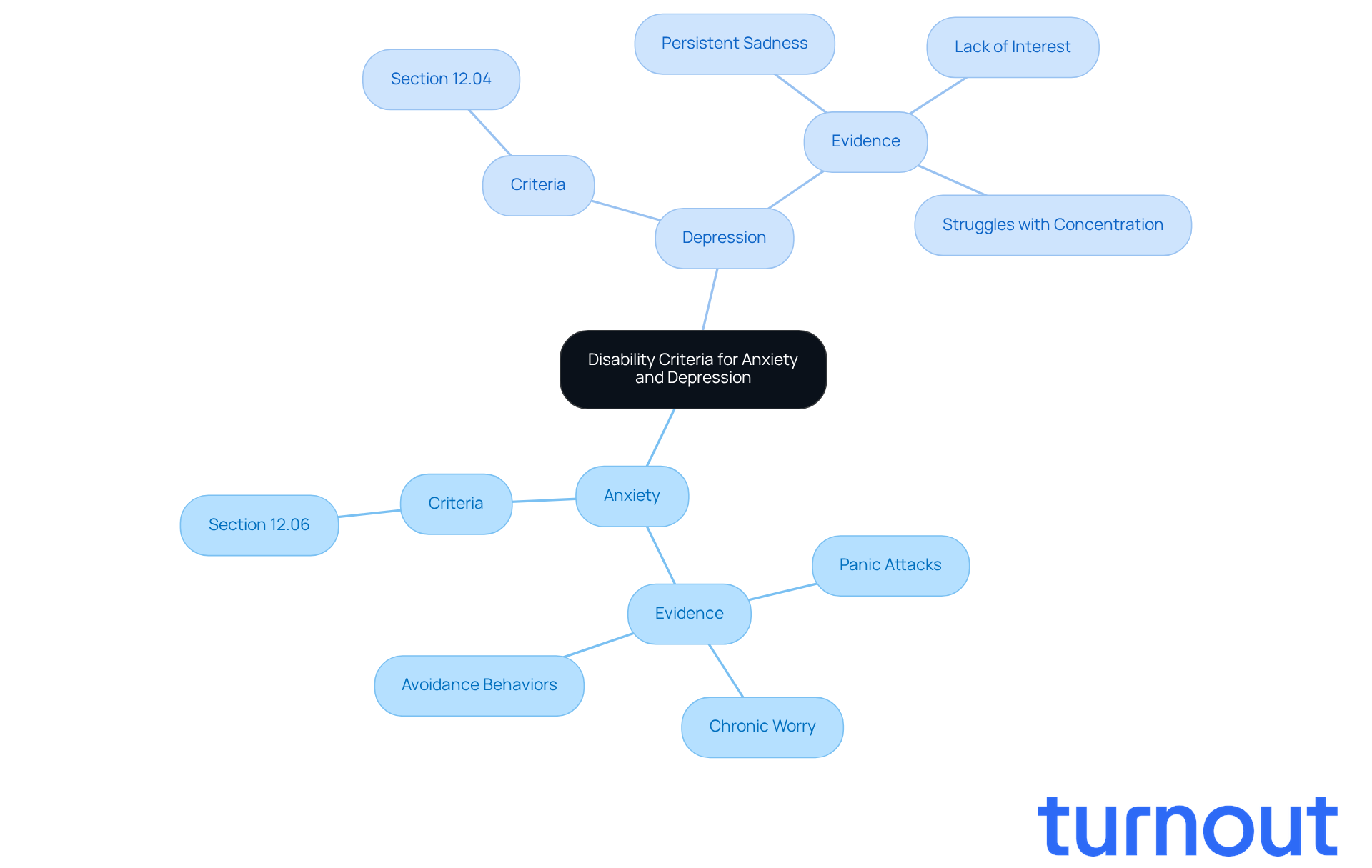
Anxiety and depression can feel overwhelming, and it’s important to understand that this leads to discussions about whether can anxiety be a disability. However, they are assessed through different criteria outlined in the SSA's Blue Book. Anxiety-related disorders fall under Section 12.06, while depressive disorders are categorized under Section 12.04. To qualify for disability benefits, it’s crucial for claimants to present compelling medical evidence that shows how their condition significantly impacts their daily functioning.
For anxiety, this evidence might include:
- Documented instances of panic attacks
- Chronic worry
- Avoidance behaviors that make social interactions or job performance difficult
On the other hand, claims for depression typically require proof of:
- Persistent sadness
- A lack of interest in activities
- Struggles with concentration or decision-making
Understanding the differences between these conditions is essential. Anxiety may manifest through physical symptoms like a rapid heartbeat or sweating during panic attacks, while depression often leads to emotional withdrawal and a pervasive sense of hopelessness. These distinctions can greatly influence the evaluation process and the outcome of disability claims.
We understand that navigating this process can be daunting. The SSA's criteria require detailed medical documentation, including treatment history and functional assessments, to substantiate the severity of symptoms. Since mental health issues can fluctuate, consistent records from healthcare providers are vital to demonstrate the ongoing impact on your ability to work and engage in daily activities. It’s worth noting that mental health conditions account for nearly 40% of all long-term disability requests, which leads to the question: can anxiety be a disability, highlighting the importance of addressing these issues.
Moreover, the stigma surrounding mental health can complicate the journey of seeking benefits. It’s common to feel overwhelmed, but individuals seeking benefits for anxiety and depression can find support from trained nonlawyer advocates who understand the complexities of the SSD claims process. These advocates offer tools and services designed to help clients navigate these challenges, ensuring you have the necessary support to present your case effectively.
By recognizing the hurdles faced by those with mental health conditions, you can better navigate the disability benefits system and advocate for your rights. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and there are resources available to help you every step of the way.
Anxiety vs. PTSD: Evaluating Disability Claims
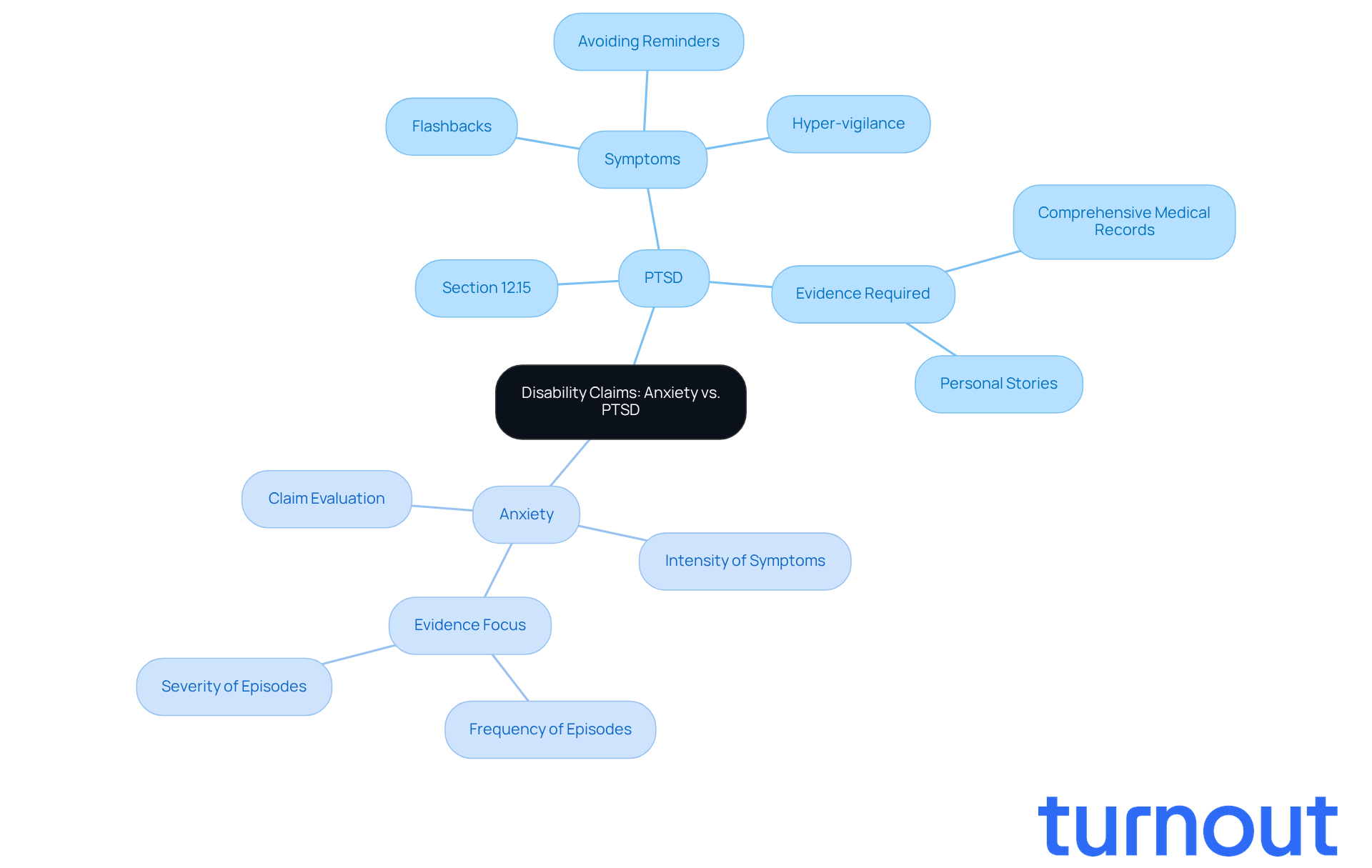
Anxiety conditions and PTSD can significantly impact daily life, which leads to the inquiry of how can anxiety be a disability under Social Security Administration (SSA) guidelines. PTSD falls under Section 12.15, which focuses on trauma- and stressor-related conditions. To qualify for disability benefits, individuals with PTSD need to show that their symptoms - like flashbacks, hyper-vigilance, and avoiding reminders of trauma - seriously limit their daily activities.
On the other hand, stress-related conditions are evaluated based on the intensity of symptoms and their overall effect on functioning. This distinction is crucial. The type of evidence required can differ greatly. For instance, successful claims for PTSD often rely on comprehensive medical records and personal stories detailing how the disorder affects everyday life. In contrast, anxiety claims may focus more on the frequency and severity of anxiety episodes to determine if anxiety can be a disability.
Understanding these nuances can empower applicants to prepare more effectively for their requests, ultimately improving their chances of approval. We understand that navigating this process can feel overwhelming, but you are not alone. Turnout offers valuable tools and services to help you through these complex procedures. With trained nonlawyer advocates for SSD requests, you can find the support you need.
By providing resources like preparation guides and personalized assistance, Turnout enhances your ability to present your case effectively. Real-world examples, such as individuals who successfully navigated the claims process by documenting their PTSD symptoms thoroughly, can serve as inspiring guides for others facing similar challenges.
It's also important to note that the average time to get approved for disability benefits can exceed two years. This highlights the lengthy and often complicated nature of the application process. Remember, we’re here to help you every step of the way.
Navigating Disability Applications for Mental Health Conditions
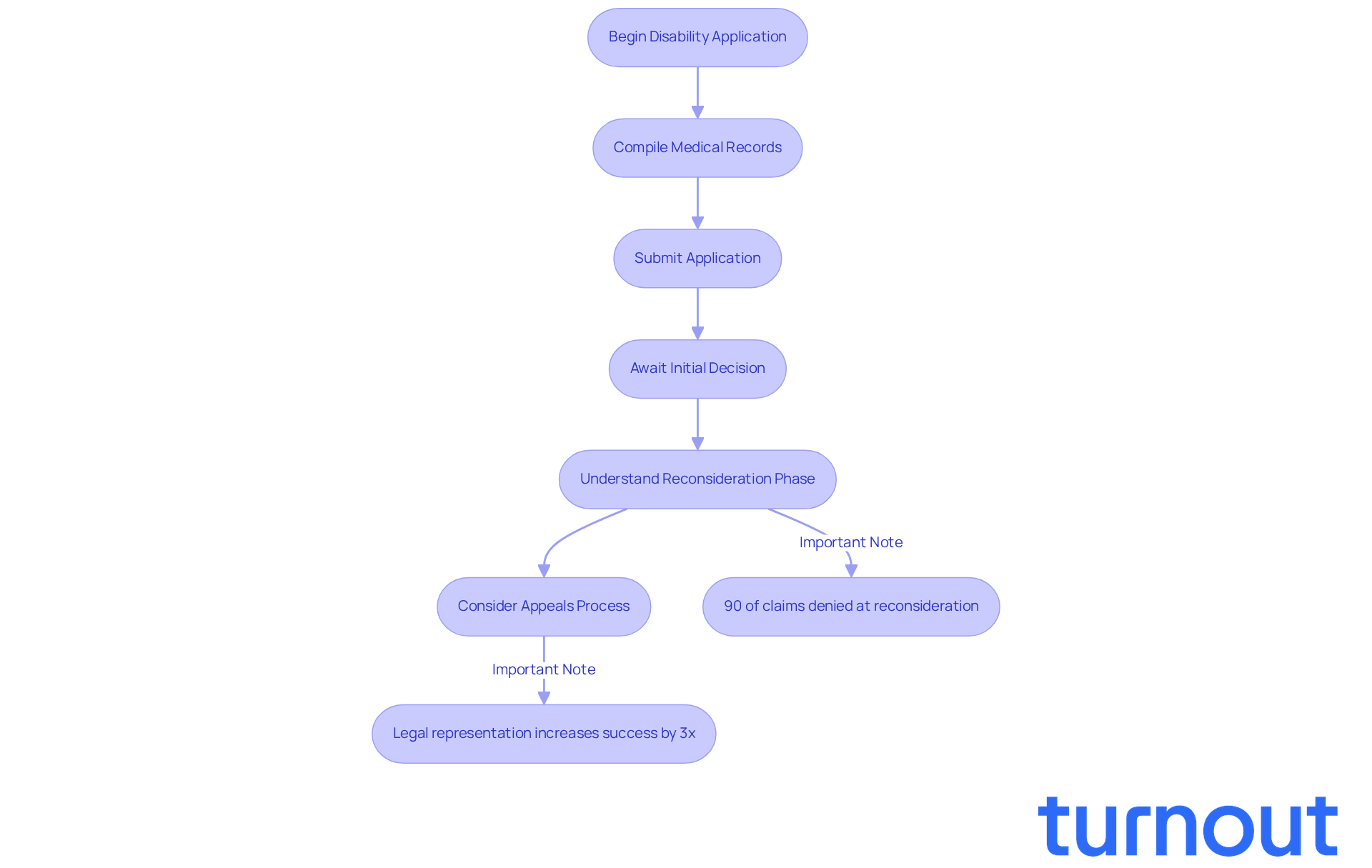
Requesting disability assistance for mental health issues like worry and sadness often leads to the question: can anxiety be a disability? We understand that meticulous planning and comprehensive paperwork are necessary, and it’s common to feel daunted by the process. To help you navigate this journey, it’s important to compile thorough medical records. This includes:
- Diagnoses from licensed mental health professionals
- Treatment histories
- Specific evidence detailing how your conditions impact daily functioning
Articulating how anxiety can be a disability that affects your work performance and social interactions is crucial. This information plays a vital role in the evaluation process. Unfortunately, mental health requests often face more scrutiny than physical health requests, leading to a higher chance of initial denials. In fact, around 90% of requests are denied at the reconsideration phase. This highlights the importance of a strong application.
Understanding the appeals process is essential. Seeking help from knowledgeable advocates can significantly improve your chances of a successful outcome. Did you know that individuals represented by legal professionals are three times more likely to win benefits than those who go it alone?
Real-world examples show that many applicants have successfully secured benefits by sharing detailed accounts of their conditions and how they affect their ability to work. Resources like Turnout can provide invaluable support in navigating these complex systems, ensuring you receive the benefits you deserve.
On average, processing mental health disability claims takes over two years. This makes persistence and informed advocacy essential. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you every step of the way.
Conclusion
The exploration of whether anxiety can be classified as a disability reveals the complexities surrounding mental health conditions and their impact on daily life. We understand that anxiety disorders, when severe enough to hinder major life activities, can indeed meet the criteria for disability under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) and the Social Security Administration (SSA). This understanding is crucial for those seeking support and benefits, as it emphasizes that mental health challenges are valid and deserving of recognition.
Throughout this discussion, we highlighted the distinct criteria for assessing anxiety compared to other mental health conditions such as depression and PTSD. It’s common to feel overwhelmed by the necessity for thorough documentation, including medical histories and personal testimonies. These elements play a pivotal role in determining eligibility for disability benefits. The statistics presented also shed light on the prevalence of mental health issues, reinforcing the importance of addressing these conditions with the seriousness they warrant.
In conclusion, advocating for mental health awareness and support systems that recognize anxiety as a legitimate disability is essential. Individuals facing these challenges should be encouraged to seek assistance from knowledgeable advocates who can help navigate the often daunting disability application process. By understanding the nuances of anxiety and its implications for daily functioning, we can foster a more inclusive environment that acknowledges the struggles of those living with anxiety disorders. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we're here to help.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can anxiety be considered a disability?
Yes, anxiety can be considered a disability if it significantly hinders your ability to carry out major life activities, such as working, learning, or social interactions.
What does the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) say about anxiety as a disability?
The ADA raises the question of whether anxiety can be classified as a disability if a mental impairment substantially limits one or more major life activities.
How does the Social Security Administration (SSA) view anxiety in relation to disability benefits?
The SSA acknowledges that anxiety may serve as a criterion for disability benefits if you can demonstrate the severity and impact of your condition.
What types of anxiety disorders may qualify as a disability?
Conditions such as generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder may qualify as a disability if they significantly interfere with daily functioning.
How common are mental health issues among U.S. adults?
Approximately 31.1% of U.S. adults will encounter a mental health issue at some point in their lives.
What percentage of adults with emotional disorders experience serious impairment?
Among adults with any emotional disorder, 22.8% experience serious impairment, which can greatly affect their ability to maintain employment.
What challenges do individuals with anxiety face in daily life?
Individuals with anxiety often report difficulties in work performance and social interactions, leading to substantial challenges in their daily lives.
What resources are available for those seeking disability benefits related to anxiety?
Turnout offers vital resources and services to help manage the complexities of Social Security Disability (SSD) claims, including access to trained nonlawyer advocates.




