Introduction
Navigating the complexities of Social Security can feel overwhelming, especially for those with disabilities seeking financial support. We understand that the various payment categories, eligibility requirements, and potential challenges can make this journey seem daunting. It's crucial to grasp how to access these benefits effectively.
This article aims to address your common questions and concerns about Social Security. We’ll provide insights into the different categories of payments, discuss what it means to work while receiving benefits, and explore the implications of overpayments. As uncertainties about the future of Social Security loom, how can you ensure that you’re making informed decisions to safeguard your financial well-being?
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. We're here to help you navigate these waters with confidence.
Identify Different Categories of Social Security Payments
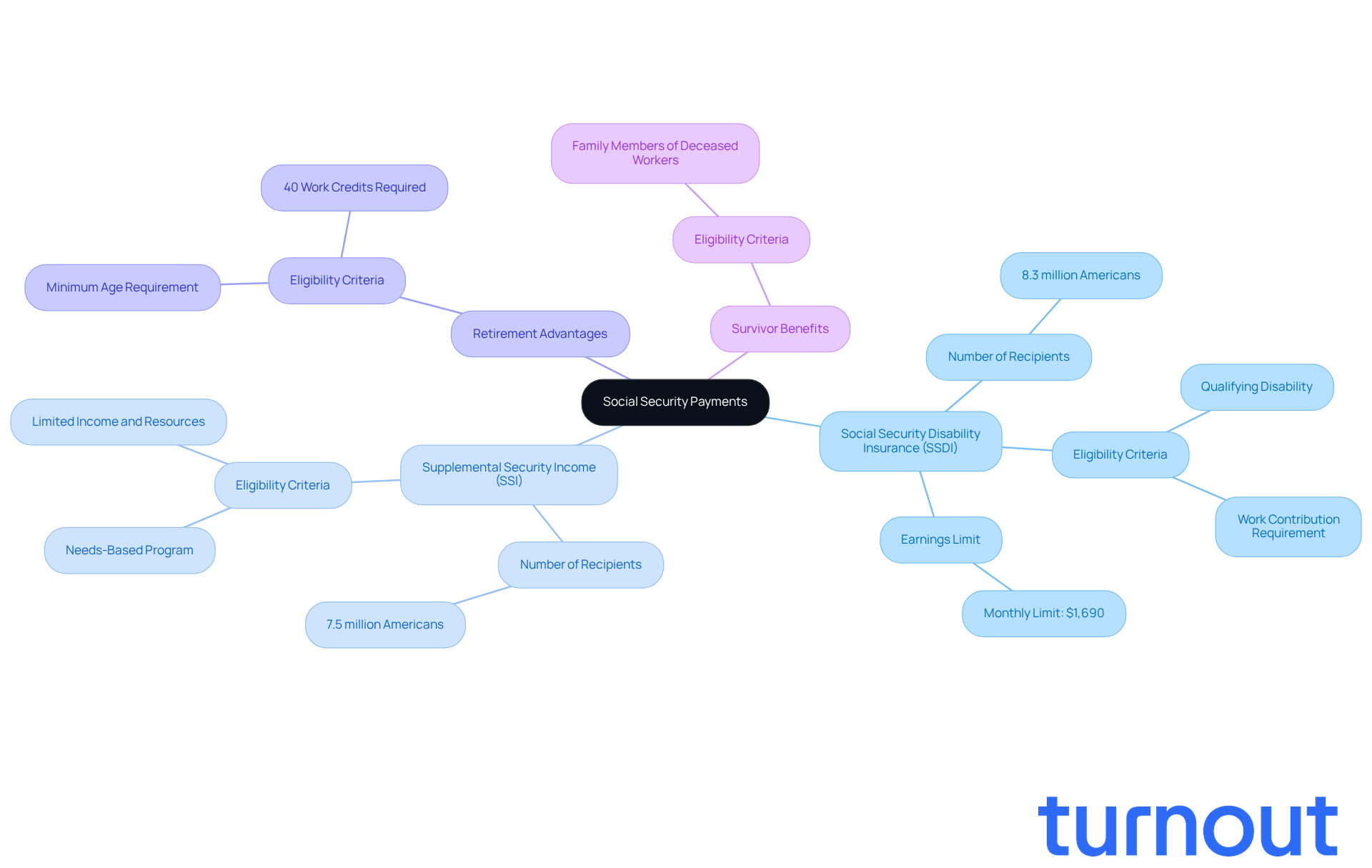
Social Security offers several key categories of payments designed to support individuals in various circumstances:
-
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI): This program is for those who have contributed to Social Security through their work but can no longer continue due to a qualifying disability. As of 2026, around 8.3 million Americans receive SSDI benefits, highlighting its vital role in providing financial support. We recognize that navigating the SSDI claims process can be overwhelming, so we provide social security questions answered free. That’s why Turnout offers help through trained nonlawyer advocates, ensuring you can access the support you need without the complexities of legal representation.
-
Supplemental Security Income (SSI): Unlike SSDI, SSI is a needs-based program aimed at individuals with limited income and resources, regardless of their work history. In 2026, nearly 7.5 million recipients benefit from SSI, underscoring its importance for those facing financial hardships. Turnout is here to streamline the SSI application process, helping you understand your eligibility and providing social security questions answered free to guide you through the necessary steps to obtain these benefits.
-
Retirement Advantages: These provisions are available to individuals who have reached the specified retirement age and have accumulated enough work credits, typically requiring at least 40 credits earned through employment.
-
Survivor Benefits: This category provides financial assistance to family members of deceased workers who qualified for Social Security, ensuring that loved ones receive support during difficult times.
Understanding these categories is essential for determining eligibility and accessing the appropriate support, which includes having social security questions answered free. Recent updates indicate that in 2026, the earnings limit for SSDI beneficiaries under full retirement age is set at $24,480, with $1 withheld for every $2 earned above this threshold. Additionally, the significant gainful activity threshold for SSDI recipients is $1,690 monthly, allowing for more flexibility in balancing work and assistance.
Turnout’s services, including tax debt relief assistance, are designed to guide you through these complexities, making the process of obtaining government support more accessible. Remember, you are not alone in this journey. Please note that Turnout is not a law firm and does not provide legal representation.
Determine Eligibility for Social Security Benefits
Navigating the world of Social Security benefits can feel overwhelming, but understanding the eligibility criteria is the first step toward ensuring that your social security questions are answered free. Here’s what you should know:
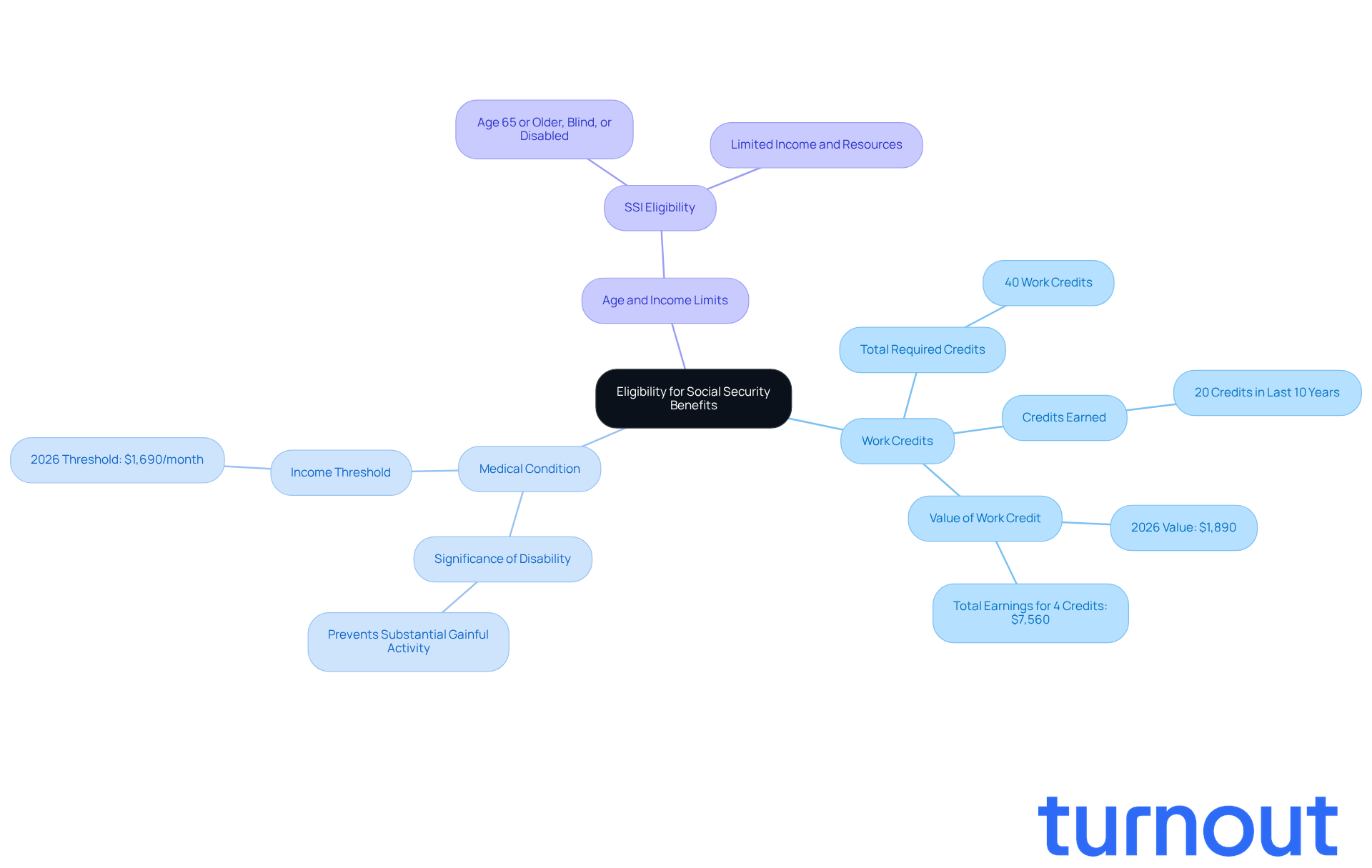
- Work Credits: Typically, you’ll need 40 work credits, with at least 20 earned in the last 10 years before becoming disabled. In 2026, one work credit will be valued at $1,890, meaning you’ll need to earn a total of $7,560 to obtain the maximum four credits each year.
- Medical Condition: Your disability must be significant enough to prevent you from engaging in substantial gainful activity, which is defined as earning more than $1,690 per month for most SSDI beneficiaries in 2026. This condition should last at least one year or lead to death.
- Age and Income Limits: For SSI, applicants must be 65 or older, blind, or disabled, and have limited income and resources. The income threshold for SSI eligibility is vital, ensuring that assistance reaches those who need it most.
We understand that applying for benefits can be a daunting process. Recent statistics reveal that many SSDI applicants meet the work credit requirements, highlighting the importance of maintaining steady employment and contributing to social benefits. There are countless success stories of individuals who have faced challenges and emerged victorious, proving that with persistence and a solid understanding of the system, positive outcomes are possible.
Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. We’re here to help you every step of the way.
Understand Working While Receiving Social Security Benefits
If you're a disabled individual considering work while receiving Social Security benefits, it's important to understand a few key points that can help you navigate this journey with confidence:
-
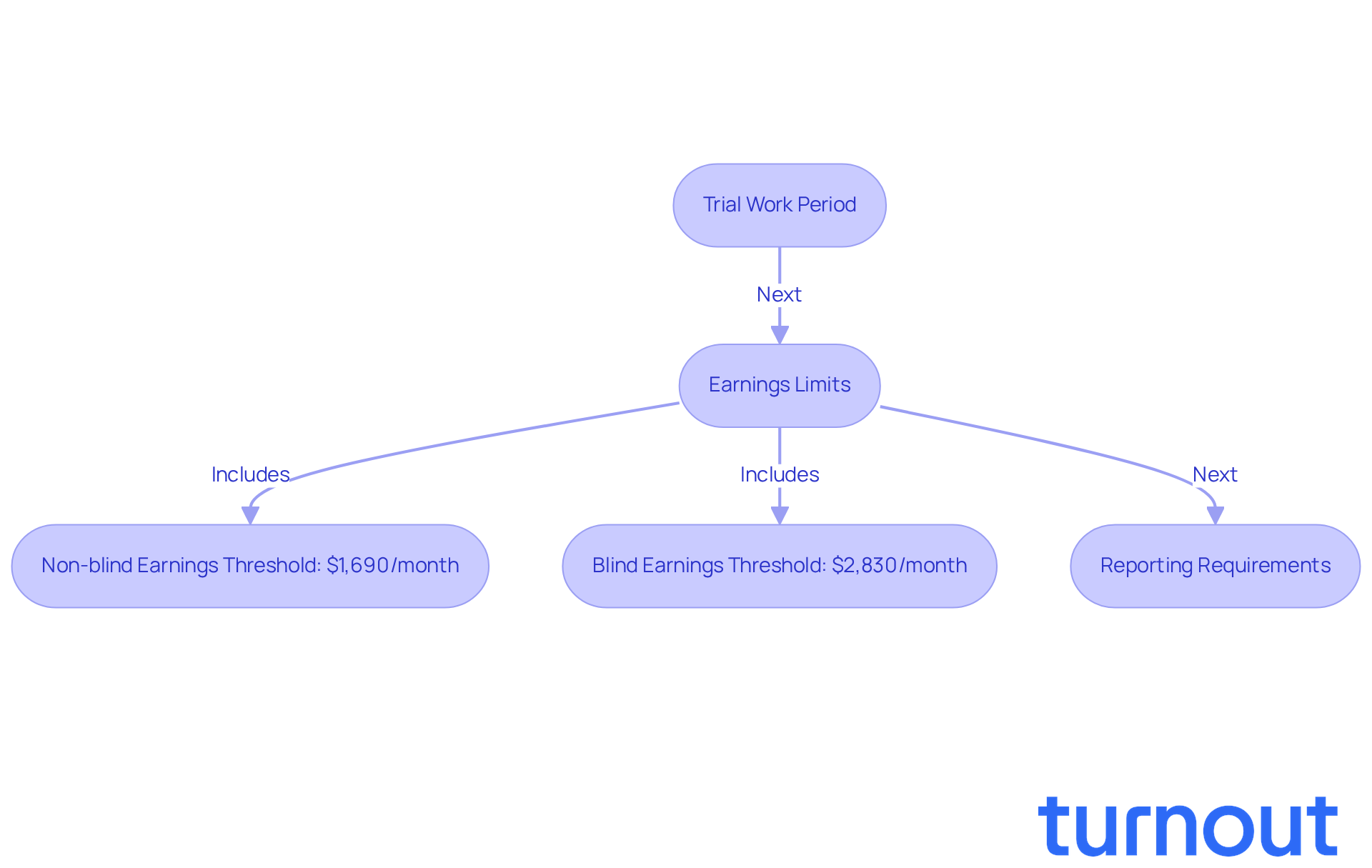
Trial Work Period: You can test your ability to work for up to nine months without losing your benefits. This time allows you to explore your capacity to return to the workforce while still having financial support.
-
Earnings Limits: In 2026, if your earnings exceed $24,480, your assistance may be reduced. Specifically, for every $2 you earn over this limit, $1 in assistance is withheld. For non-blind workers, the earnings threshold is $1,690 per month, while for blind workers, it’s $2,830 per month. This structure encourages you to seek employment opportunities without the immediate worry of losing your assistance.
-
Reporting Requirements: It’s essential to report any work activity to the Social Security Administration (SSA) to avoid overpayments. Keeping the SSA informed is crucial for maintaining your eligibility for assistance.
Understanding these rules is vital for managing the complexities of working while receiving assistance. For instance, Barbara, a recipient, found that as her health improved, she could engage in work-readiness training and explore job opportunities while still receiving some support. She highlighted the importance of staying in touch with her service providers to assess her work interests and capabilities.
To clarify your options, we encourage you to consult with service providers or utilize resources available through Turnout. They simplify access to government benefits and financial support, including assistance with SSD claims and tax relief. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and we're here to help you every step of the way.
Explain the Cost-of-Living Adjustment (COLA) for Benefits
The Cost-of-Living Adjustment (COLA) is more than just a number; it’s a vital yearly increase in welfare payments designed to help you keep pace with inflation. Let’s explore what this means for you:
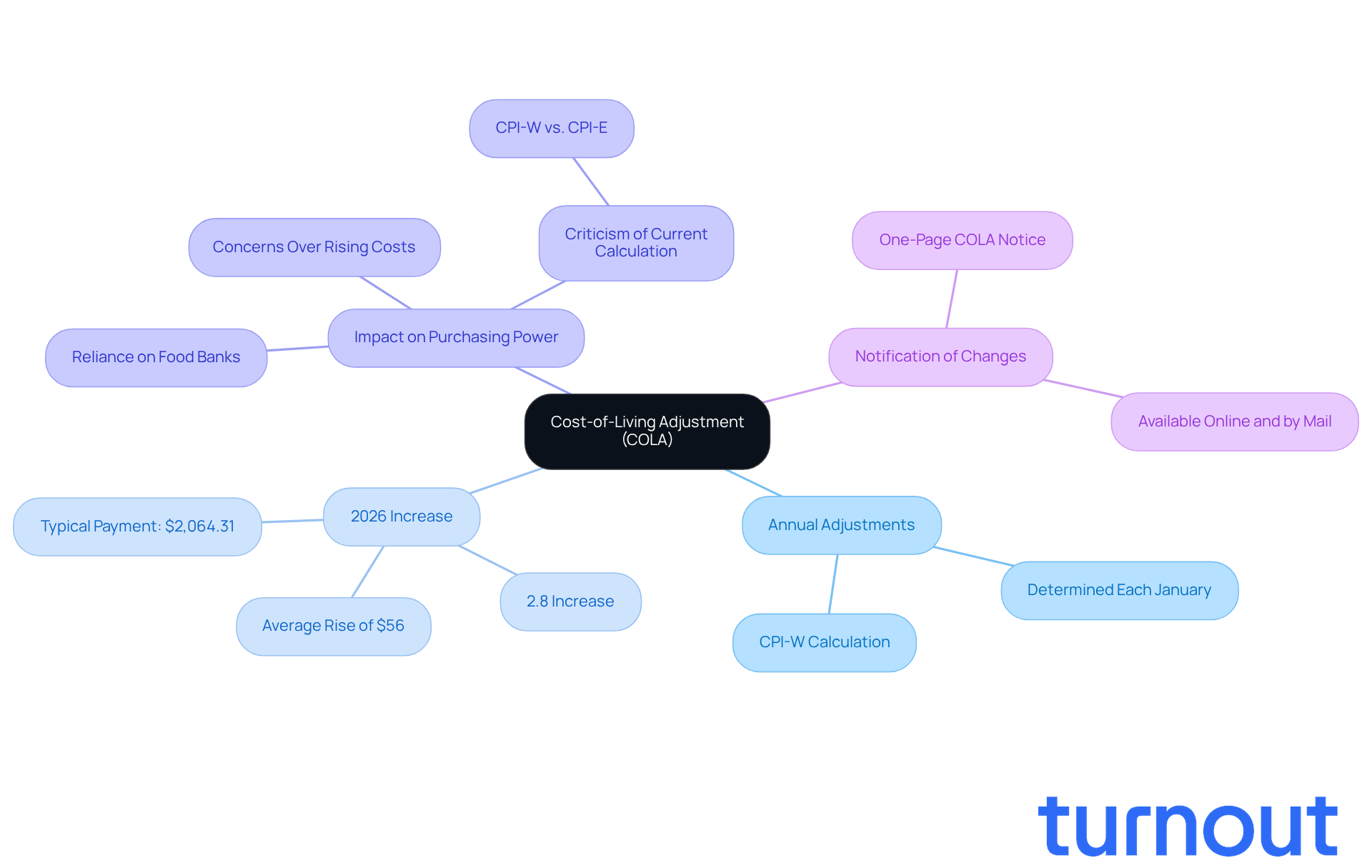
- Annual Adjustments: Each January, the COLA is determined based on the Consumer Price Index for Urban Wage Earners and Clerical Workers (CPI-W). This ensures that your benefits reflect the current economic landscape, helping you stay afloat.
- 2026 Increase: Starting January 2026, you can expect a 2.8% increase in your monthly payments. This change translates to an average rise of about $56, bringing the typical retirement payment to around $2,064.31. Every bit helps, right?
- Impact on Purchasing Power: The COLA plays a crucial role in preserving your purchasing power, especially if you rely on a fixed income. We understand that many of you worry that this increase might not fully cover the rising costs of living, particularly in healthcare. Some have shared their struggles, like having to rely on food banks due to insufficient income from welfare. As Casey Schwarz pointed out, "Costs in retirement have outpaced inflation," highlighting the ongoing challenges many face.
- Notification of Changes: To keep you informed, recipients will receive a straightforward, one-page COLA notice detailing your new payment amounts. We want to ensure you’re well-informed about these important adjustments.
Understanding the COLA is essential for you as it helps you anticipate changes in your financial situation and plan accordingly. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey, and we’re here to help.
Clarify Tax Implications on Social Security Benefits
Navigating federal income tax can feel overwhelming, especially when seeking social security questions answered free regarding payments related to Social Security benefits. We understand that many individuals are concerned about how their total income might affect their financial situation. Here are some important points to consider:
- Tax Thresholds: If your combined income exceeds $25,000 (or $32,000 for married couples), you may find yourself facing taxes on your benefits. It’s worth noting that around 50% of Americans receiving Social Security retirement payments do encounter taxation.
- Tax Rates: Depending on your income levels, up to 85% of your benefits could be taxable. For instance, single filers with a combined income over $34,000 might see a significant portion of their support taxed. Similarly, married couples filing jointly with incomes above $44,000 face comparable tax consequences.
- State Taxes: In addition to federal taxes, some states impose their own taxes on retirement benefits. For example, in Colorado, taxpayers aged 55 to 64 can deduct up to $95,000 if married filing jointly or $75,000 if single from their taxable income. Vermont even offers a complete exemption of retirement income from state taxation for seniors who meet specific income criteria.
Understanding these tax implications is crucial for managing your finances effectively and ensuring that social security questions are answered free to avoid unexpected tax liabilities. Remember, you’re not alone in this journey. The IRS provides an online tool that can help you determine the taxable portion of your Social Security income, which can be an invaluable resource. We're here to help you navigate these complexities with confidence.
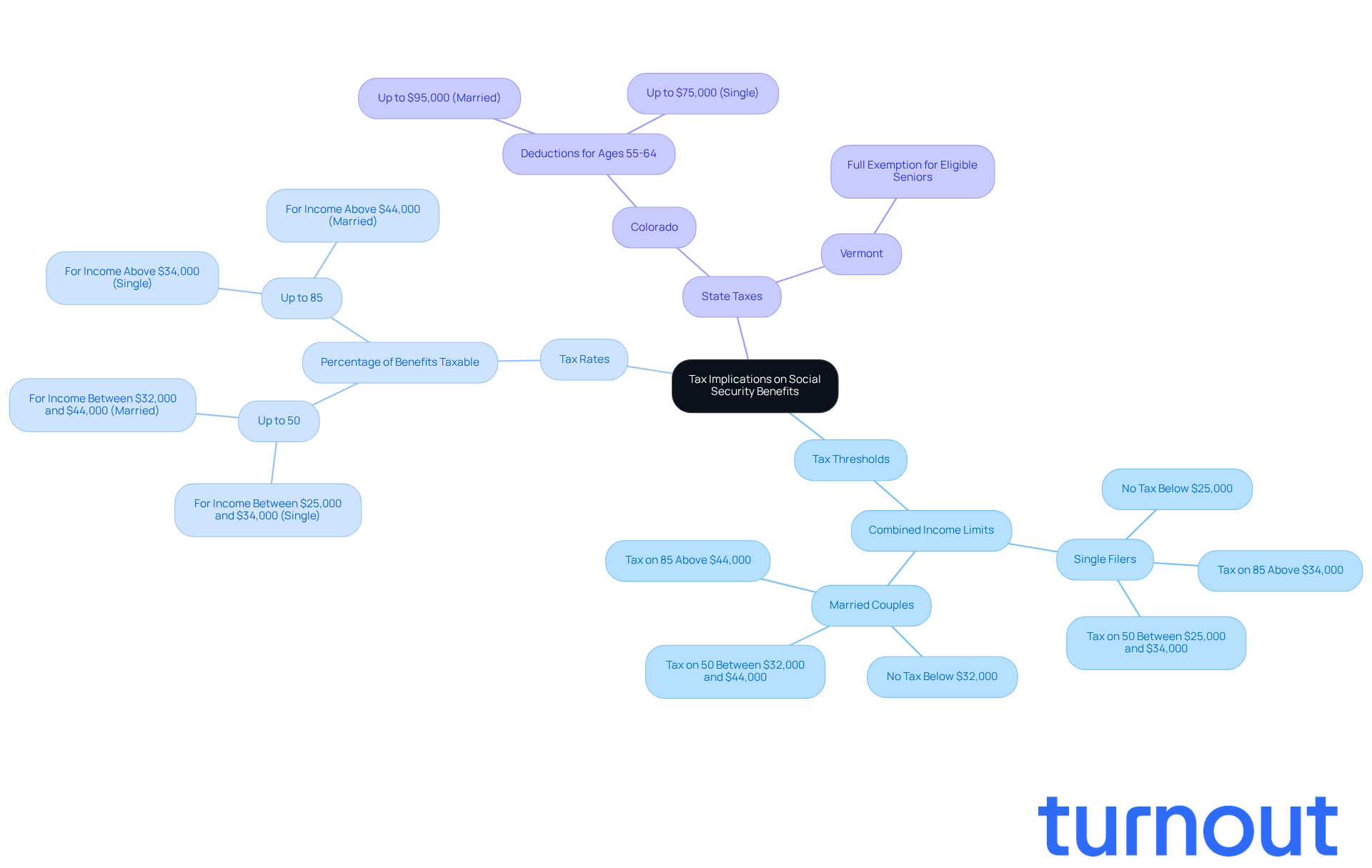
Explore Spousal Benefits Under Social Security
Spousal advantages can offer vital financial support based on a spouse's work record. Understanding these benefits is essential, especially if you're navigating financial challenges. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Eligibility: To claim spousal benefits, you need to be at least 62 years old or caring for a qualifying child. If you're divorced, it's important to know that you must have been separated for at least two years to qualify for assistance based on your ex-spouse's work history. This ensures that those who may not have a strong work history can still receive support.
- Amount Received: The spousal allowance can be as much as 50% of the working spouse's primary insurance amount (PIA) at their full retirement age (FRA). For example, if a spouse's allowance at FRA is $2,000, the other spouse could receive $1,000 each month. It's encouraging to note that over 1.9 million individuals receive an average monthly spousal allowance of $887, showcasing the financial support available.
- Divorced Partners: If you were married for at least 10 years, you may qualify for spousal assistance based on your former partner's work record, even if they have remarried. This means you can receive support without affecting your ex-spouse's payments, and importantly, they won't be notified about the assistance you receive.
We understand that navigating these options can feel overwhelming. Comprehending these spousal advantages is crucial for effective financial planning, especially for those who are disabled and exploring their choices. Remember, you're not alone in this journey. As retirement experts emphasize, knowing your eligibility for spousal advantages can significantly enhance your financial stability.
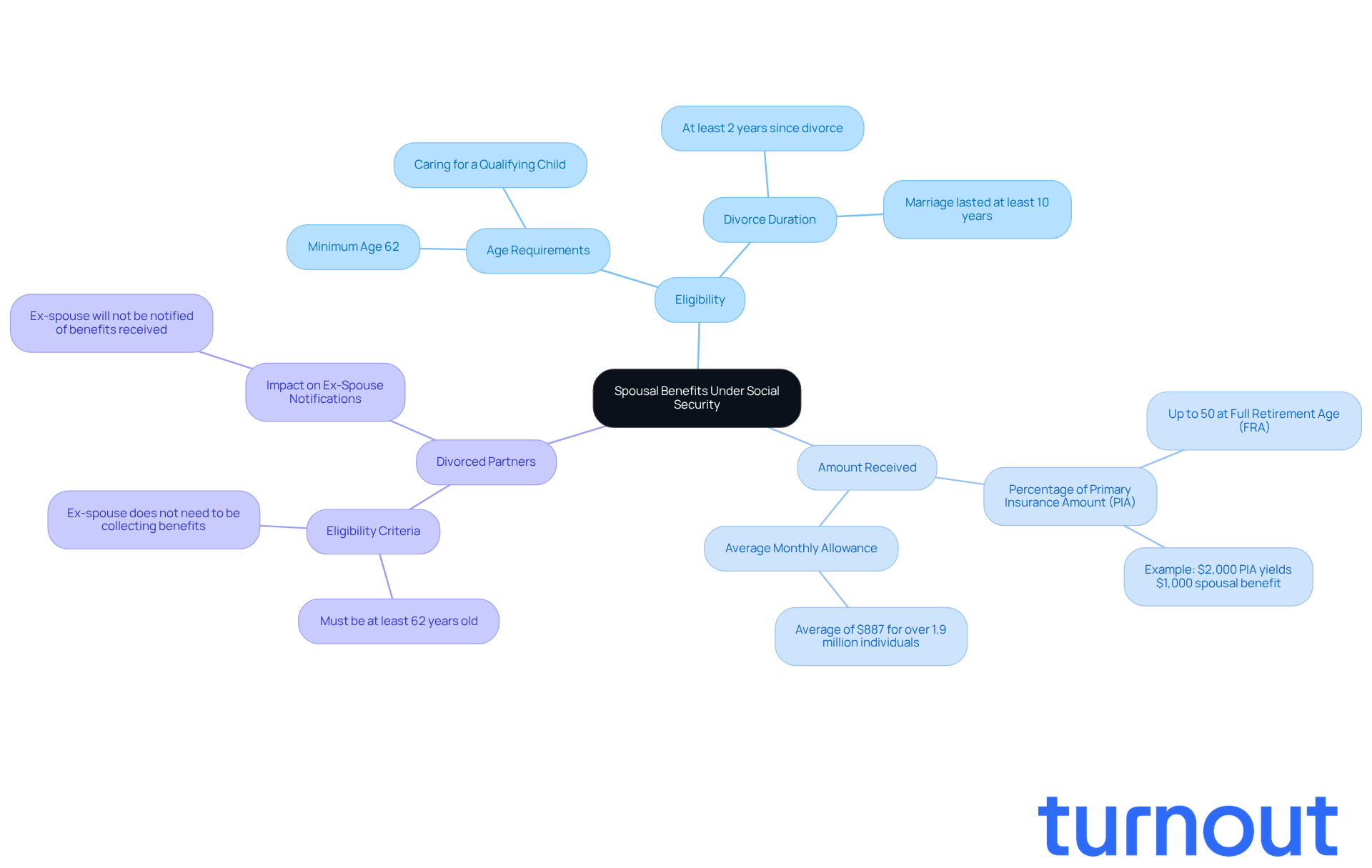
Review Options for Changing Social Security Benefit Decisions
Navigating financial assistance can be challenging, and it's important to know that you're not alone in this journey. Individuals may need to modify their financial assistance payment choices for various reasons. Here are some key options to consider:
-
Requesting Reconsideration: If your claim is denied, you can request a reconsideration within 60 days of receiving that decision. This step is crucial, as around 70% of initial claims are denied. Understanding the reconsideration process can make a significant difference. Remember, Turnout is here to assist you through this process with trained nonlawyer advocates who can help you navigate the complexities of SSD claims.
-
Changing Assistance Types: As you reach full retirement age, you may transition from Disability Insurance (SSDI) to retirement payments. This change could lead to a potentially greater monthly payout. Turnout is ready to guide you in making this transition smoothly, ensuring you get the most out of your benefits.
-
Appealing Decisions: If the outcome of your reconsideration isn't what you hoped for, you have the right to appeal to an administrative law judge. Turnout's support extends to helping you understand your rights and options during this appeal process, so you can feel empowered every step of the way.
-
Tax Debt Relief: Beyond SSD claims, Turnout also offers assistance with tax debt relief. Our IRS-licensed enrolled agents are here to help you manage any tax-related issues you may face.
Staying informed about these choices is crucial for successfully maneuvering the intricacies of the assistance system. You deserve to obtain the benefits that can make a real difference in your life. Remember, we're here to help you every step of the way.
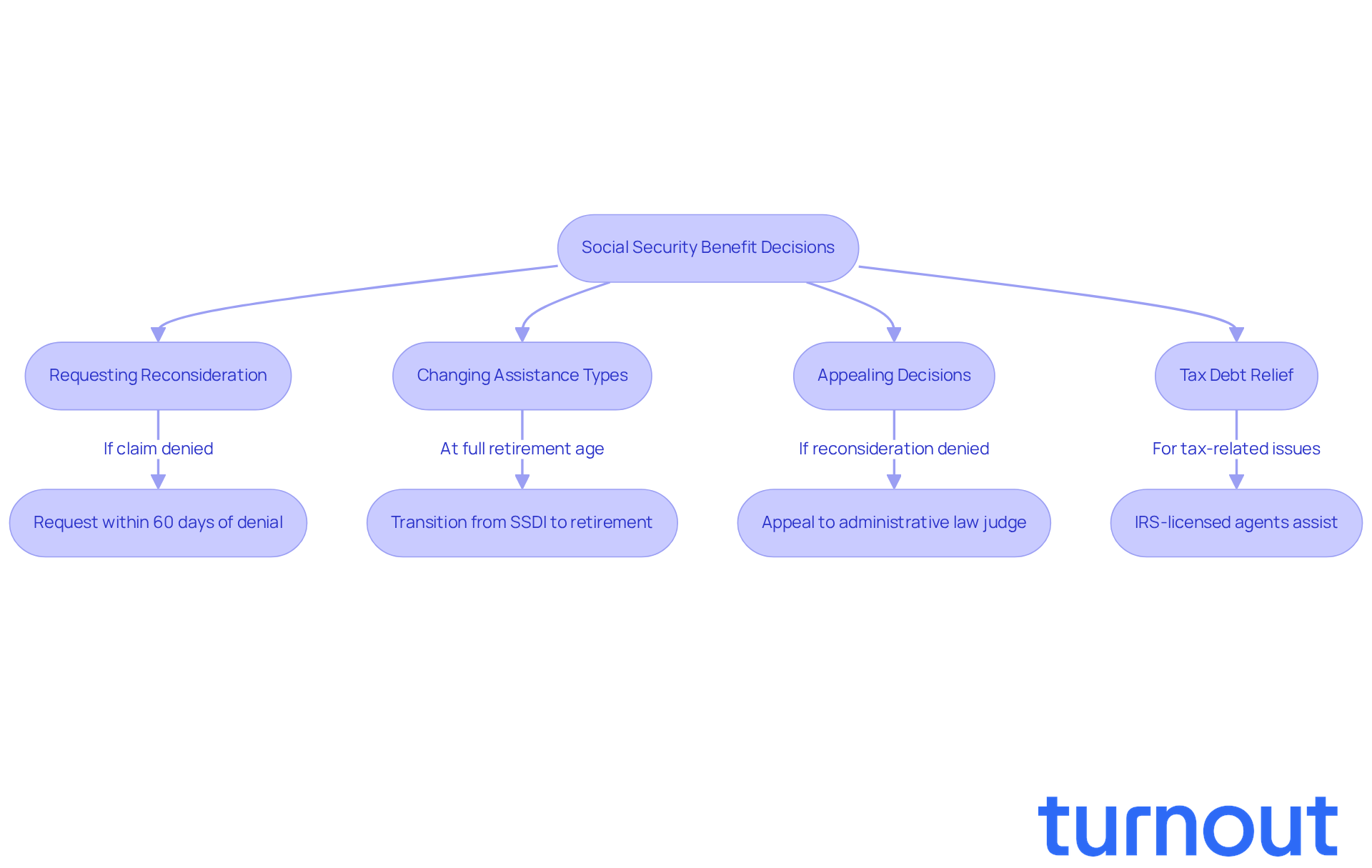
Address Overpayments and Their Consequences in Social Security
Overpayments can be a challenging experience for many beneficiaries, as they may receive more money than they are entitled to. This situation affects a significant number of individuals, and it’s important to understand what steps to take when it happens. When an overpayment is identified, beneficiaries receive a notice detailing the amount owed. This notice is crucial for grasping their financial obligations. Did you know that approximately 1 in 10 beneficiaries encounter overpayments? This highlights just how common this issue is. If the overpayment is $2,000 or less, the agency will waive collection unless you were at fault.
You have several options for addressing overpayments, and we’re here to assist you with social security questions answered free as you navigate this process. If you believe the overpayment wasn’t your fault, you can request a waiver, which may relieve you of the obligation to repay. As the Administration of Services states, "Whether or not you believe you were overpaid, you can also request the agency to waive the overpayment by submitting a Request for Waiver Form (SSA-632-BK)." For example, under the SSI $50 Rule, Social Security will waive overpayments of $50 or less, providing a safety net for those facing minor issues. Additionally, you can negotiate a repayment plan, allowing you to manage your financial obligations more effectively.
It’s essential to address overpayments promptly. If left unresolved, future benefits may be withheld until the debt is repaid, which can create financial instability. Remember, you have only 60 days from the date of the Notice of Overpayment to file a Request for Reconsideration. Understanding how to handle overpayments is vital for maintaining your financial stability and ensuring access to essential assistance. You are not alone in this journey, and taking action can help you regain control.
Identify Benefits for Widows and Widowers in Social Security
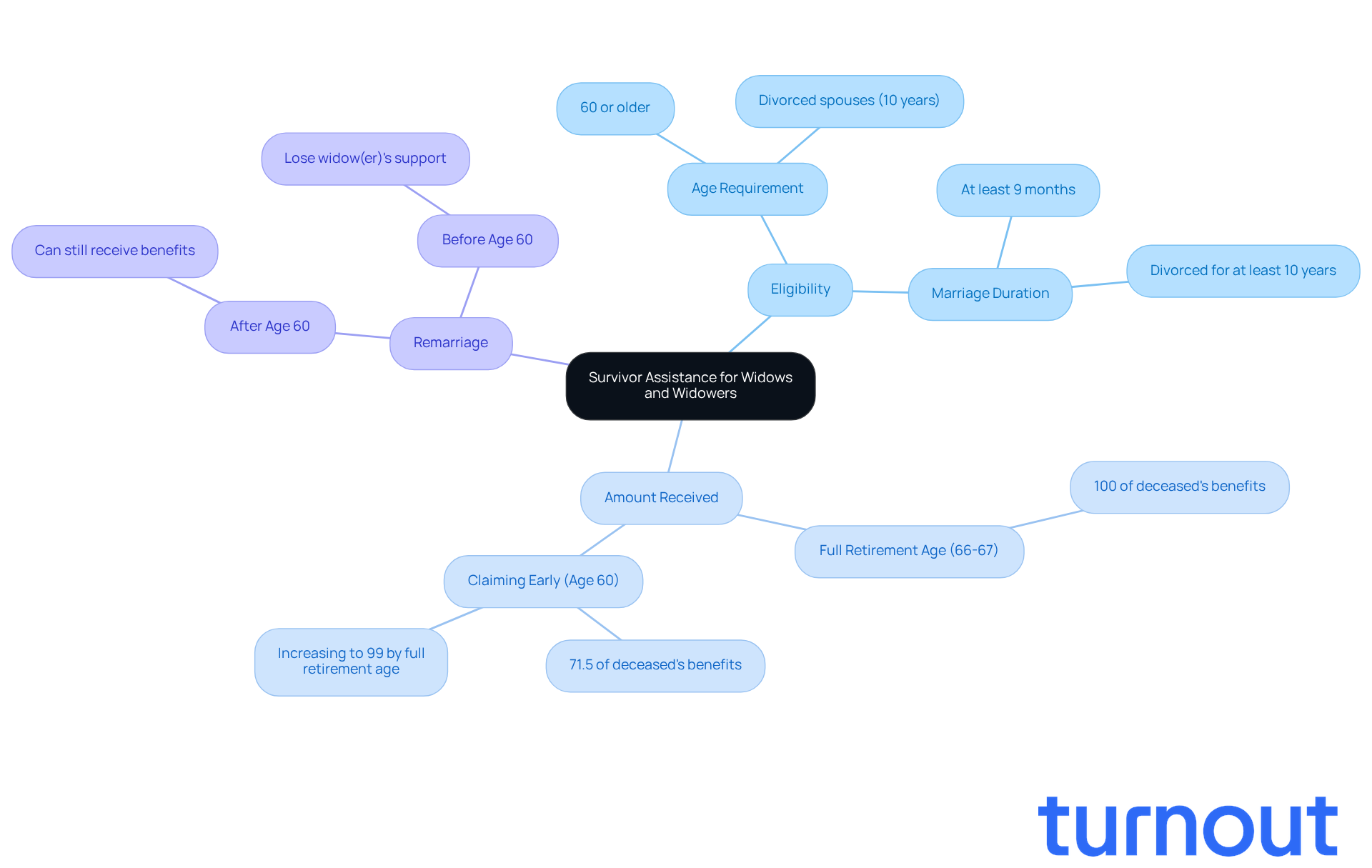
Survivor assistance offers vital financial support to widows and widowers, rooted in their deceased spouse's work history. Understanding this can be a lifeline during a challenging time. Here’s what you need to know:
- Eligibility: If you’re a widow or widower aged 60 or older and were married to your spouse for at least nine months, you can claim benefits. This also applies to divorced spouses who were married for a minimum of ten years and are currently single.
- Amount Received: The assistance can be as much as 100% of your deceased spouse's allocation if you’ve reached full retirement age, typically between 66 and 67 years. If you choose to claim earlier, the payments may be reduced, starting at 71.5% of the deceased's amount at age 60 and increasing to 99% as you near full retirement age.
- Remarriage: If you remarry after age 60, you can still receive survivor payments based on your deceased spouse's record. However, remarrying before age 60 (or 50 if disabled) means you’ll lose the right to widow(er)'s support.
For effective financial planning after losing a spouse, it is crucial to have social security questions answered free. We know this can be a difficult journey. As of March 2022, about 6 million individuals were receiving survivor assistance, making up 9.0% of the total OASDI recipient population. This highlights how important this support system is for families navigating the aftermath of loss. Remember, you are not alone in this journey; we’re here to help.
Discuss the Future State of Social Security Benefits
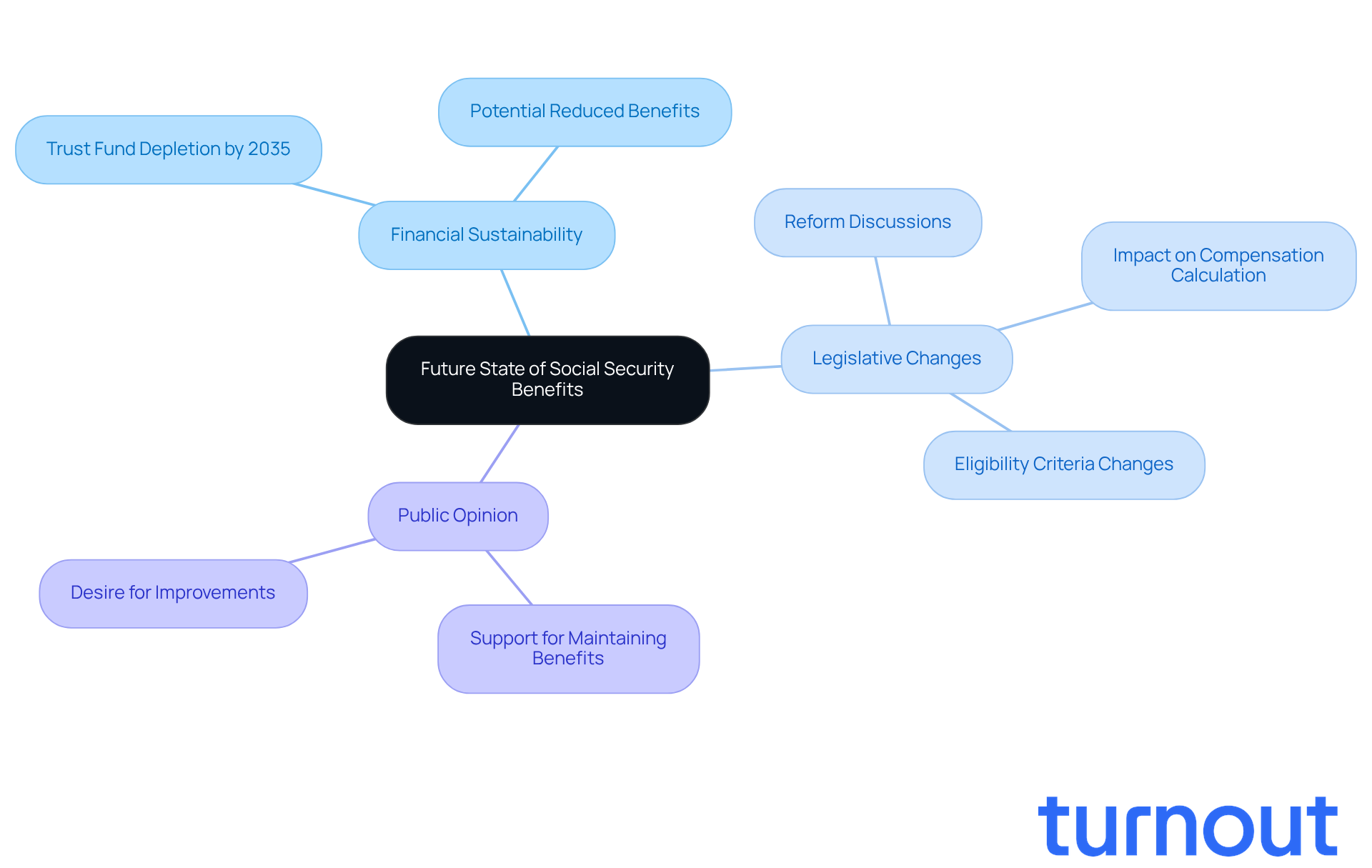
The future of public welfare payments is a topic that weighs heavily on many minds. We understand that concerns about financial security can be overwhelming. Here are some key points to consider:
- Financial Sustainability: Projections suggest that the Social Security Trust Fund could be depleted by 2035. This may lead to reduced benefits, which is understandably worrying for many.
- Legislative Changes: Ongoing discussions about reforms could impact how compensation is calculated and who qualifies for benefits. It’s common to feel uncertain about these changes.
- Public Opinion: Many Americans are in favor of maintaining and even improving national insurance advantages. This highlights just how significant this program is for millions of people.
Understanding the future state of Social Security benefits is essential. You are not alone in this journey. Planning your financial future effectively can help ease some of these worries. We're here to help you navigate these changes and ensure you feel secure in your financial planning.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of Social Security benefits can feel overwhelming, especially for those with disabilities seeking the support they truly deserve. This article has aimed to provide a clear overview of the various categories of Social Security payments, such as SSDI, SSI, and spousal benefits. We’ve also discussed eligibility requirements, work incentives, and the effects of recent legislative changes. By grasping these essential aspects, you can better prepare yourself to access the financial assistance you need.
We understand that knowing your rights and options regarding Social Security benefits is crucial. From the details of eligibility criteria to the implications of working while receiving assistance, each section has been designed to empower you with the knowledge necessary to navigate your unique situation. Additionally, the information on overpayments and survivor benefits highlights the importance of staying informed and proactive in managing your financial future.
Remember, you don’t have to face the journey through Social Security benefits alone. With resources like Turnout available to guide you through the complexities of the system, seeking help and clarification is essential. Understanding the evolving landscape of Social Security is vital for ensuring your financial stability and security. Taking that first step toward clarity can lead to a more confident and informed approach to securing the benefits that can truly make a difference in your life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main categories of Social Security payments?
The main categories of Social Security payments include Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI), Supplemental Security Income (SSI), Retirement Advantages, and Survivor Benefits.
Who is eligible for Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI)?
SSDI is for individuals who have contributed to Social Security through their work but can no longer work due to a qualifying disability.
What is Supplemental Security Income (SSI)?
SSI is a needs-based program aimed at individuals with limited income and resources, regardless of their work history.
What are the eligibility requirements for SSI?
To qualify for SSI, applicants must be 65 or older, blind, or disabled, and have limited income and resources.
How many work credits are typically needed for SSDI eligibility?
Typically, you need 40 work credits, with at least 20 earned in the last 10 years before becoming disabled.
What is the significant gainful activity threshold for SSDI beneficiaries in 2026?
The significant gainful activity threshold for SSDI beneficiaries in 2026 is $1,690 monthly.
Can individuals work while receiving Social Security benefits?
Yes, individuals can work while receiving benefits, but they must adhere to certain earnings limits and reporting requirements.
What is the Trial Work Period?
The Trial Work Period allows individuals to test their ability to work for up to nine months without losing their benefits.
What are the earnings limits for SSDI beneficiaries in 2026?
In 2026, the earnings limit for SSDI beneficiaries under full retirement age is $24,480, with $1 withheld for every $2 earned above this threshold.
What should beneficiaries do if they start working?
Beneficiaries must report any work activity to the Social Security Administration (SSA) to avoid overpayments and maintain their eligibility for assistance.




